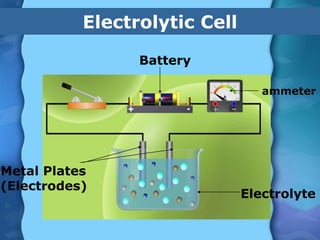
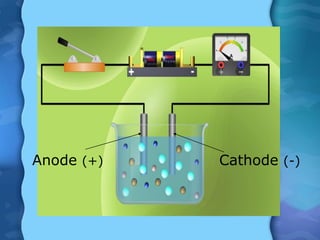
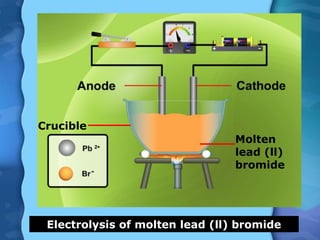
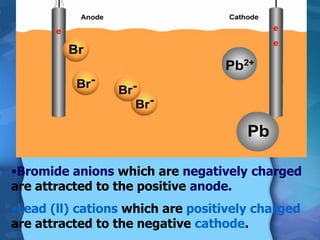
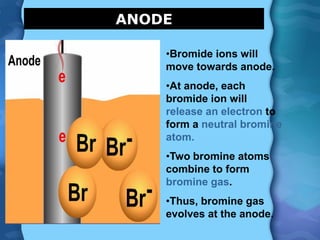
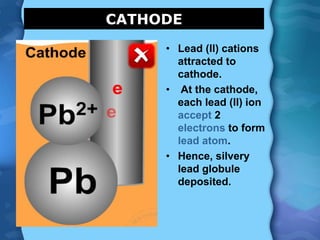
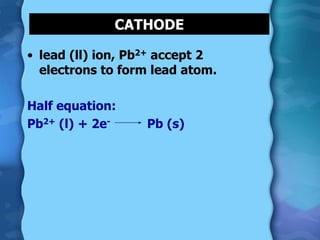
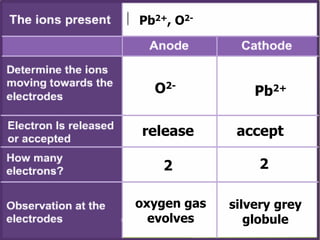
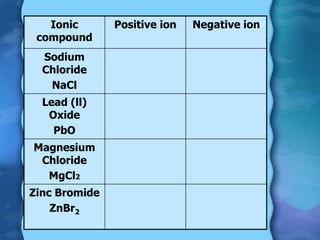
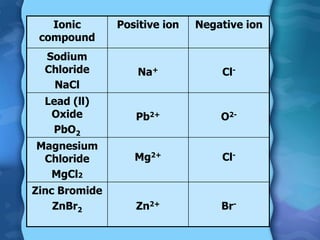
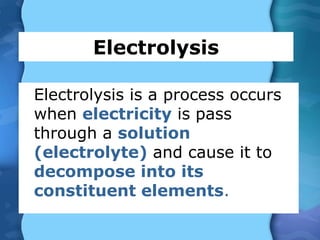
Electrolytes are substances that can conduct electricity in the molten or liquid state and undergo chemical changes. Electrolysis is a process where electrolytes are broken down into their constituent elements by passing electricity through them. During electrolysis, ions migrate to the oppositely charged electrodes. At the anode, ions lose electrons and form gases or dissolve. At the cathode, ions gain electrons and form solid elements. Examples of electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide and lead(II) oxide are described through their half reactions at the anode and cathode and overall reactions.



![Electrolytes are substances able to conduct
electricity in [ ] state or [ ]
state and undergo [ ] change.
Electrolysis is a process where the [ ]
are broken down into its [ ]
elements by passing [ ] through it.
electrolytes molten chemical
liquid electricity constituent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electrolysismoltensubstances-130813050103-phpapp01/85/Electrolysis-molten-substances-8-320.jpg)
![Electrolytes are substances able to
conduct electricity in [molten] state or
[liquid] state and undergo [chemical]
change.
Electrolysis is a process where the
[electrolytes] are broken down into its
[constituent] elements by passing
[electricity] through it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electrolysismoltensubstances-130813050103-phpapp01/85/Electrolysis-molten-substances-9-320.jpg)