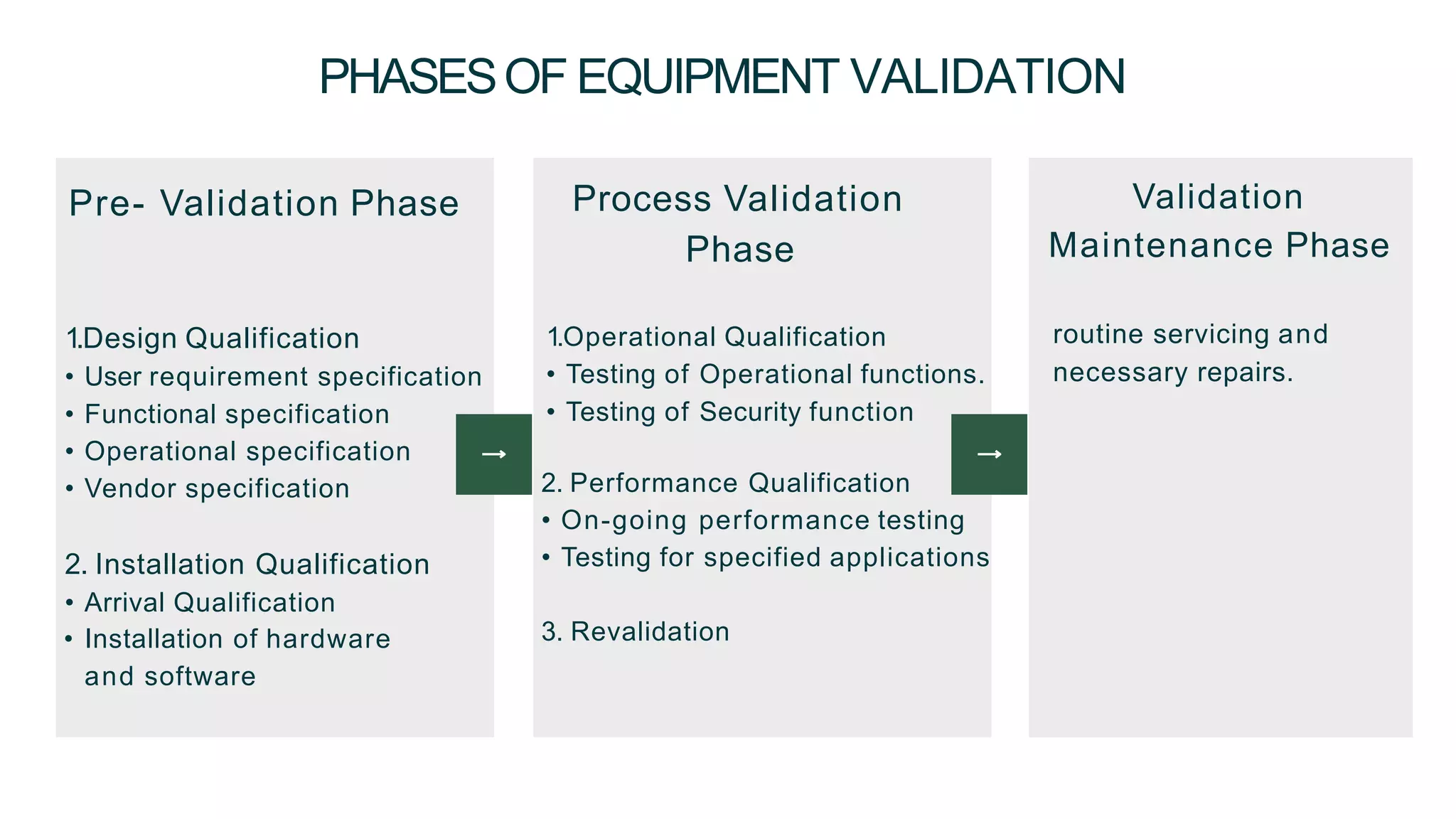
