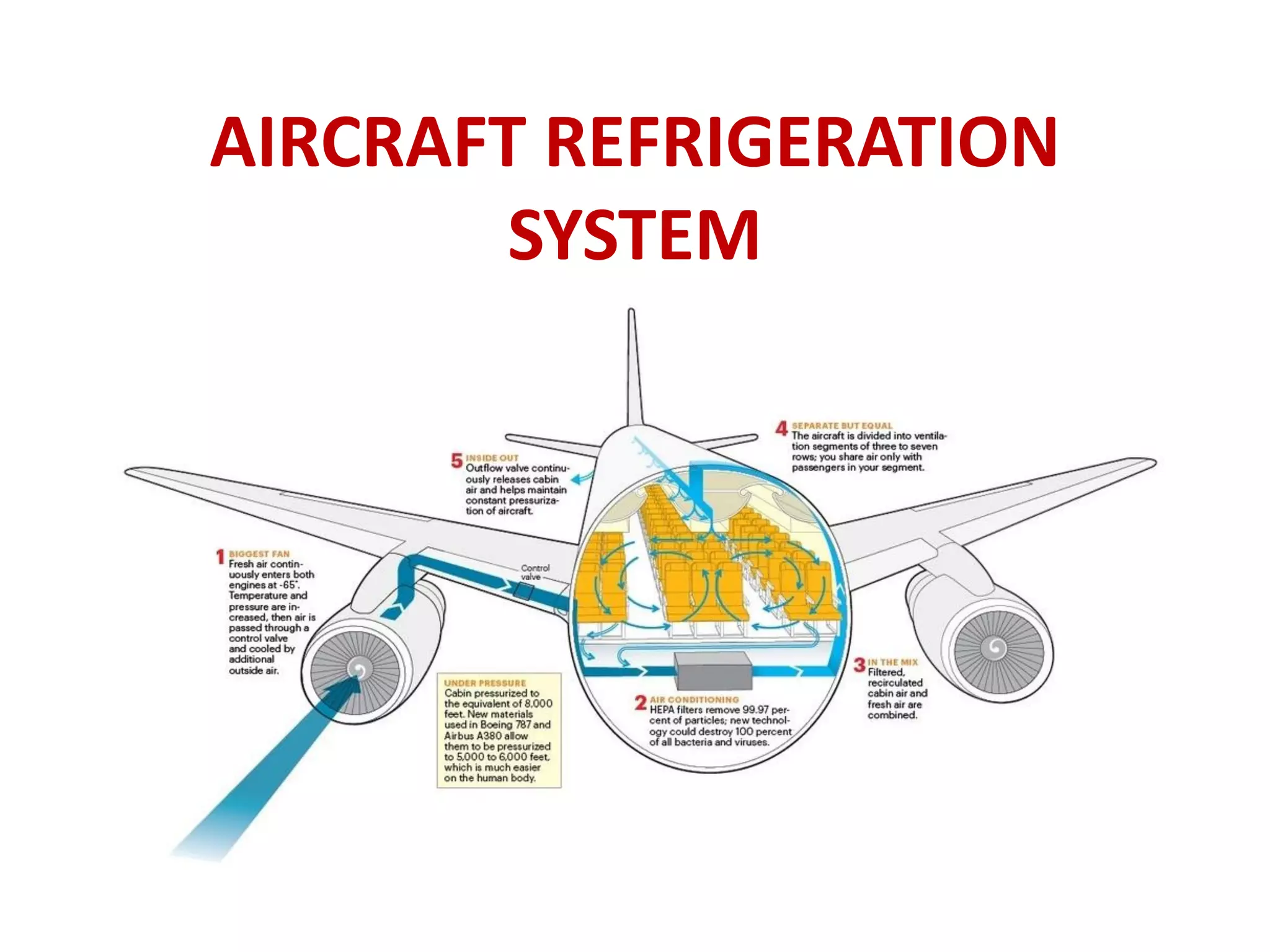
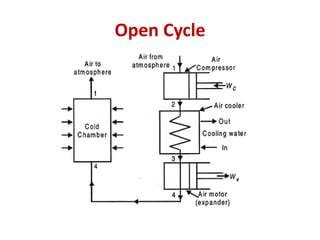
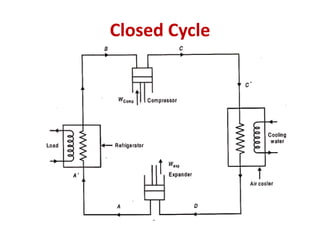
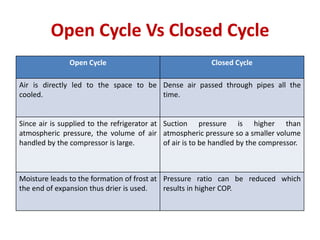
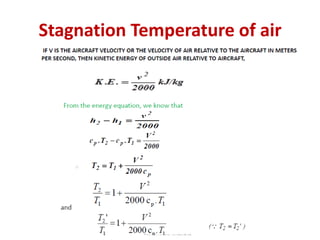
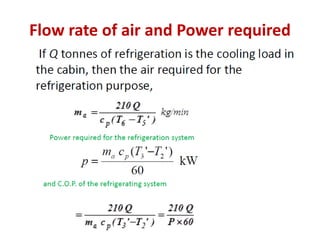
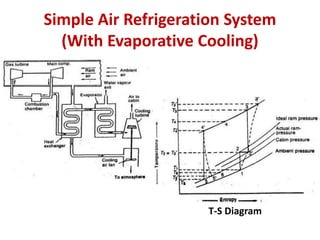
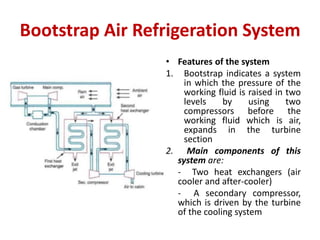
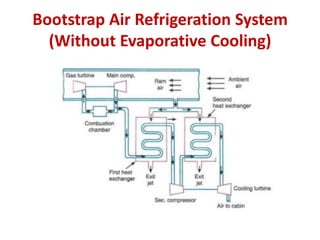
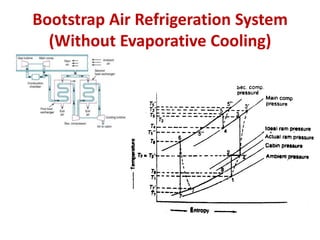
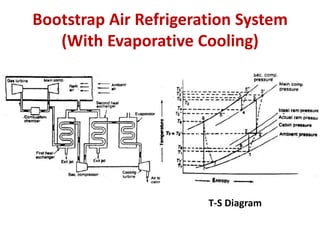
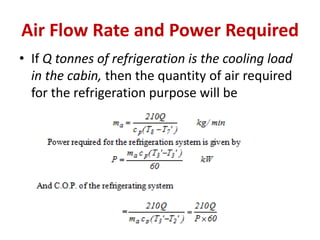
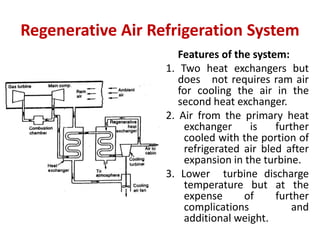
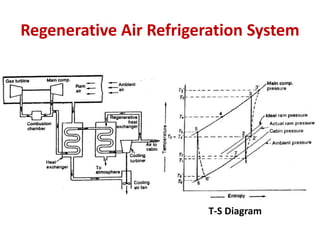
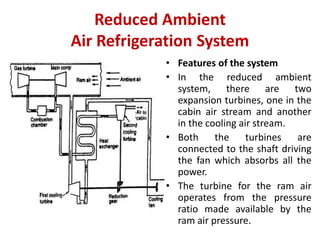
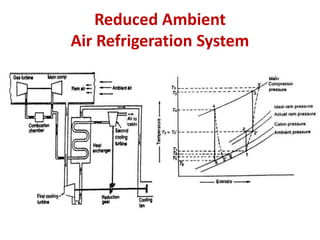
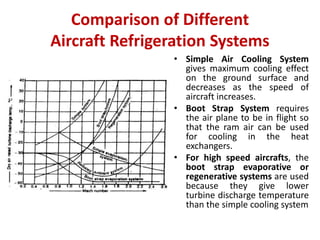
The document details various aircraft refrigeration systems, highlighting the need for cooling due to both external and internal heat sources. It describes several types of air refrigeration cycles, including simple, bootstrap, regenerative, and reduced ambient systems, and compares their advantages and disadvantages. Key features and operational principles of these systems are discussed, focusing on their cooling efficiencies and application in different aircraft environments.