Embed presentation
Downloaded 45 times
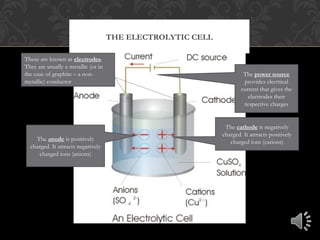
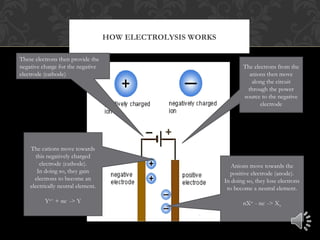
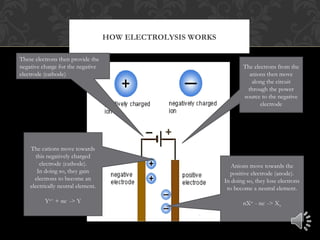

Electrolysis is the process of using electrical current to separate compounds into their component ions. In an electrolytic cell, anions move toward the positively charged anode where they lose electrons and cations move toward the negatively charged cathode where they gain electrons, resulting in the production of neutral elements at each electrode. The flow of electrons through the circuit provides the charges needed at each electrode to attract the opposite ions.





