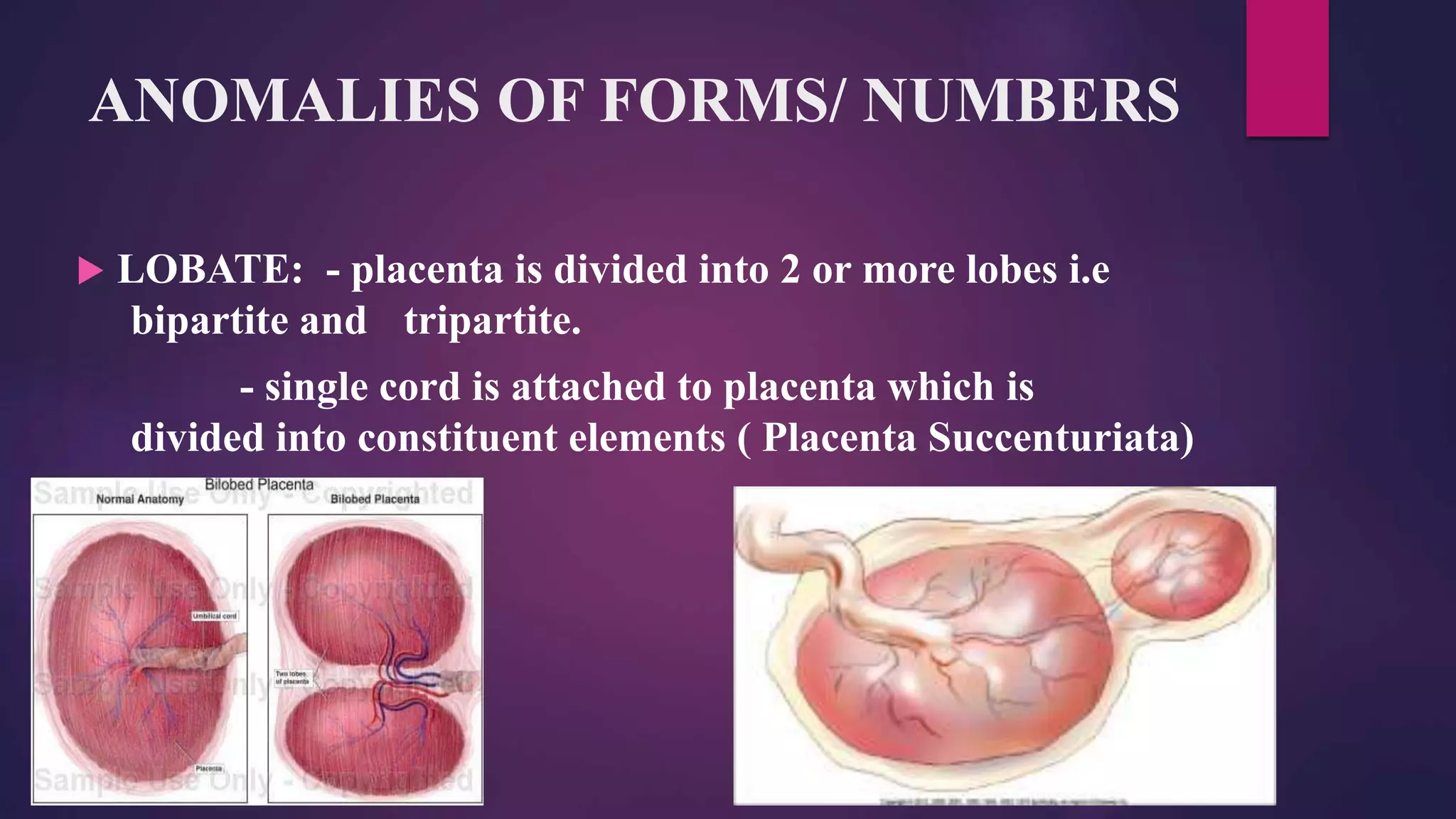
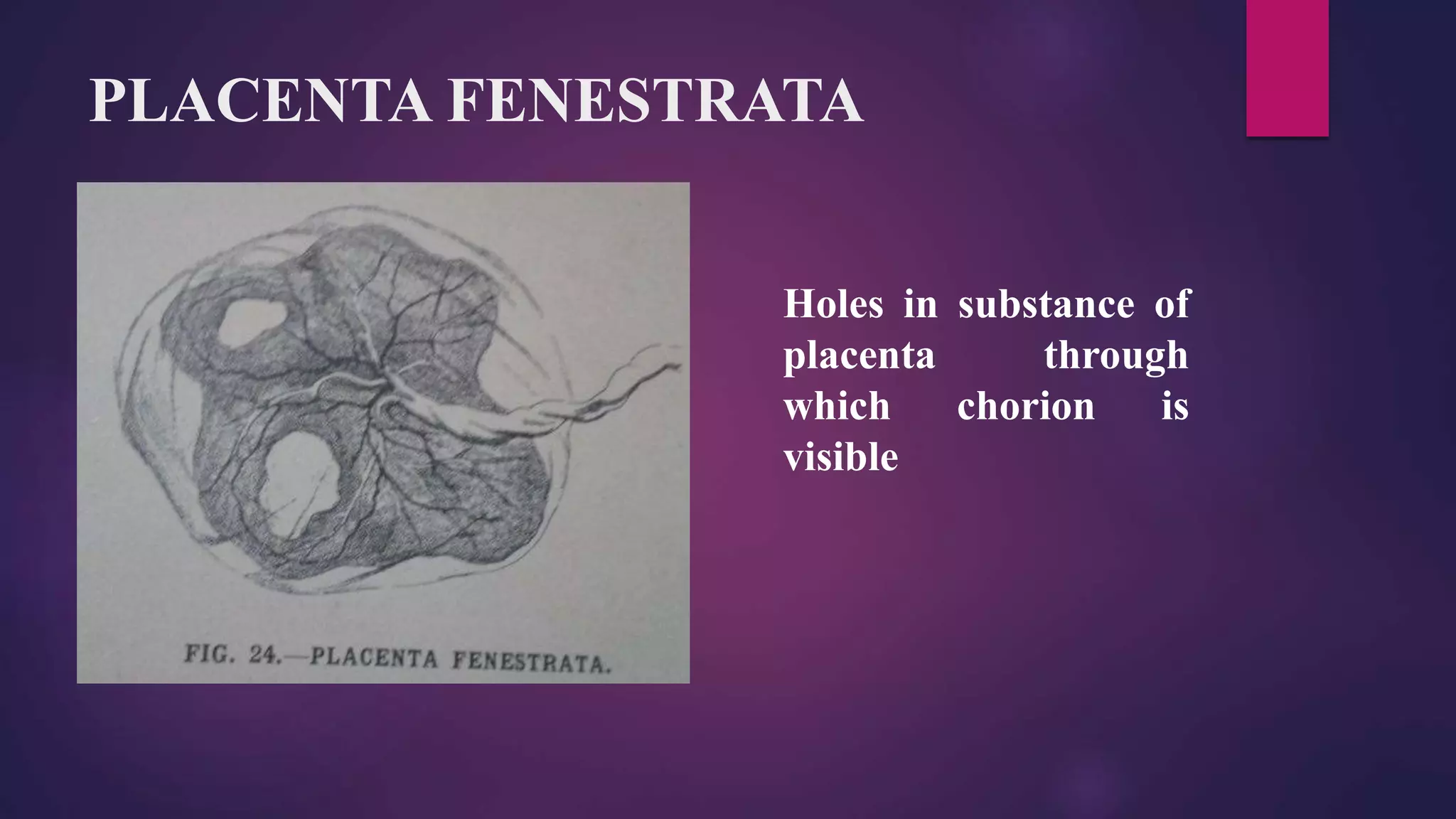
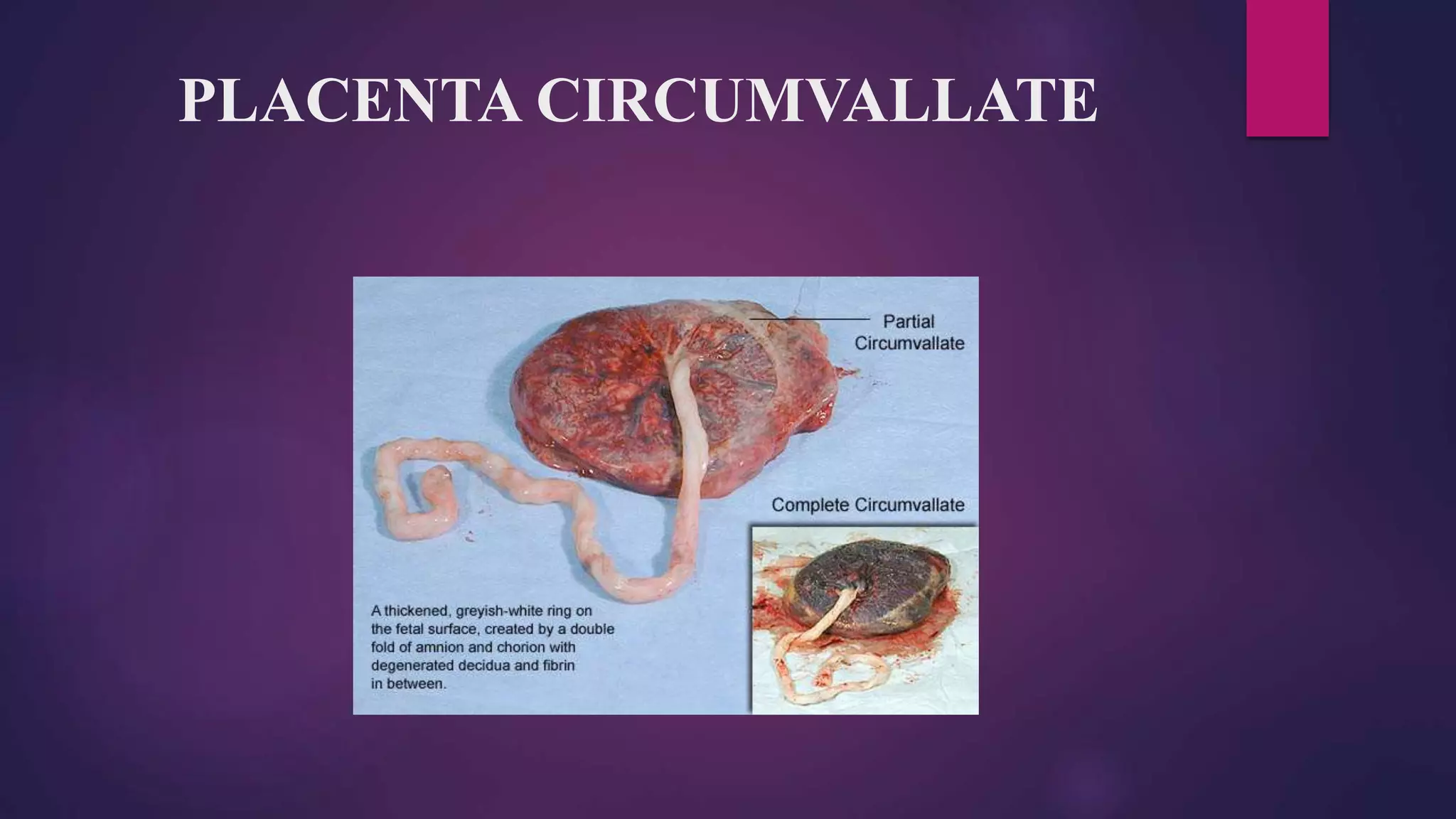
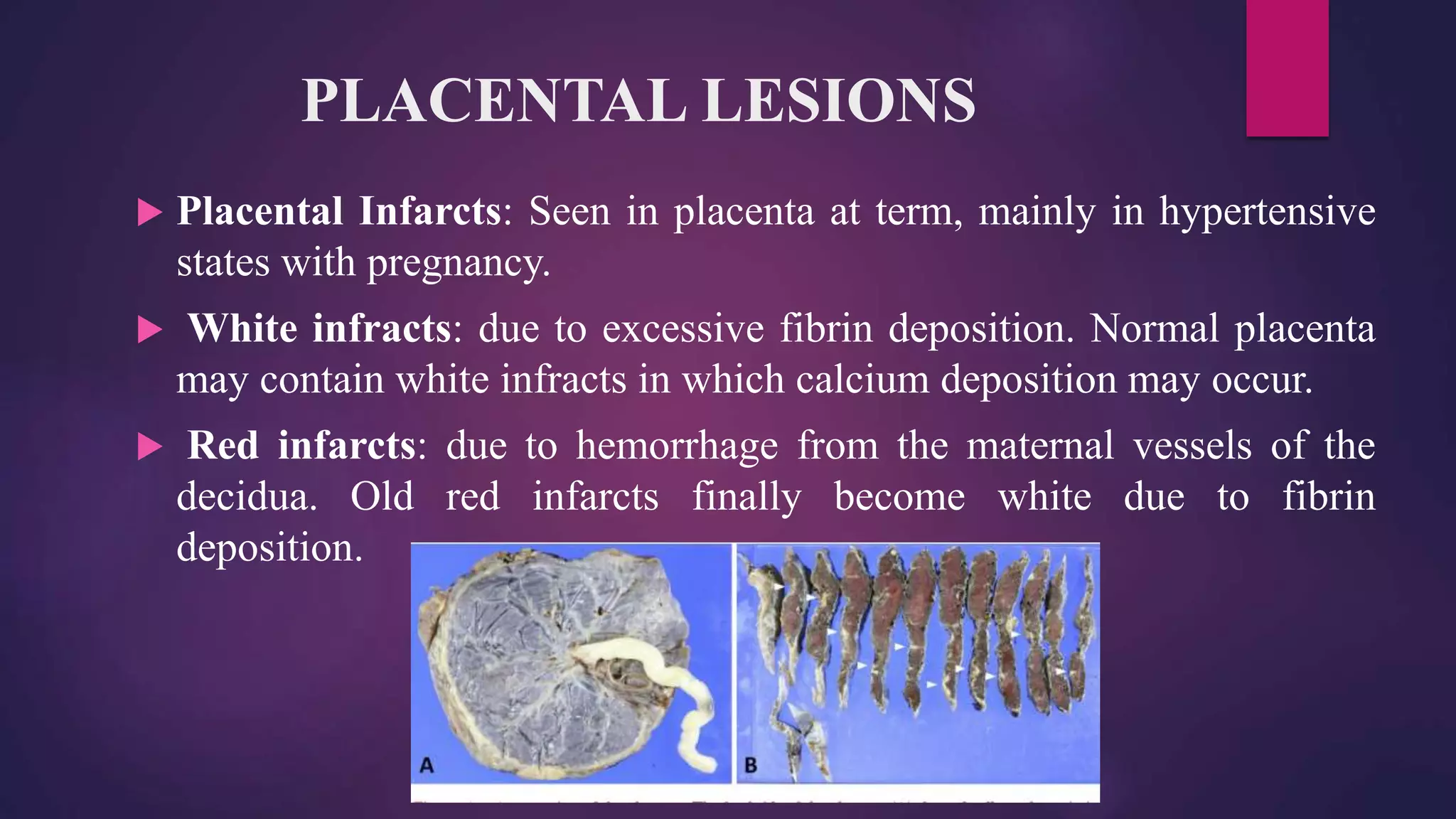
