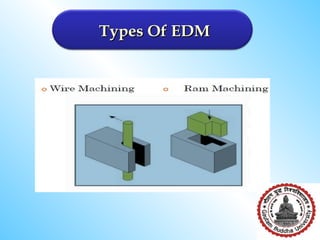
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) involves using electrical sparks to erode metal surfaces. Key aspects include:
1) An electrode is used to shape electrical discharges that melt and vaporize small amounts of material from the workpiece. Common electrode materials include copper, tungsten, and graphite.
2) A dielectric fluid is used to separate the electrode and workpiece and to flush away debris. Typical fluids include oil-based fluids like kerosene.
3) An electrical charge creates sparks that momentarily melt and vaporize metal. Process parameters like voltage, gap size, and flush rate must be optimized to control the erosion process.