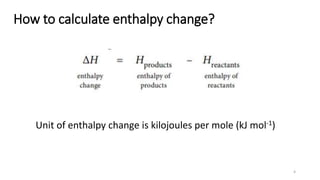
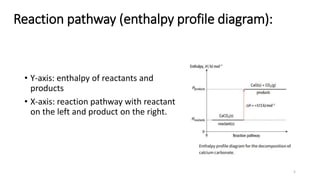
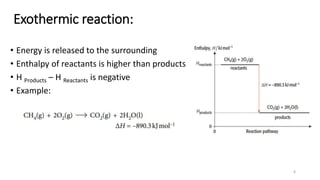
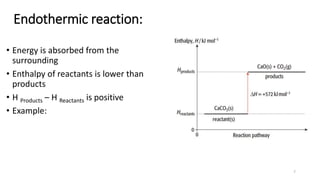
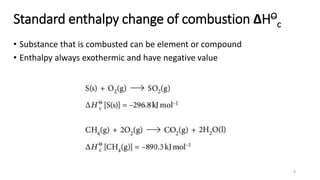
This document summarizes different types of enthalpy changes in chemical reactions. It defines exothermic reactions as releasing energy to the surroundings and endothermic reactions as absorbing energy from the surroundings. Enthalpy change is the energy exchange between a reaction and its surroundings at constant pressure. The document explains how to calculate enthalpy change and represents reaction pathways using enthalpy profile diagrams to show enthalpy changes for exothermic and endothermic reactions. It also defines standard enthalpy changes of combustion, neutralization, solution, and hydration of salts.