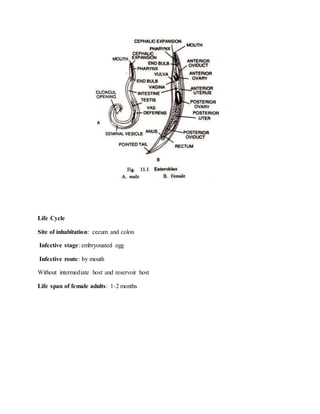
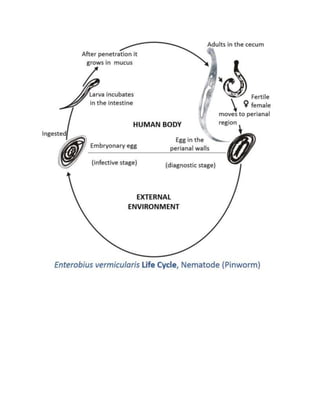
Enterobius vermicularis, also known as pinworms, are one of the most common intestinal nematodes that inhabit the cecum and colon. The adult female pinworms migrate out of the anus at night to lay eggs on the perianal skin, causing itching. People become infected by ingesting pinworm eggs. Pinworms have a simple lifecycle within the human host without needing an intermediate host. Common symptoms include irritation and itching in the anal area, though many infections are asymptomatic. Pinworm infections are diagnosed via cellophane tape test or NIH swab to detect eggs on the skin. Treatment involves a single dose of anthelmintic medication repeated after two weeks.