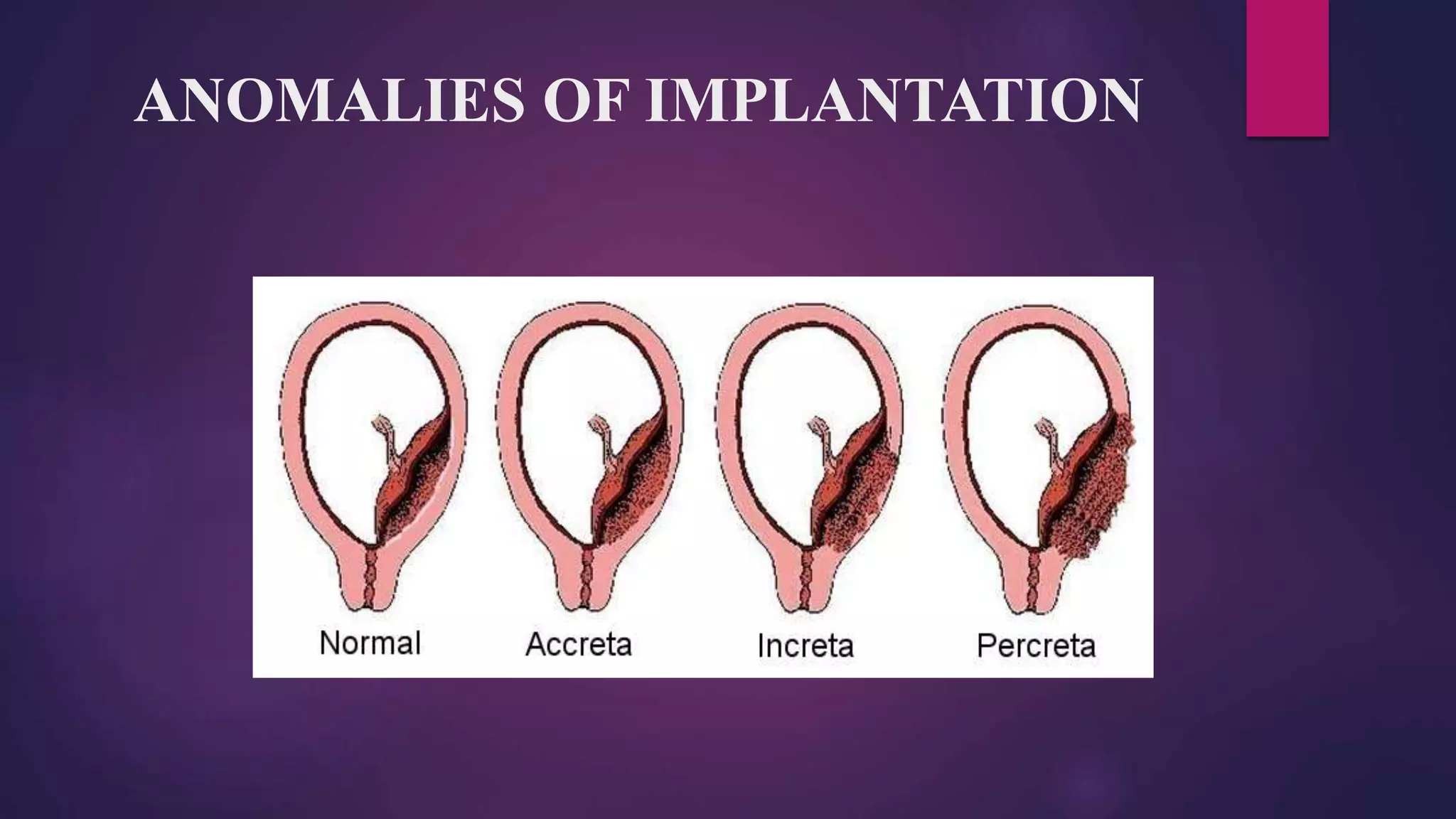
This document discusses placental and umbilical cord abnormalities. It begins by describing normal placental anatomy and development. It then covers various types of placental anomalies including abnormalities of form, position, relationships to cord/membranes, and diseases. Umbilical cord abnormalities such as short/long length, knots, torsion, and single umbilical artery are also reviewed. In summary, the document provides an overview of common placental and umbilical cord abnormalities for Mrs. Savita presented by Nikita Sharma.