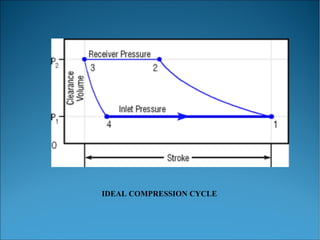
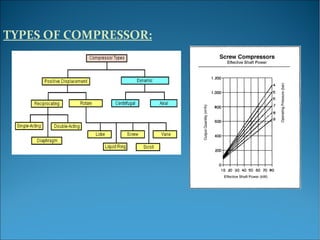
This document outlines the key aspects of air compressors, including their operation, types, and specifications for sizing and auxiliary equipment. It discusses the models of compression cycles (isothermal, adiabatic, and polytropic) and details the features of rotary screw and reciprocating compressors. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of accurate sizing and the necessary accessories for safe and efficient operation.