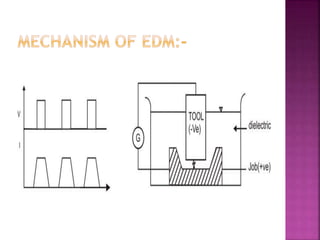
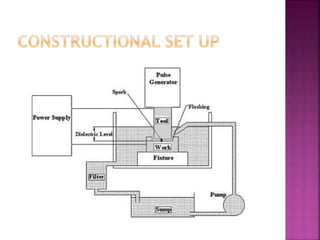
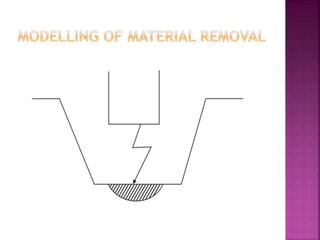
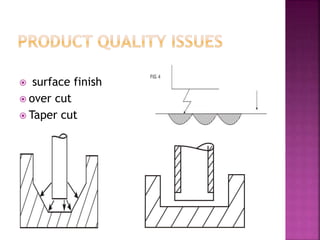
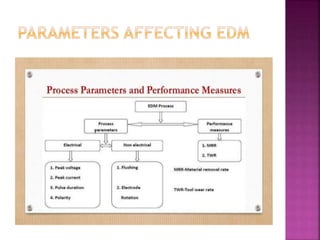
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a non-traditional machining process that uses electric sparks to erode metal. In EDM, a potential difference is created between an electrode tool and conductive workpiece, causing electric sparks that remove small amounts of metal. Key advantages of EDM include the ability to machine very hard materials and complex shapes. Main applications are for molds, dies, and parts requiring close tolerances that would be difficult with traditional cutting tools. The document discusses the history, process, equipment, parameters, advantages, and limitations of EDM.