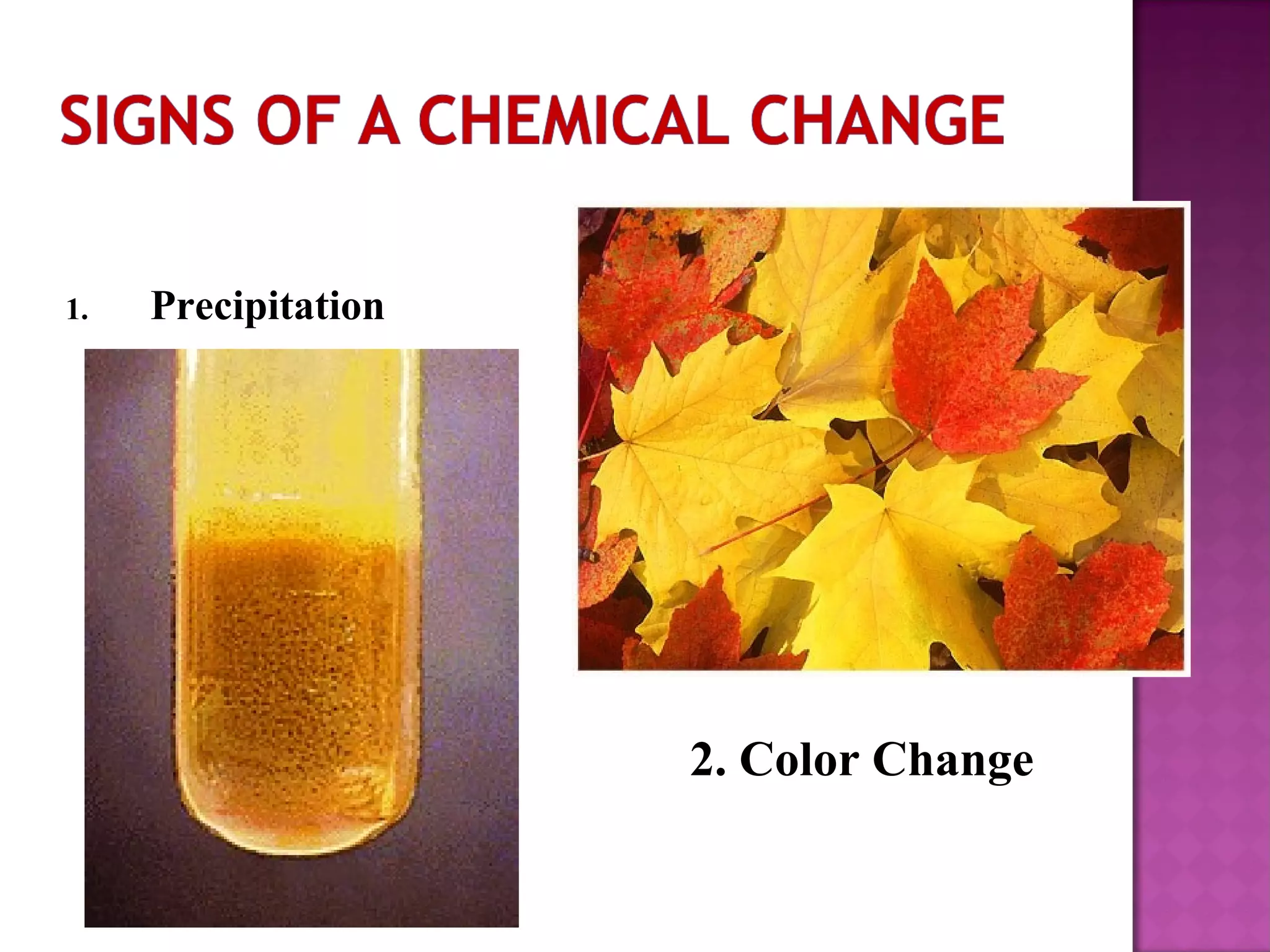
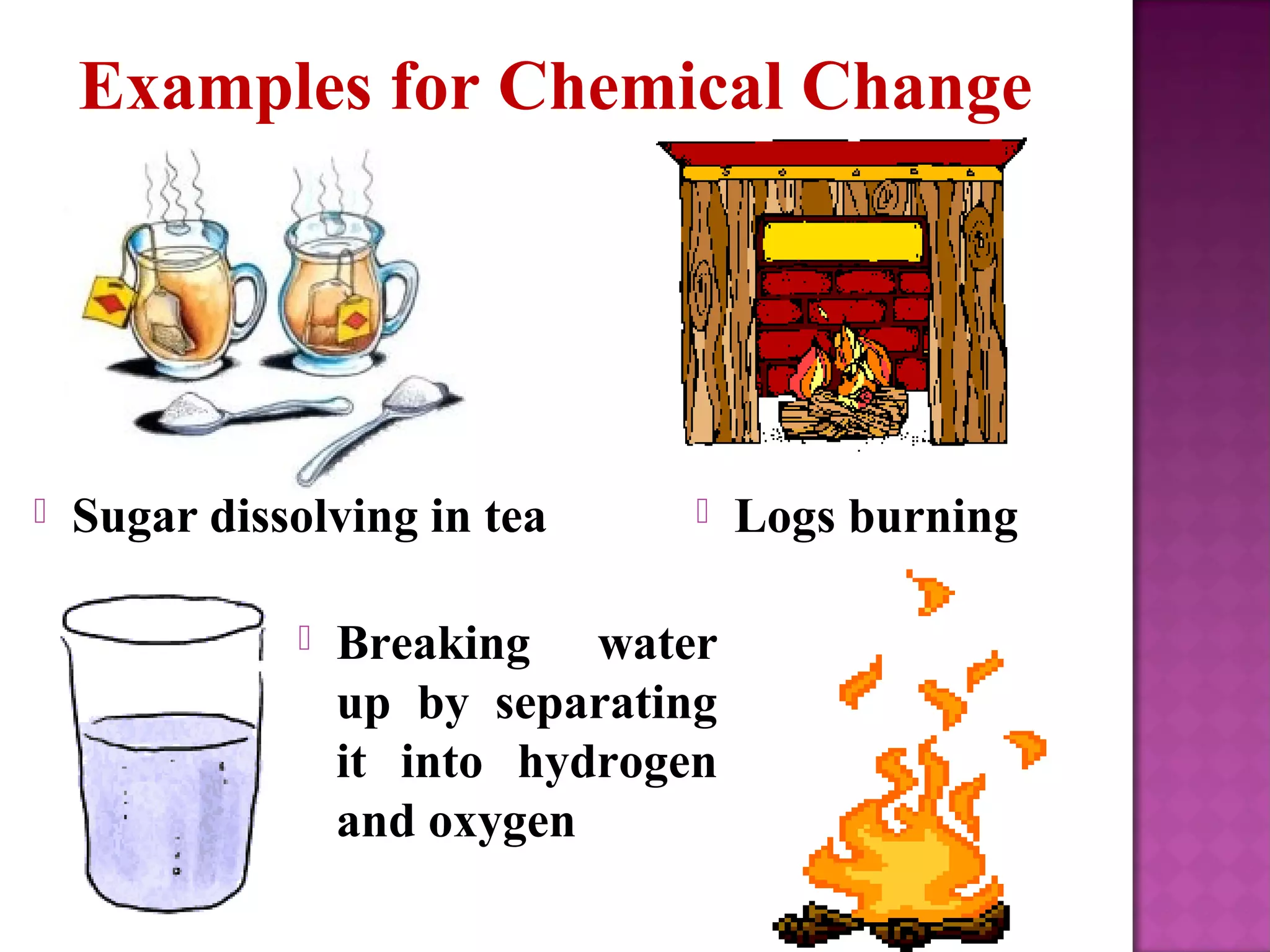
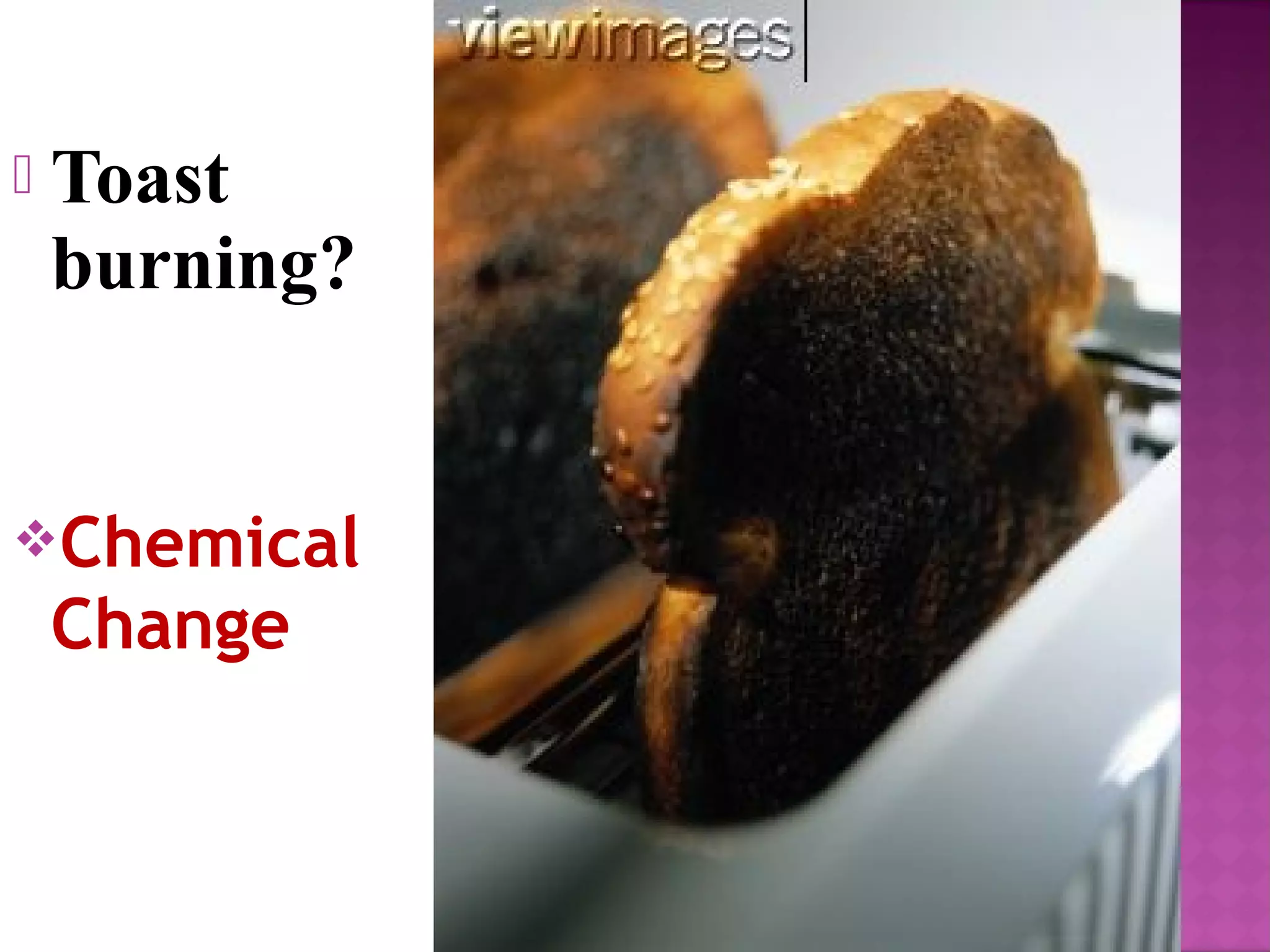This document discusses the difference between physical and chemical changes in matter. A physical change alters the form or properties of a substance without changing its chemical composition, such as cutting, crushing, dissolving, or changes in state. A chemical change results in one or more new substances being formed through chemical reactions, evidenced by signs like color change, bubbling, gas production or temperature change. Examples of physical changes given are melting ice, sawing wood, and evaporating a puddle. Chemical change examples include burning fuels, baking a cake, and dissolving sugar in tea.