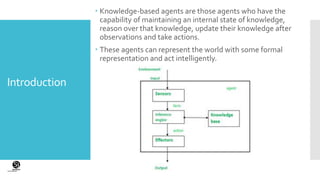
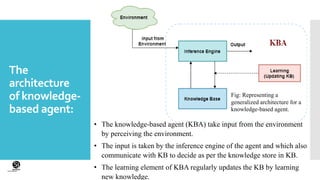
This document discusses knowledge-based agents in artificial intelligence. It defines knowledge-based agents as agents that maintain an internal state of knowledge, reason over that knowledge, update their knowledge based on observations, and take actions. Knowledge-based agents have two main components: a knowledge base that stores facts about the world, and an inference system that applies logical rules to deduce new information from the knowledge base. The document also describes the architecture of knowledge-based agents and different approaches to designing them.