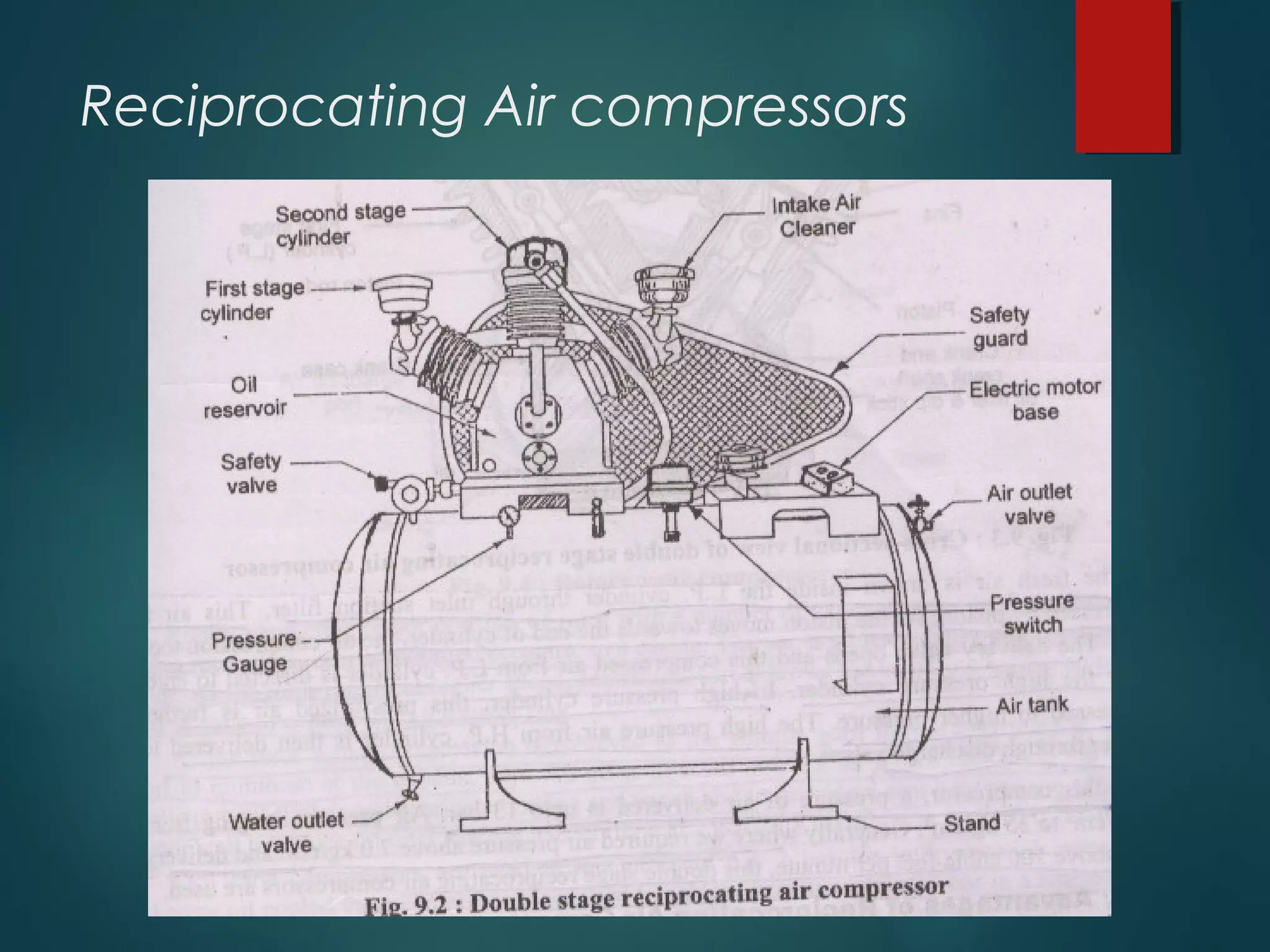
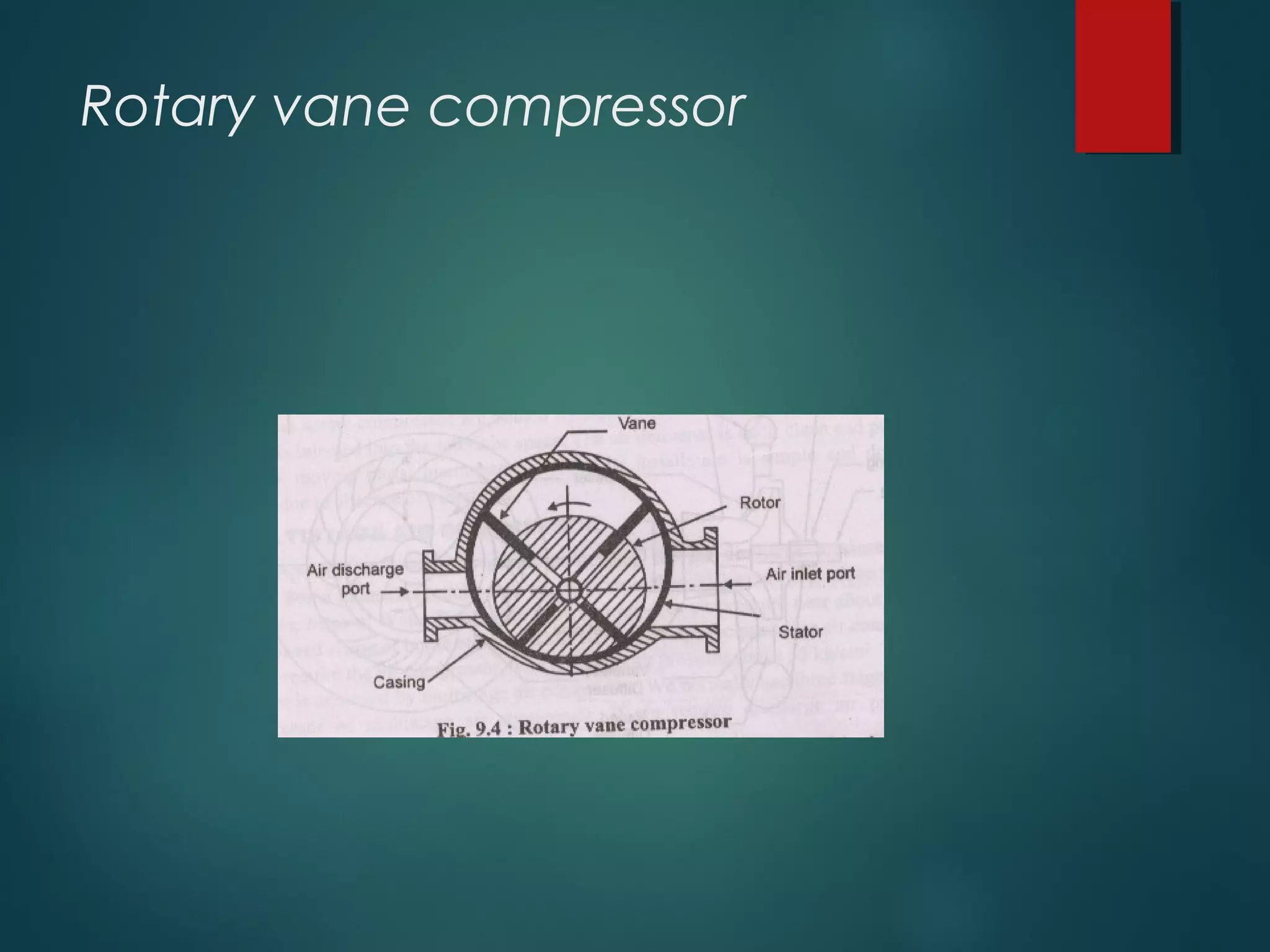
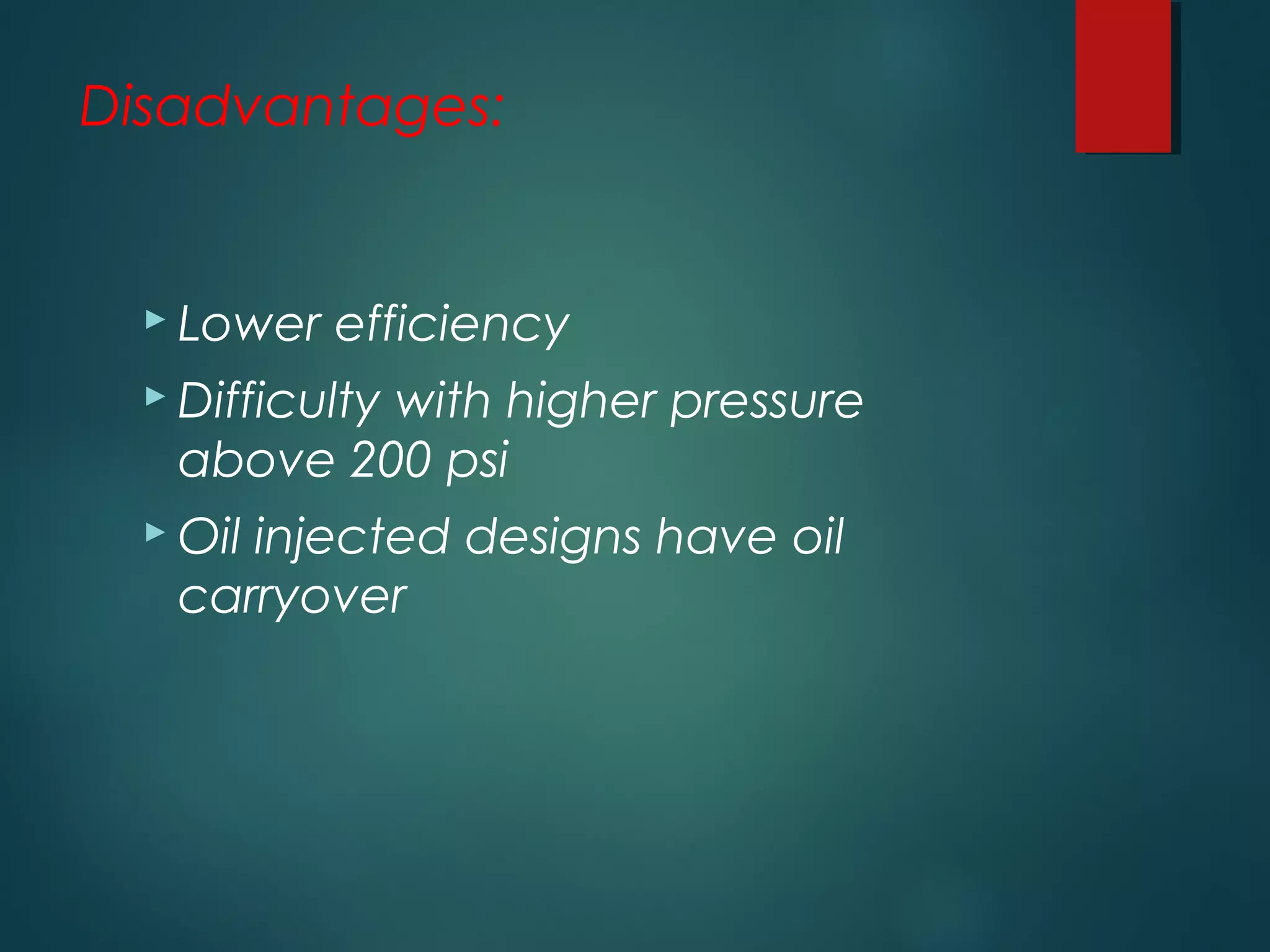
