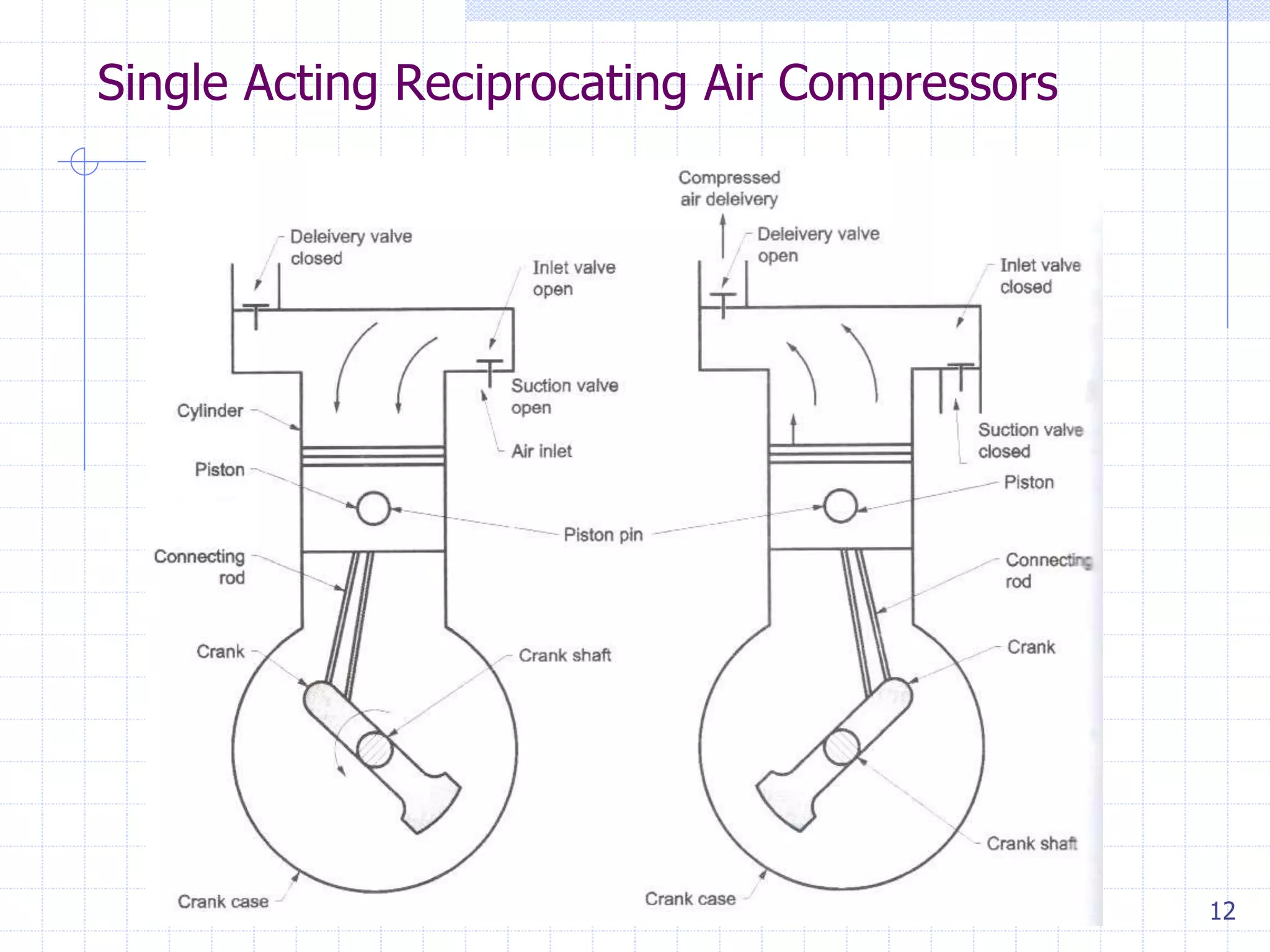
This document discusses different types of air compressors. It describes positive displacement compressors like reciprocating compressors which work on the principle of a bicycle pump and have pistons that compress air. Rotary compressors are also positive displacement compressors that provide continuous airflow. Dynamic compressors like centrifugal compressors use a rotating impeller to transfer energy and compress incoming air without boundaries containing it. Centrifugal compressors are commonly used for medium pressure applications and produce smooth compressed air output.