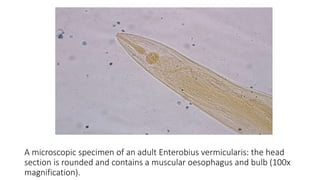
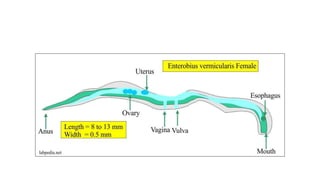
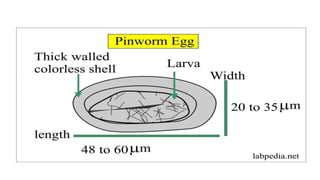
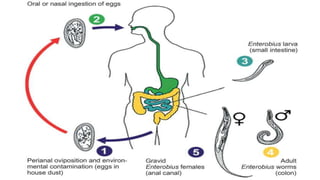
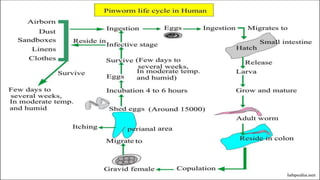
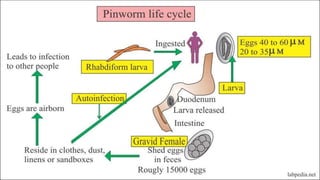
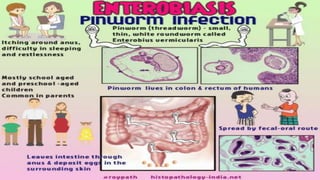
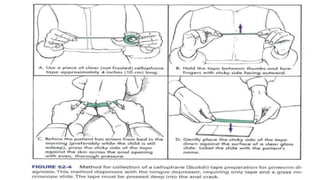
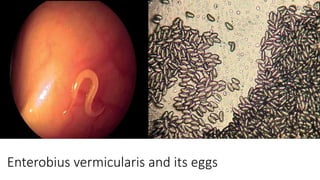
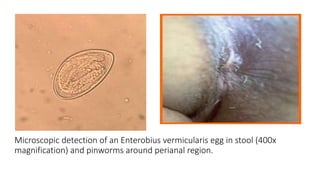
Enterobius vermicularis, commonly known as pinworm, is a nematode parasite that infects humans, especially children. The female pinworm is 9-12 mm long while the male is 3-5 mm long. Pinworms lay 10000-15000 oval shaped eggs that are 50-60 μm by 25 μm in size. Pinworm infection is common worldwide and spreads through the oral-fecal route. Symptoms include intermittent anal pruritis and restlessness. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of stool or adhesive tape samples to detect eggs. Treatment involves prescription of mebendazole, pyrantel pamoate or pyrinium embonate.