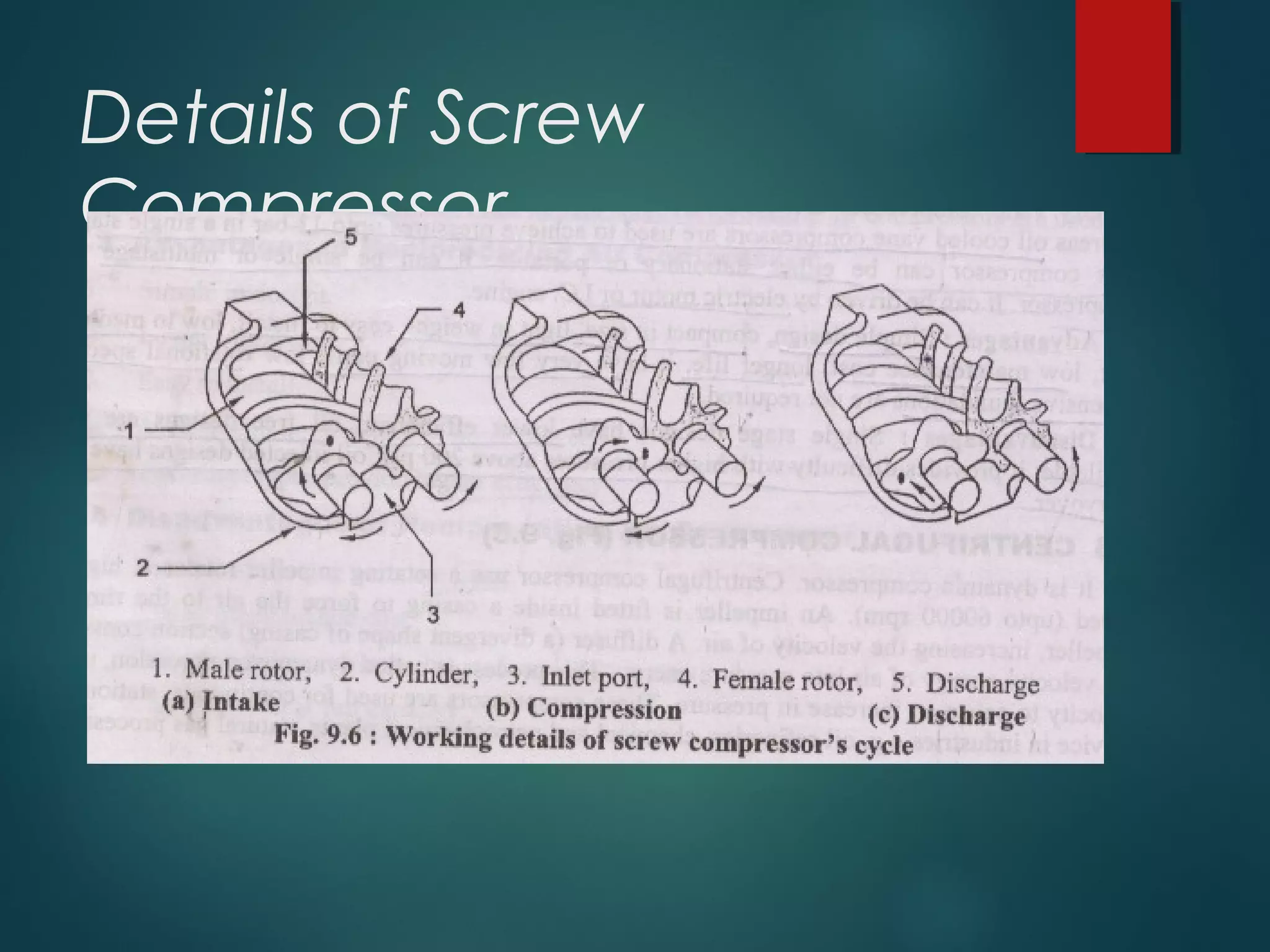
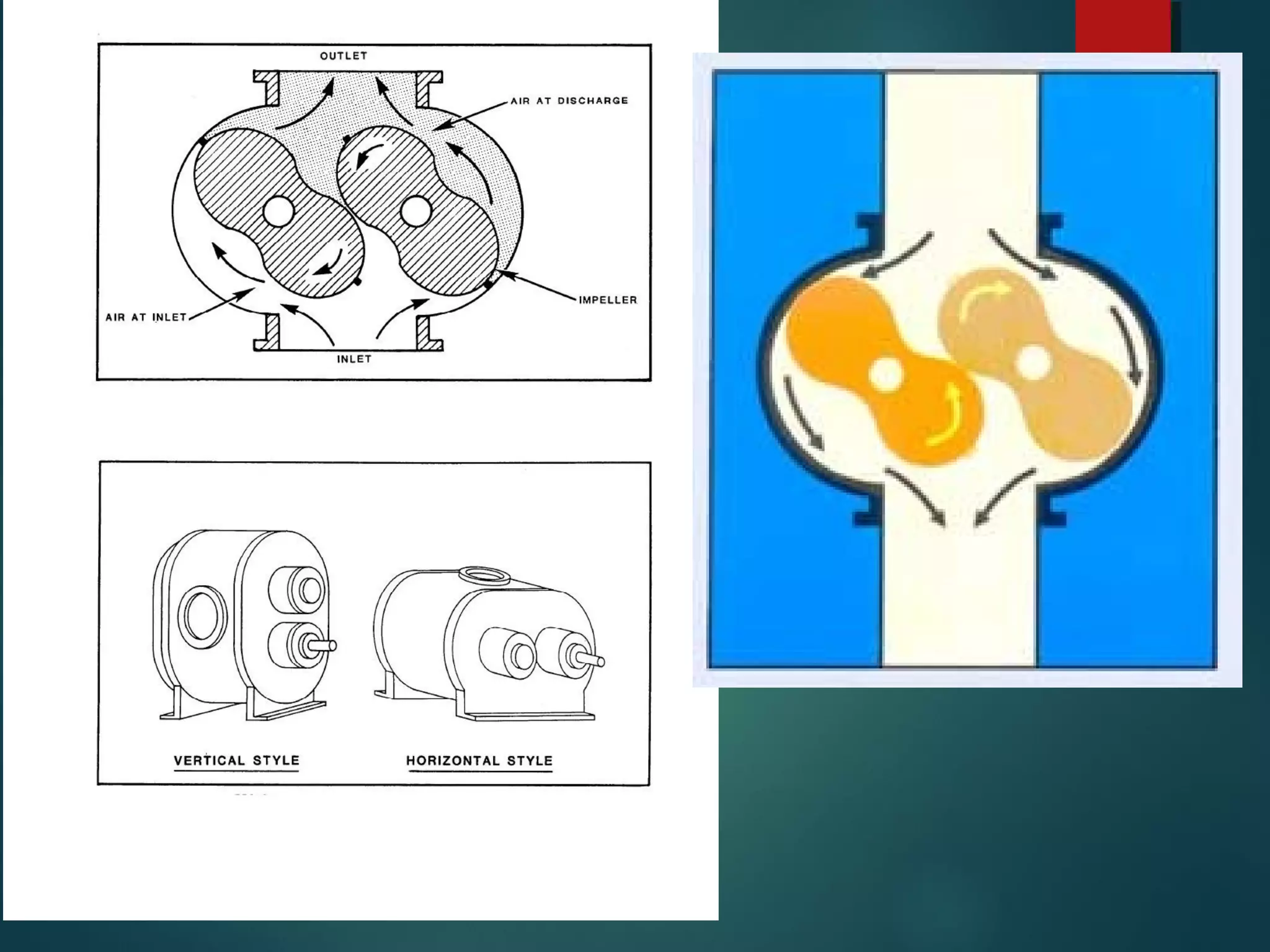
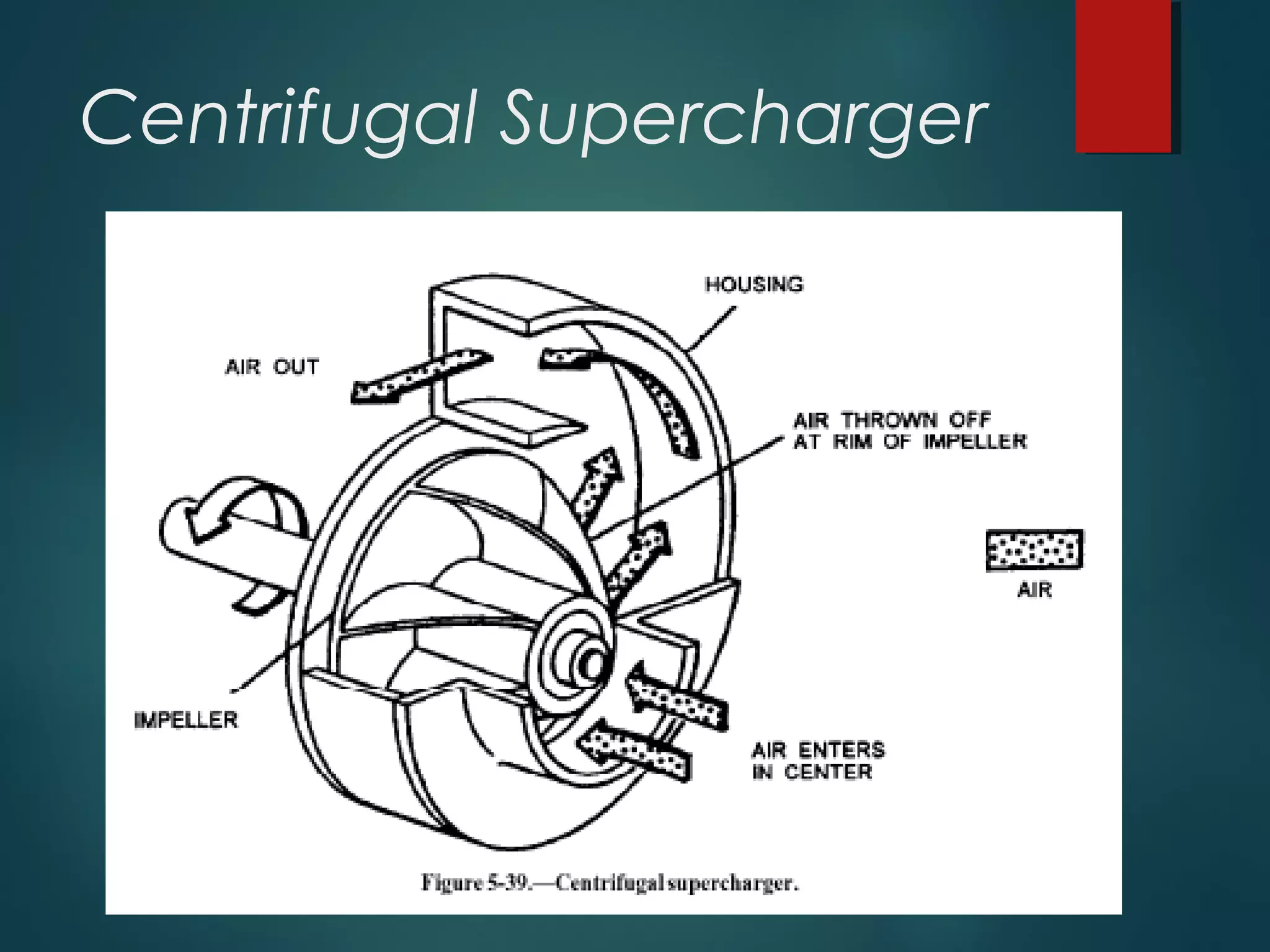
This document provides information about Group No. 2's project on air compressors. It discusses various types of compressors including reciprocating, rotary vane, screw, and centrifugal compressors. It describes the working principles, classifications, advantages and disadvantages of different compressors. It also covers topics like compressor efficiency, multi-stage compression, selection of compressors, and industrial applications of compressed air.