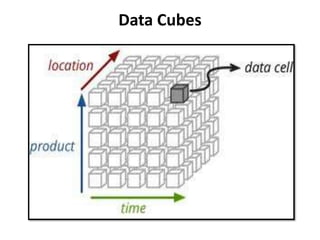
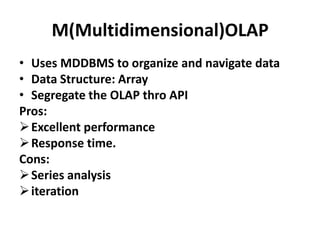
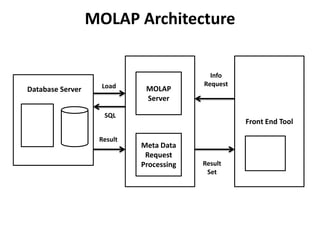
OLAP provides multidimensional analysis of large datasets to help solve business problems. It uses a multidimensional data model to allow for drilling down and across different dimensions like students, exams, departments, and colleges. OLAP tools are classified as MOLAP, ROLAP, or HOLAP based on how they store and access multidimensional data. MOLAP uses a multidimensional database for fast performance while ROLAP accesses relational databases through metadata. HOLAP provides some analysis directly on relational data or through intermediate MOLAP storage. Web-enabled OLAP allows interactive querying over the internet.