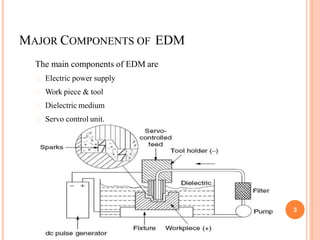
The material removal in EDM occurs due to the formation and collapse of a plasma channel between the electrode tool and workpiece. When a potential difference is applied, a spark is generated that reaches over 10,000°C, causing localized melting and vaporization of material. The plasma channel collapse then generates shock waves that remove the molten material. Proper dielectrics like kerosene are used to prevent oxidation and efficiently flush debris while maintaining the spark gap. Various power generators including RC relaxation circuits are used to control the electric spark discharge process parameters. EDM allows precision machining of electrically conductive materials, especially hard or complex shapes.