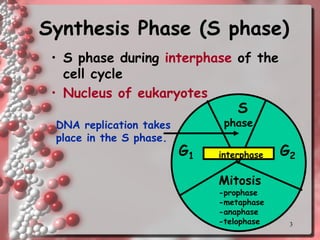
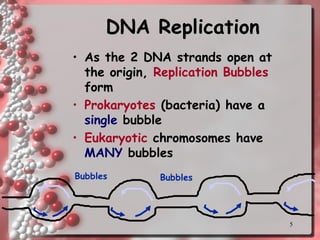
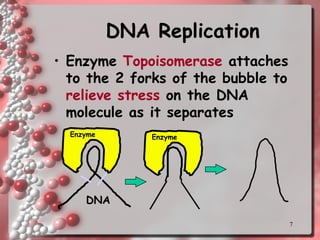
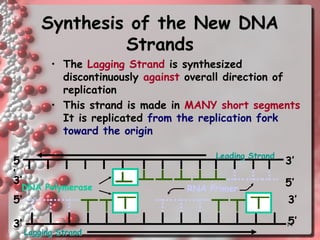
DNA replication involves copying the DNA of a cell before it divides. It occurs during the S phase of interphase and results in two identical DNA molecules, each with one original and one new strand. The double helix unwinds and an enzyme adds complementary nucleotides to each strand to replicate the DNA. On the lagging strand, DNA is synthesized discontinuously in short segments called Okazaki fragments which are later joined together. DNA replication ensures that daughter cells have identical copies of the parental DNA.