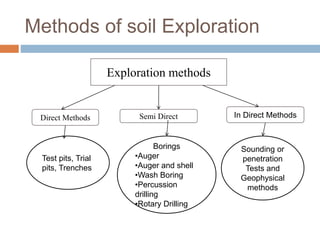
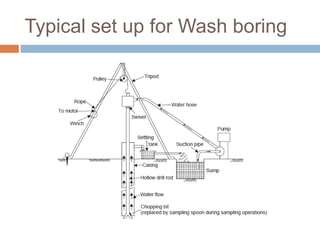
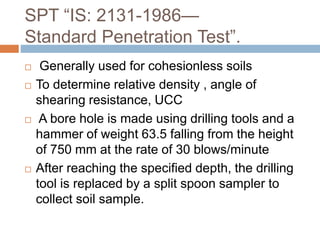
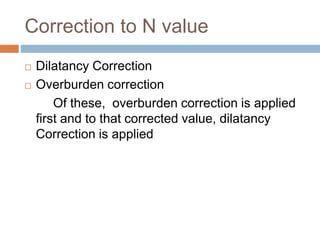
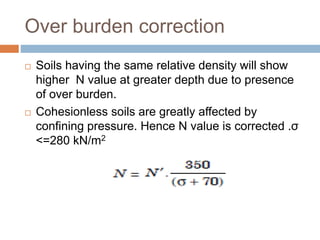
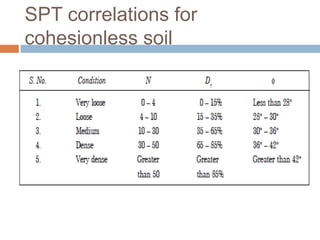
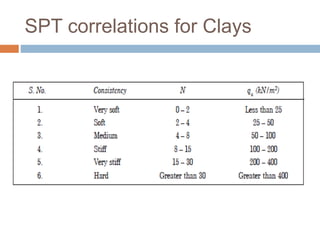
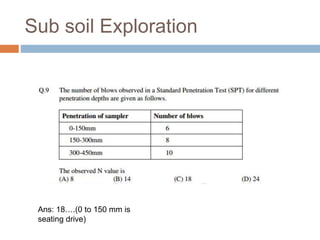
This document discusses subsoil exploration, which involves collecting soil data through field and laboratory investigations to assess soil properties at a site. The main objectives are to determine the nature, depth, thickness, and extent of soil strata, as well as groundwater depth and properties. Exploration methods include direct techniques like test pits and borings, and indirect techniques like sounding tests and geophysical methods. Standard penetration tests are commonly used to determine properties of cohesionless soils by counting blows required to penetrate the soil. Corrections are applied to penetration values to account for overburden pressure and sample dilatancy.