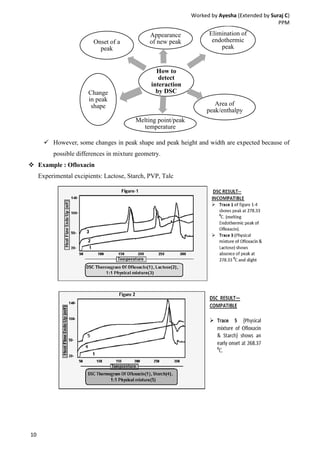
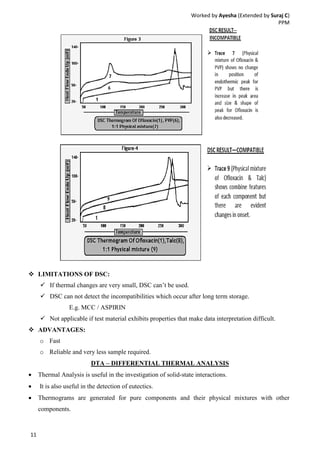
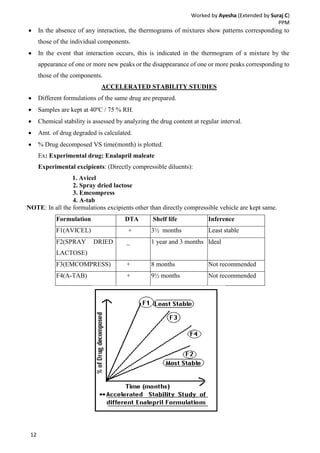
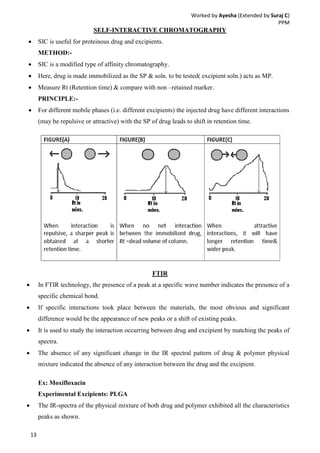
Drug-excipient compatibility studies are important to identify compatible excipients for drug formulations. Compatibility can be tested using various analytical techniques including thermal methods like DSC and DTA, accelerated stability studies, spectroscopy like FTIR, and chromatography like TLC. Incompatibilities are identified by changes in thermal behavior, degradation of the drug, or appearance of new peaks in analytical tests. Common techniques involve storing drug-excipient mixtures under accelerated conditions and monitoring the samples for physical or chemical changes over time. The results of compatibility studies provide critical information for formulation development and regulatory filings.