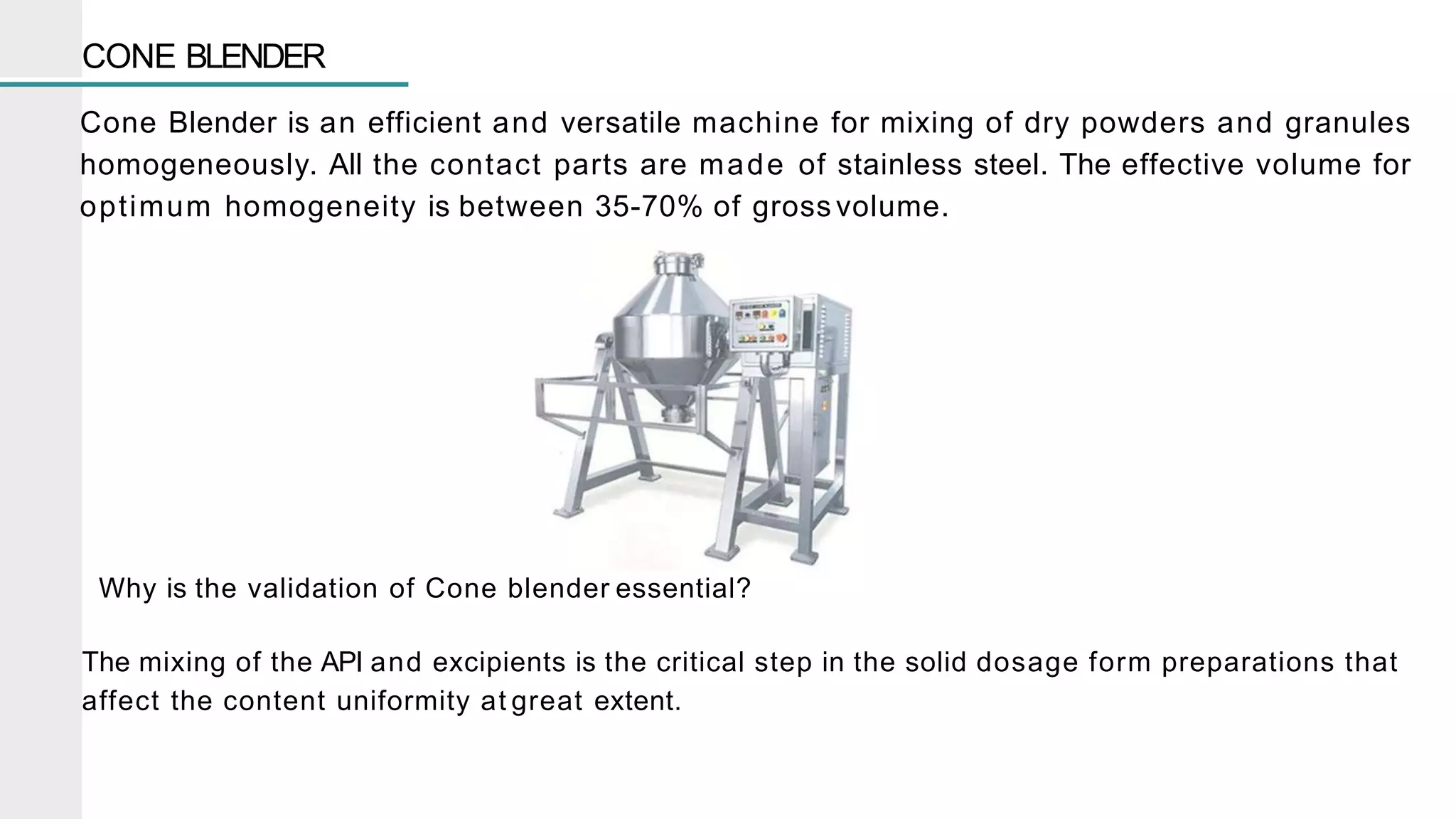
