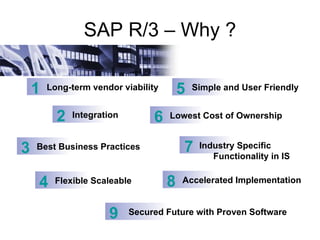
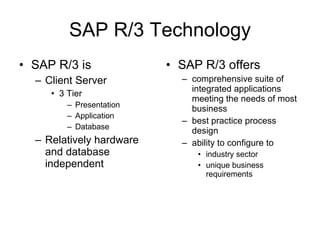
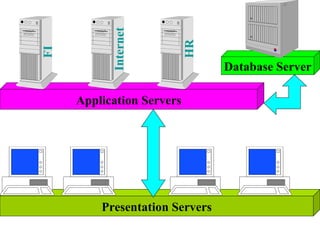
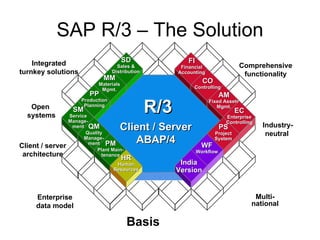
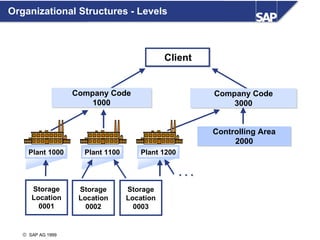
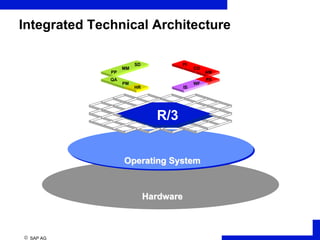
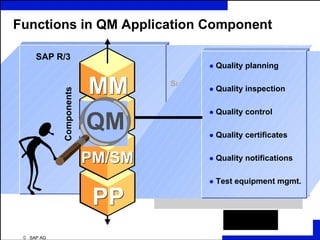
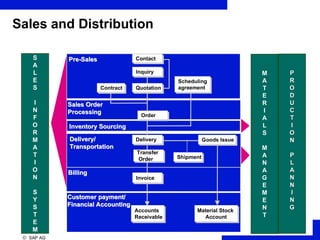
ERP is an integrated software solution that connects all departments of a company. It increases efficiency by sharing information in real-time across functional areas like finance, operations, and sales. ERP replaces isolated "islands of information" with a single database and common processes. Implementing ERP allows companies to streamline operations, reduce costs, satisfy customers, and gain a competitive advantage. SAP R/3 is a leading ERP software that offers comprehensive functionality covering various business functions on a single database.