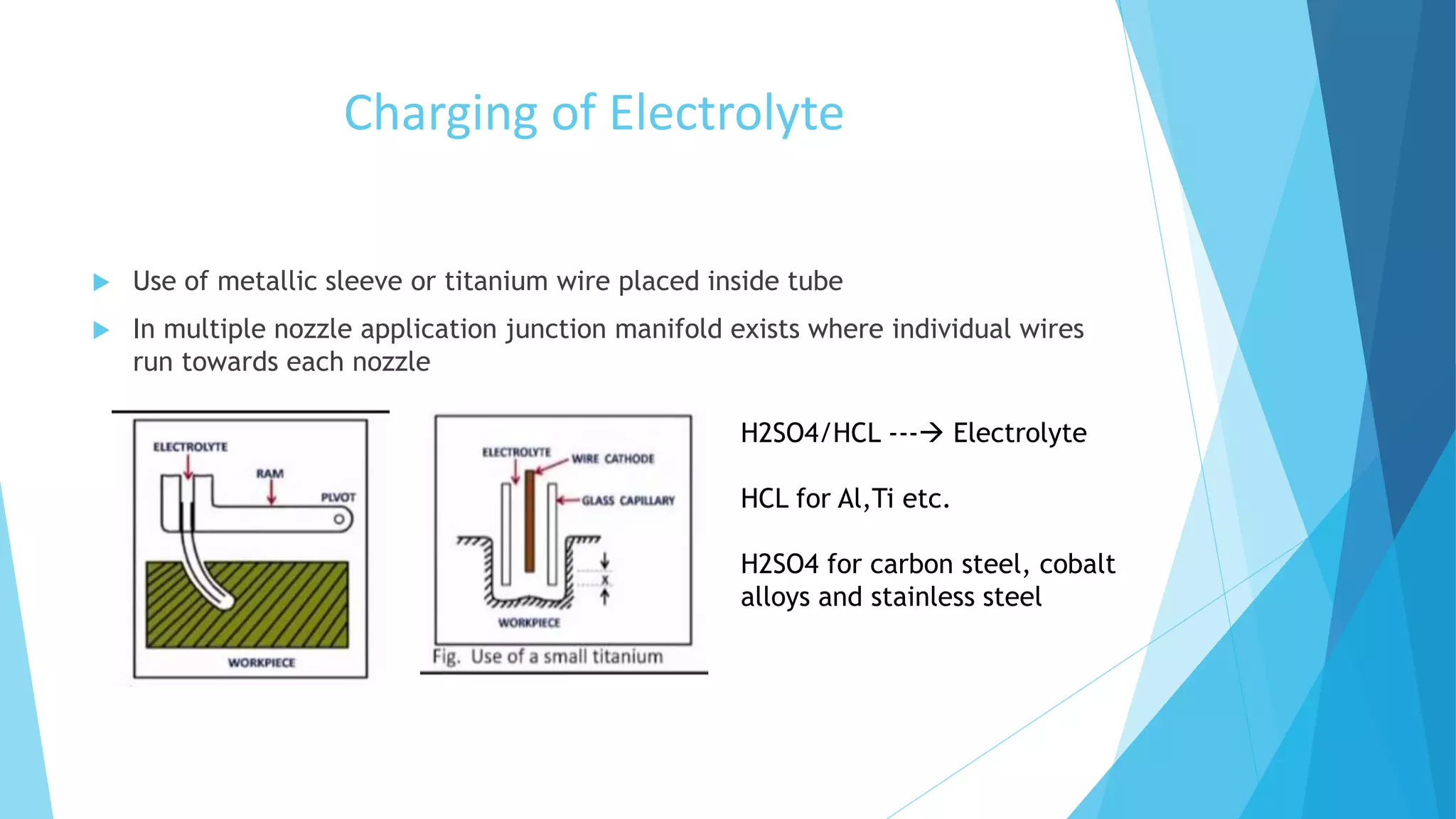
Electro Stream Drilling (ESD) is an electrochemical machining process that uses a high velocity stream of negatively charged acidic electrolyte to drill small diameter holes. It can drill holes between 0.127-0.89 mm using a voltage of 150-850 V. Unlike conventional electrochemical drilling, debris dissolved in the acidic electrolyte prevents clogging. ESD can drill deep and accurate holes through either dwell drilling or penetration drilling methods and offers advantages like high aspect ratio holes, low surface roughness, and no burrs or residual stresses. However, it has high initial costs and is limited to electrically conductive materials.