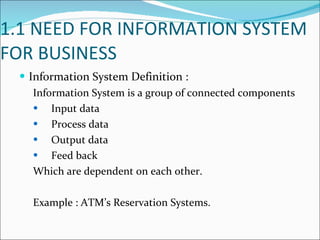
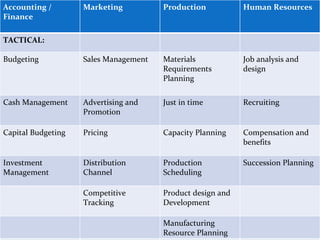
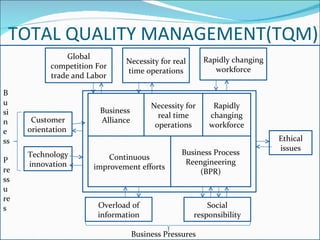
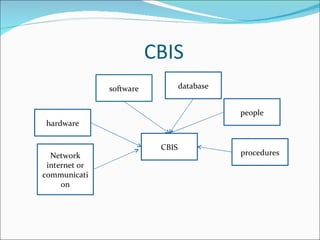
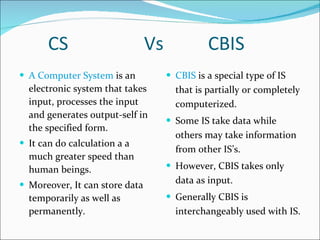
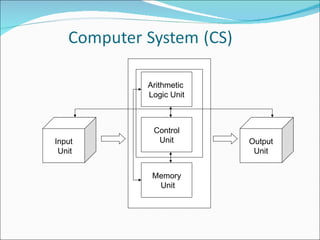
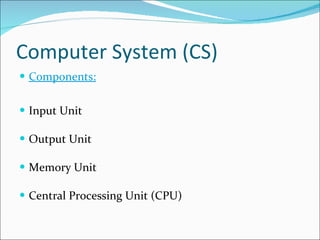
The document discusses information systems for businesses and how they have evolved. It covers the need for information systems to support fast and accurate transactions, storage, communication, and decision-making. It also discusses the pressures businesses face in today's global, technology-driven environment and how they are responding through strategic systems, business process reengineering, e-commerce, alliances, and continuous improvement efforts.