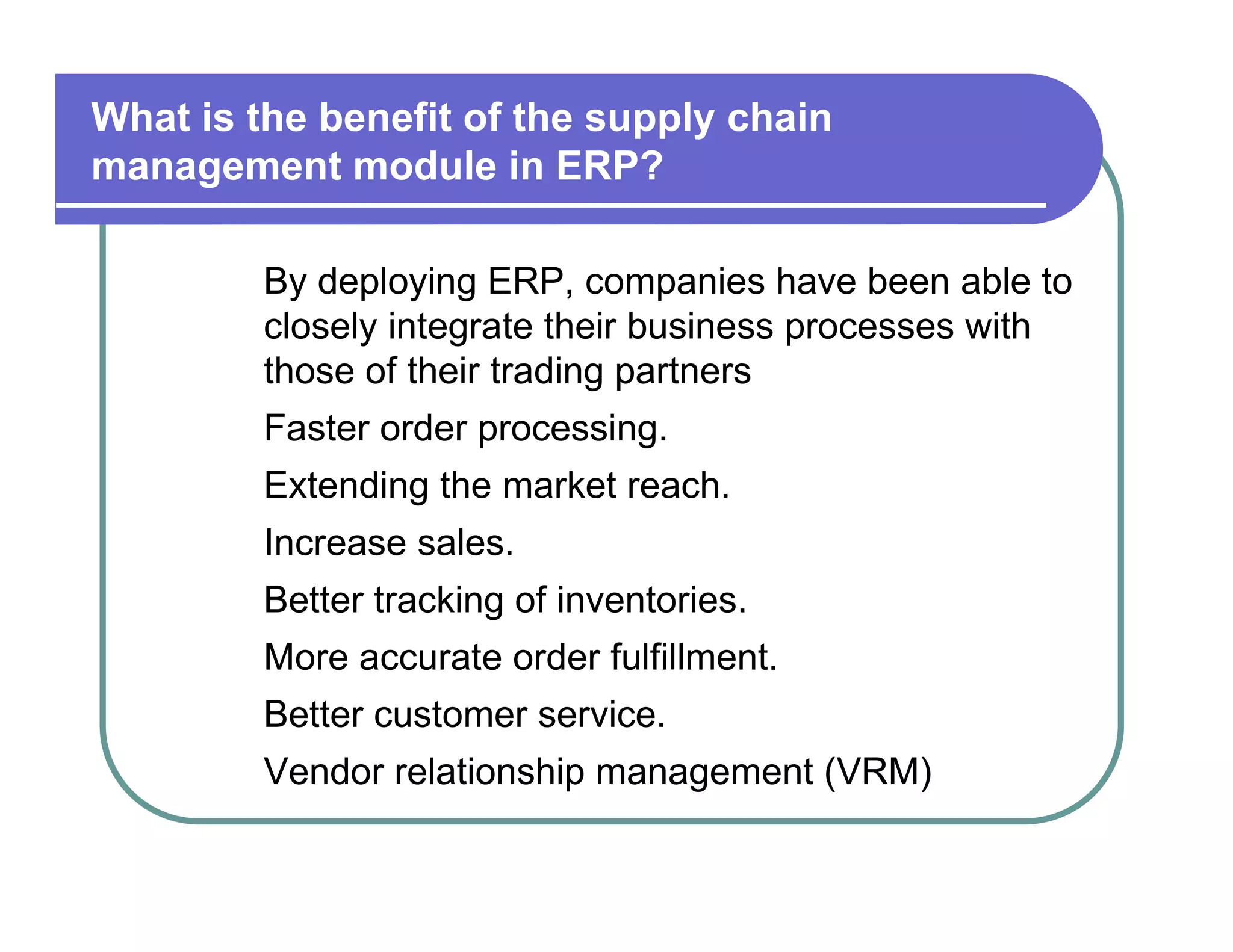
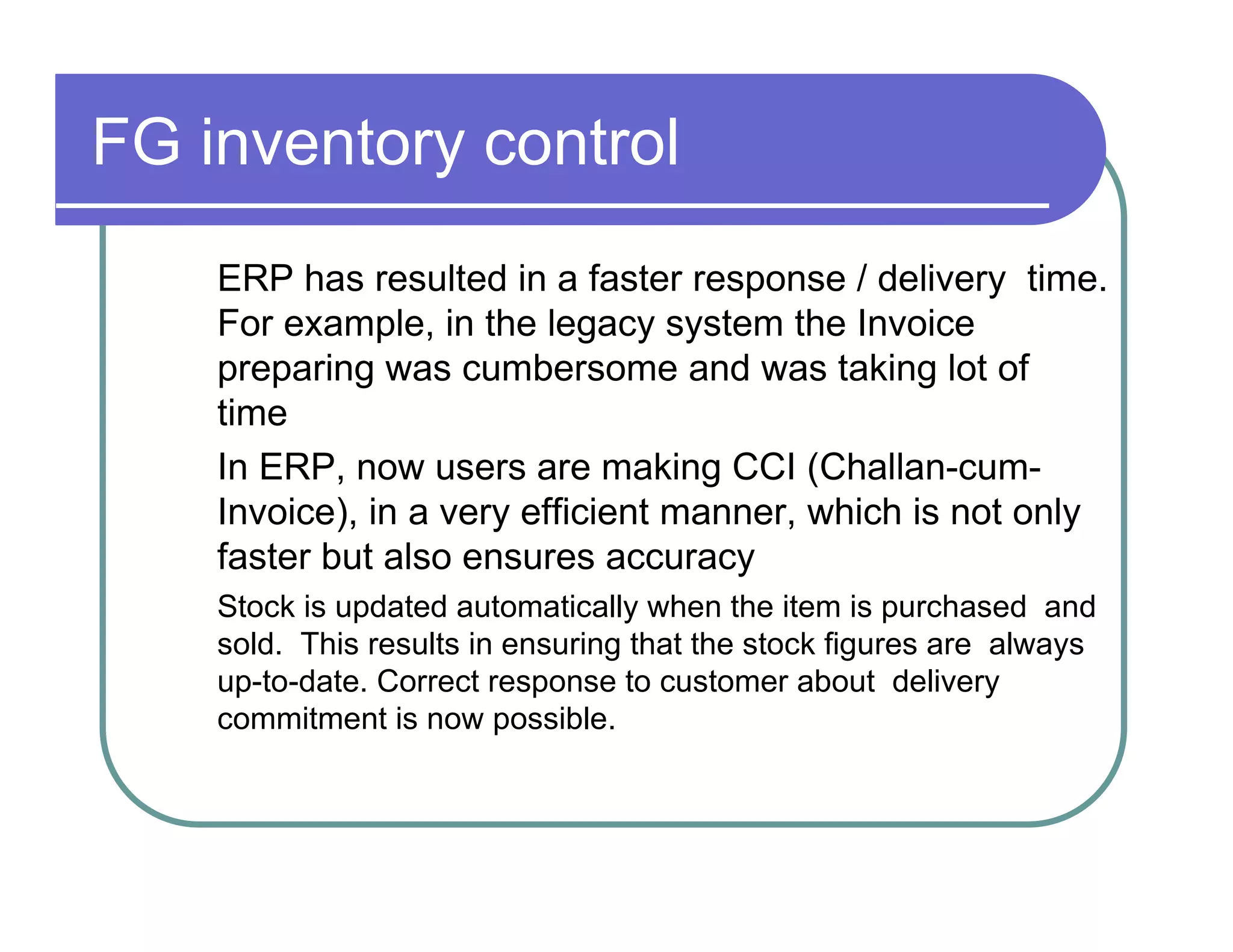
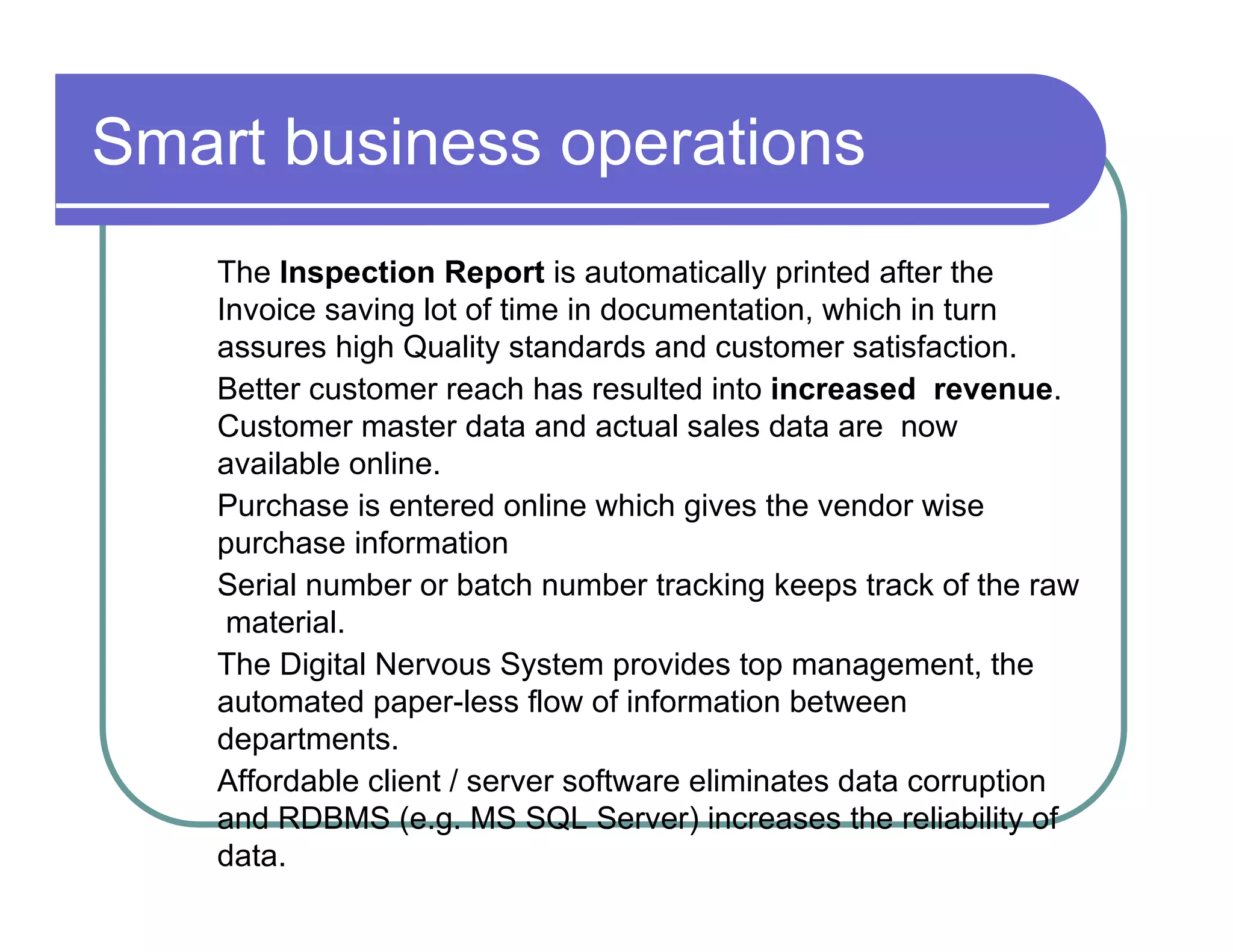
1. ERP systems provide benefits like improved operational efficiency, better inventory management, and enhanced data-driven decision making for management.
2. However, ERP implementations often fail due to lack of top management commitment, unrealistic timelines and expectations, and inadequate training and preparation of users and processes.
3. For successful ERP implementation, companies must have a well-defined system requirements specification, carefully select the appropriate ERP package, and ensure change management and proper education of users.