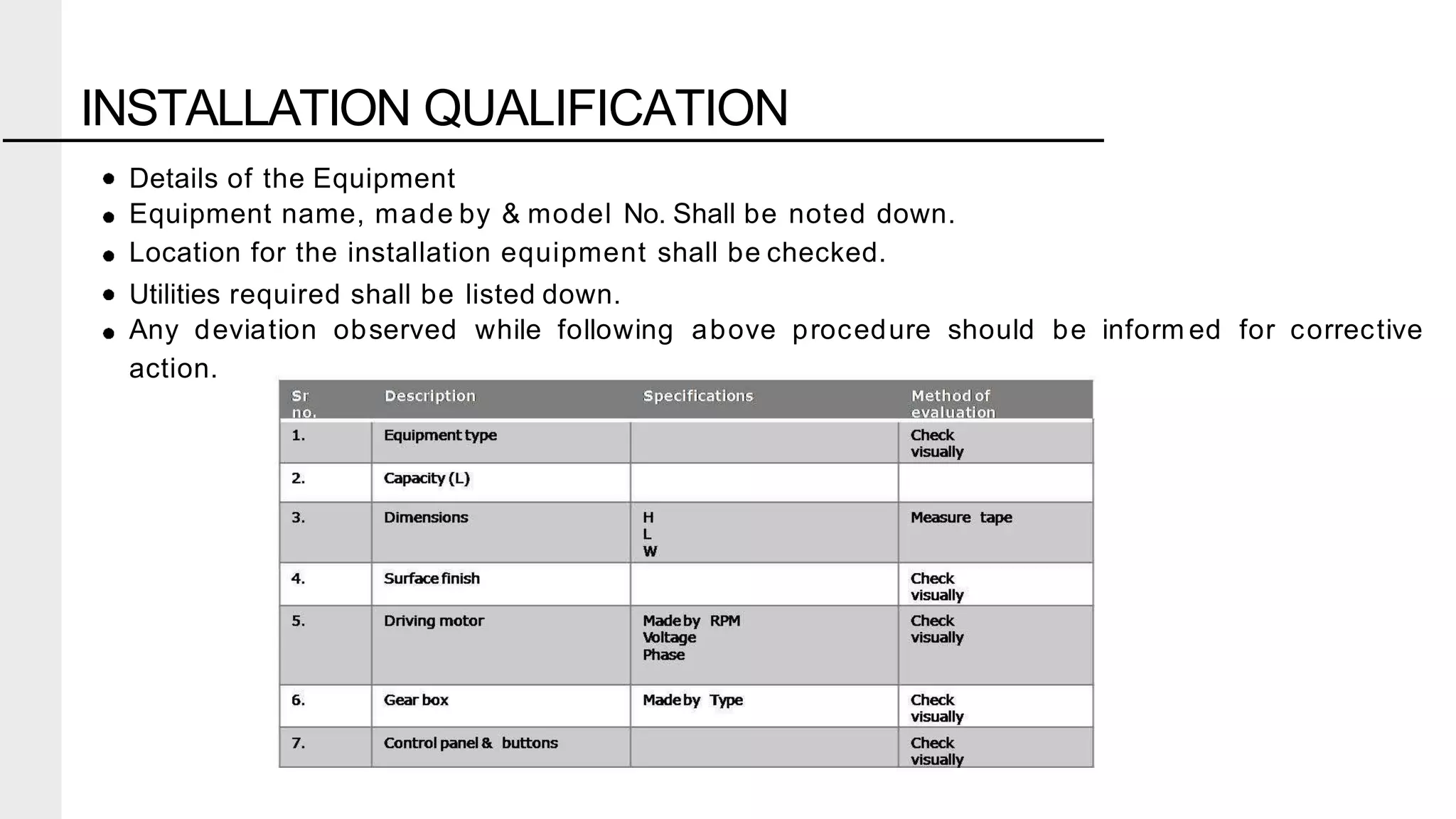
