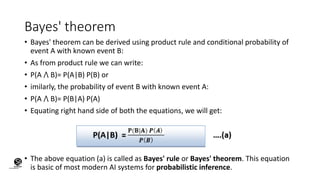
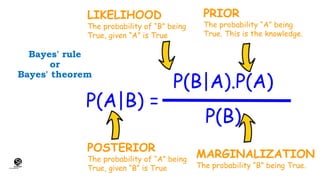
Bayes' theorem is a method for calculating conditional probabilities, linking the likelihood of events based on prior information. It incorporates new evidence to refine probability assessments and is fundamental to Bayesian statistics and probabilistic inference in AI. Applications include medical diagnosis, decision-making, and predictions in areas like weather forecasting.