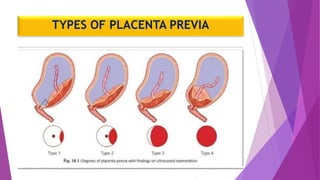
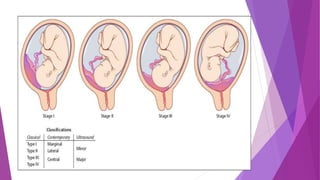
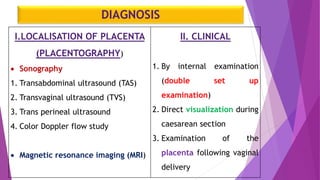
Placenta previa occurs when the placenta is implanted partially or completely over the lower uterine segment, leading to antepartum hemorrhage. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation and imaging techniques like ultrasound and MRI, while management focuses on maternal health and fetal maturity, considering hospitalization for all cases of antepartum bleeding. Active management, typically through caesarean delivery, is indicated for cases with severe bleeding, labor onset, or certain fetal conditions.