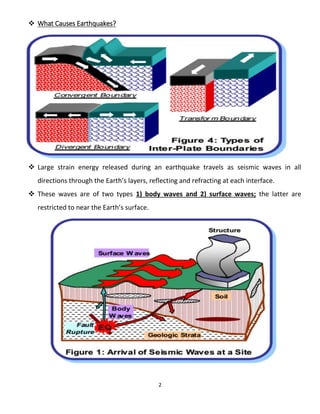
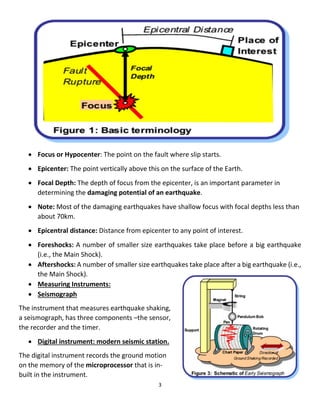
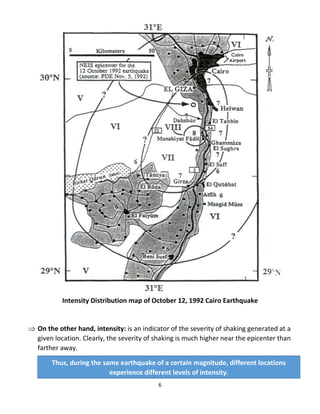
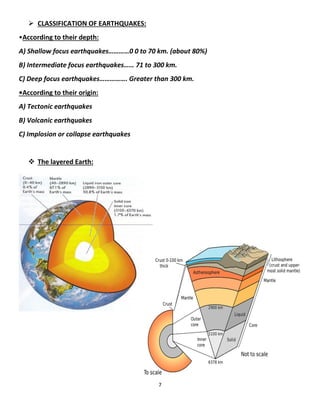
Earthquake seismology uses seismic waves generated by earthquakes to study the interior of the Earth. Seismic waves are detected by seismographs and include P-waves, S-waves, and surface waves. The location and depth of the initial rupture point within the Earth is known as the hypocenter and epicenter, respectively. Larger earthquakes with shallower depths typically cause more damage. Earthquake magnitude represents the energy released while intensity refers to the strength of shaking experienced at a particular location.