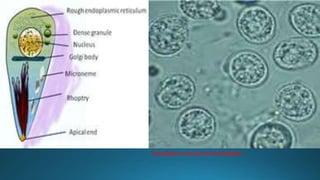
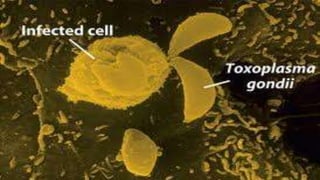
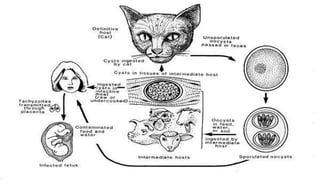
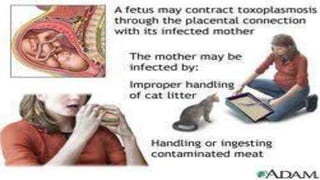
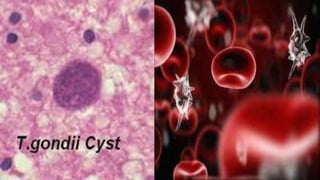
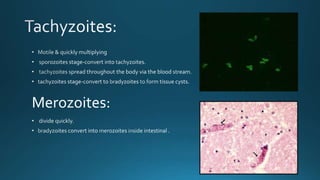
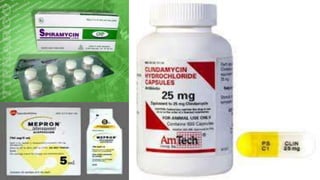
Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite that infects humans and other warm-blooded animals. It has a complex life cycle involving cats as the definitive host and intermediate hosts such as humans, cattle, birds and rodents. T. gondii infects the intestinal epithelium and muscle tissue and spreads via the bloodstream. While most infections are asymptomatic, it can cause flu-like symptoms in healthy individuals and severe eye and brain infections in immunocompromised people. Diagnosis involves serological tests and treatment consists of antibiotics. Control measures include proper hygiene and sanitation to prevent exposure from cat feces.