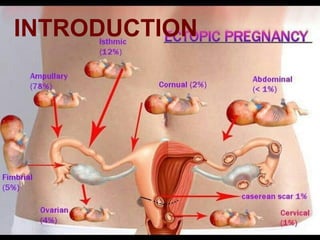
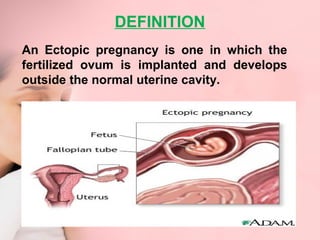
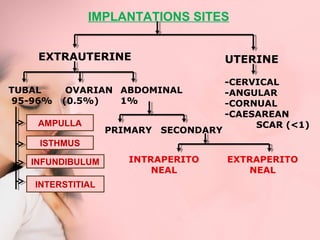
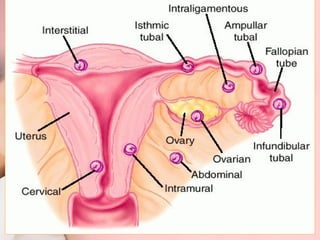
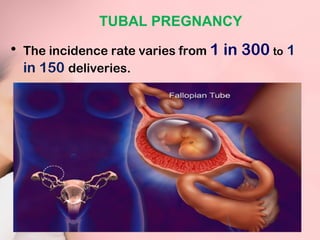
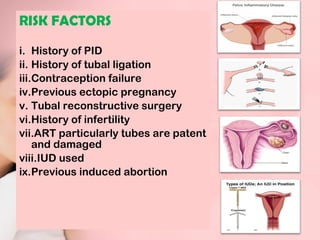
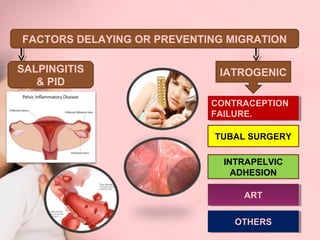
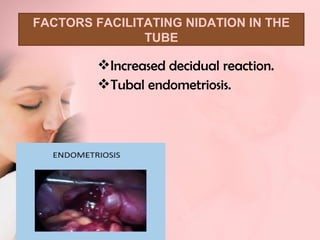
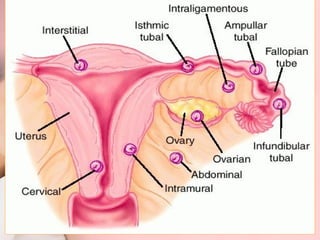
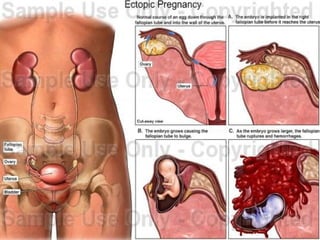
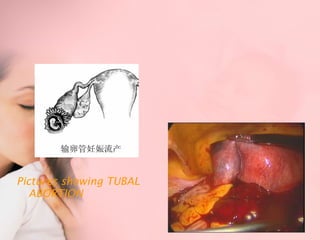
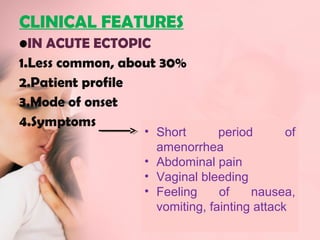
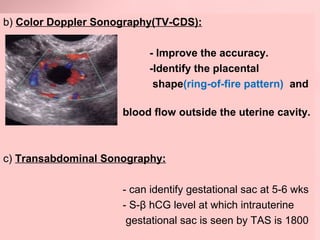
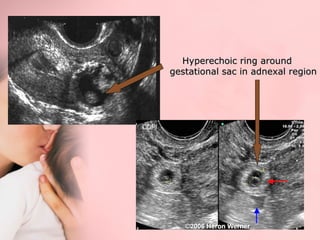
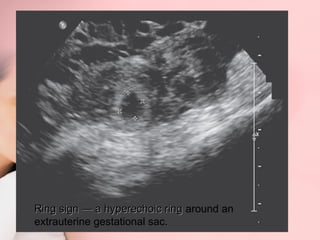
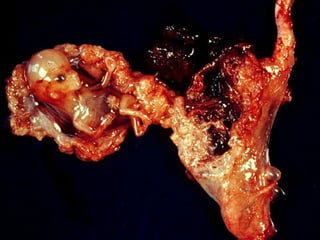
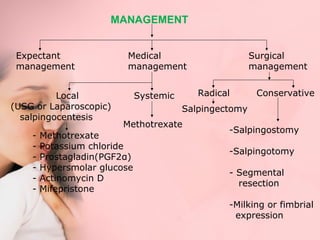
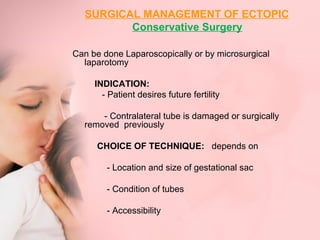
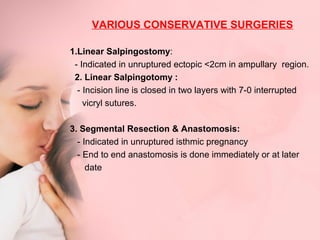
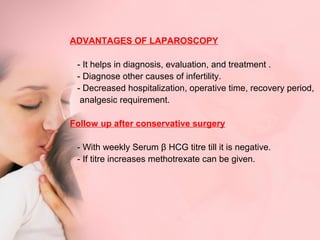
This document discusses ectopic pregnancy, which occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. It defines ectopic pregnancy and lists risk factors and causes. Symptoms can include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. Diagnosis involves beta-hCG levels, ultrasound, and laparoscopy. Management options for unruptured ectopic pregnancies include expectant monitoring, medical treatment with methotrexate, and surgical treatment such as salpingostomy or salpingotomy.