- Adsorption is the accumulation of molecular species at the surface of a solid or liquid rather than in the bulk. The substance that accumulates is called the adsorbate and the surface it accumulates on is the adsorbent.
- Examples of adsorption include gases accumulating on charcoal surfaces, dye molecules accumulating on charcoal when added to solutions, and aqueous sugar solutions becoming colorless when passed over beds of charcoal.
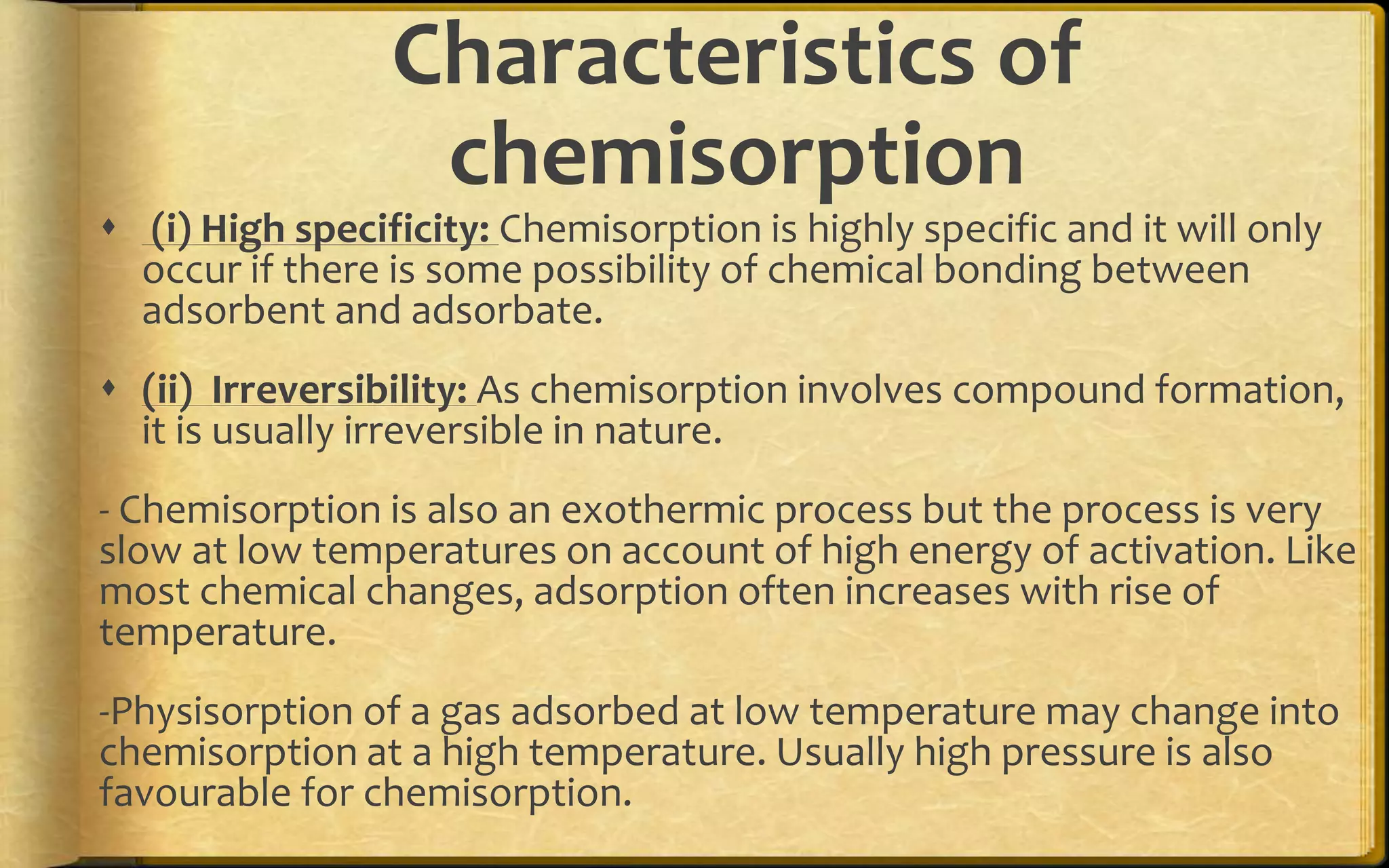
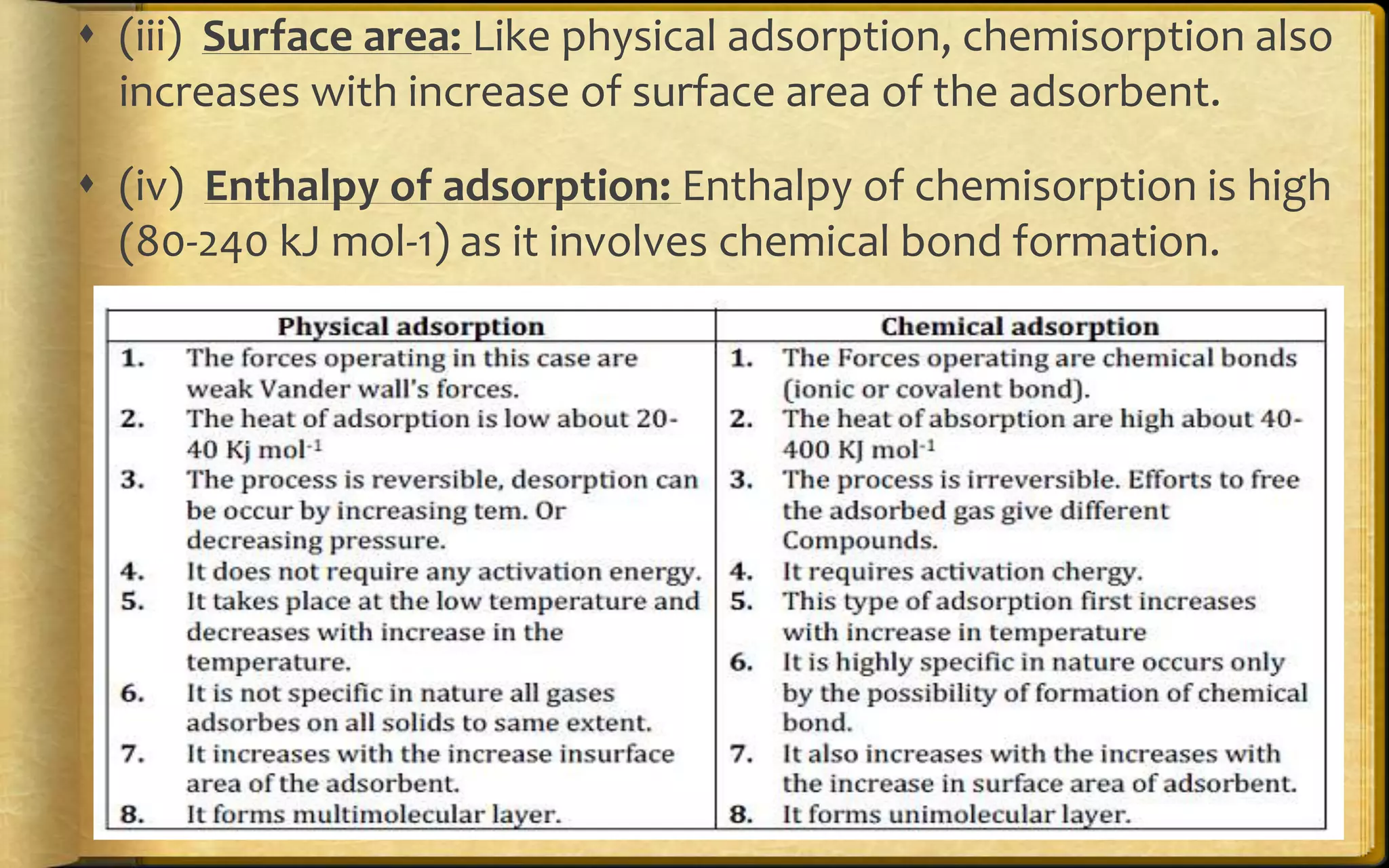
- There are two main types of adsorption - physical adsorption (physisorption) due to weak van der Waals forces, and chemical adsorption (chemisorption) due to chemical bonding between adsorbate and adsorbent.

























































![ Similarly, in the coagulation of a positive sol, the flocculating
power is in the order: [Fe(CN)6]4– > PO43– > SO42– > Cl–
The minimum concentration of an electrolyte in millimoles per
litre required to cause precipitation of a sol in two hours is
called coagulating value. The smaller the quantity needed, the
higher will be the coagulating power of an ion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surfacechemistryppt-160109134513/75/Surface-chemistry-ppt-CLASS-12-CBSE-CHAPTER-5-62-2048.jpg)







