This document discusses earthquakes, including their definition, causes, effects, and precautions. Some key points:
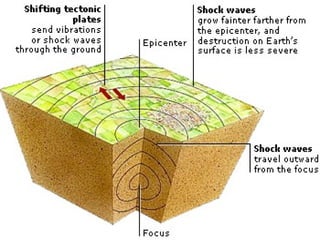
- An earthquake is caused by vibrations beneath the earth's surface due to shifting tectonic plates or other disturbances. They can be measured using seismographs.
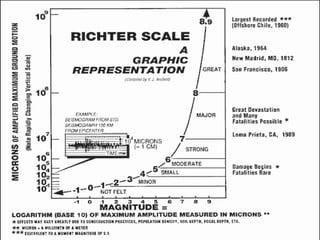
- The Richter scale measures an earthquake's magnitude - larger quakes over 8.0 occur about once per year globally.
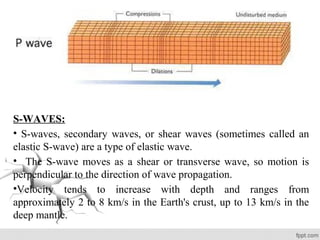
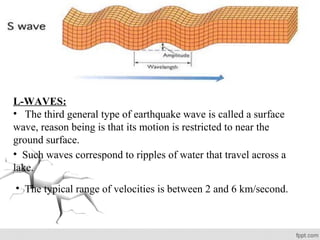
- Earthquakes generate seismic waves that travel through the earth, including P-waves, S-waves, and L-waves.
- Major effects of earthquakes include damage to buildings and infrastructure, tsunamis, landslides, and cracks in the ground.
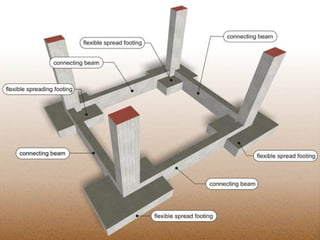
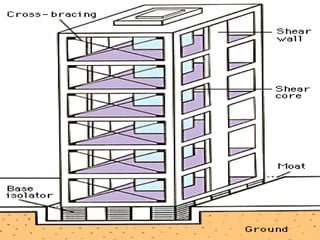
- Precautions