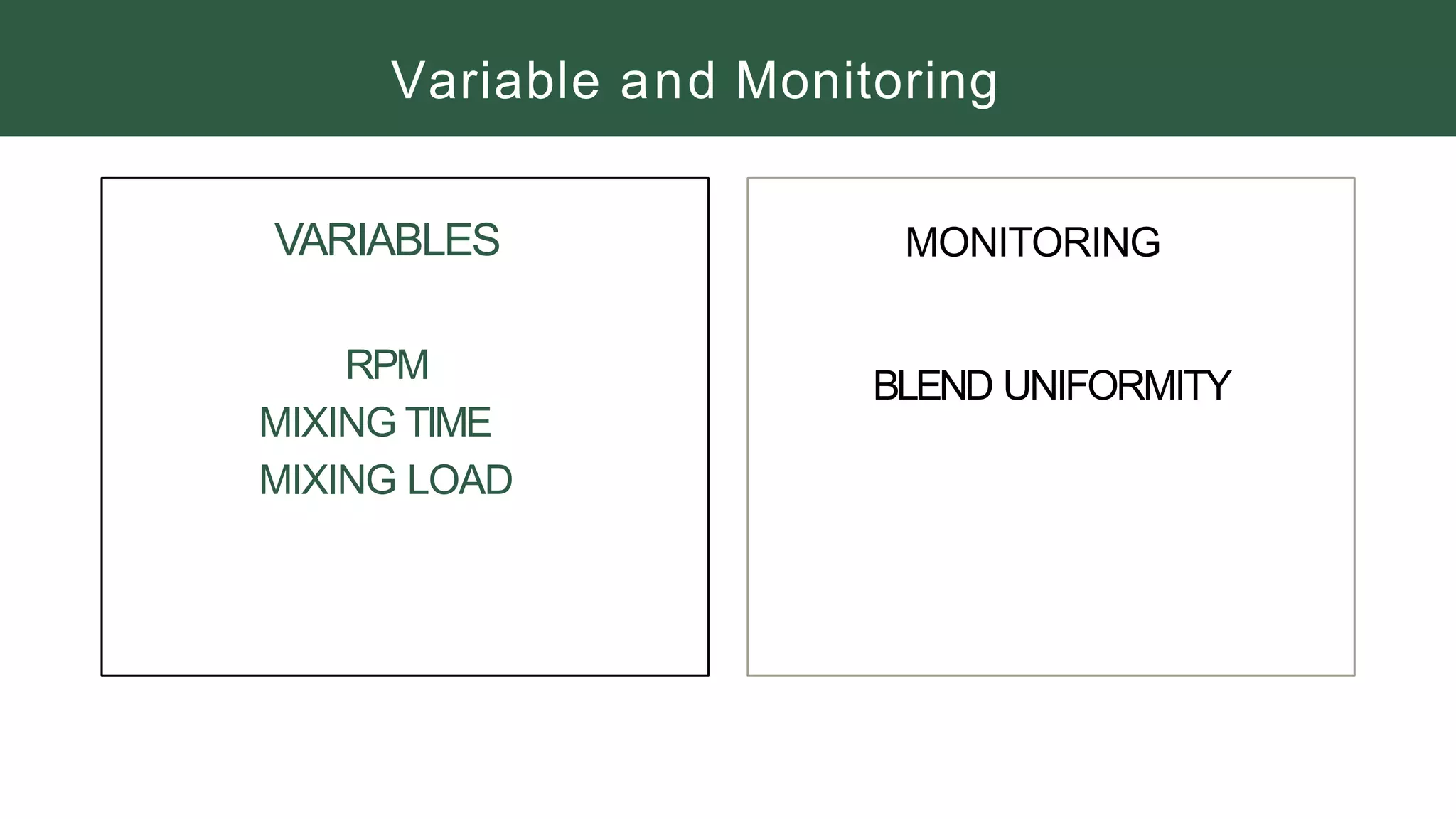
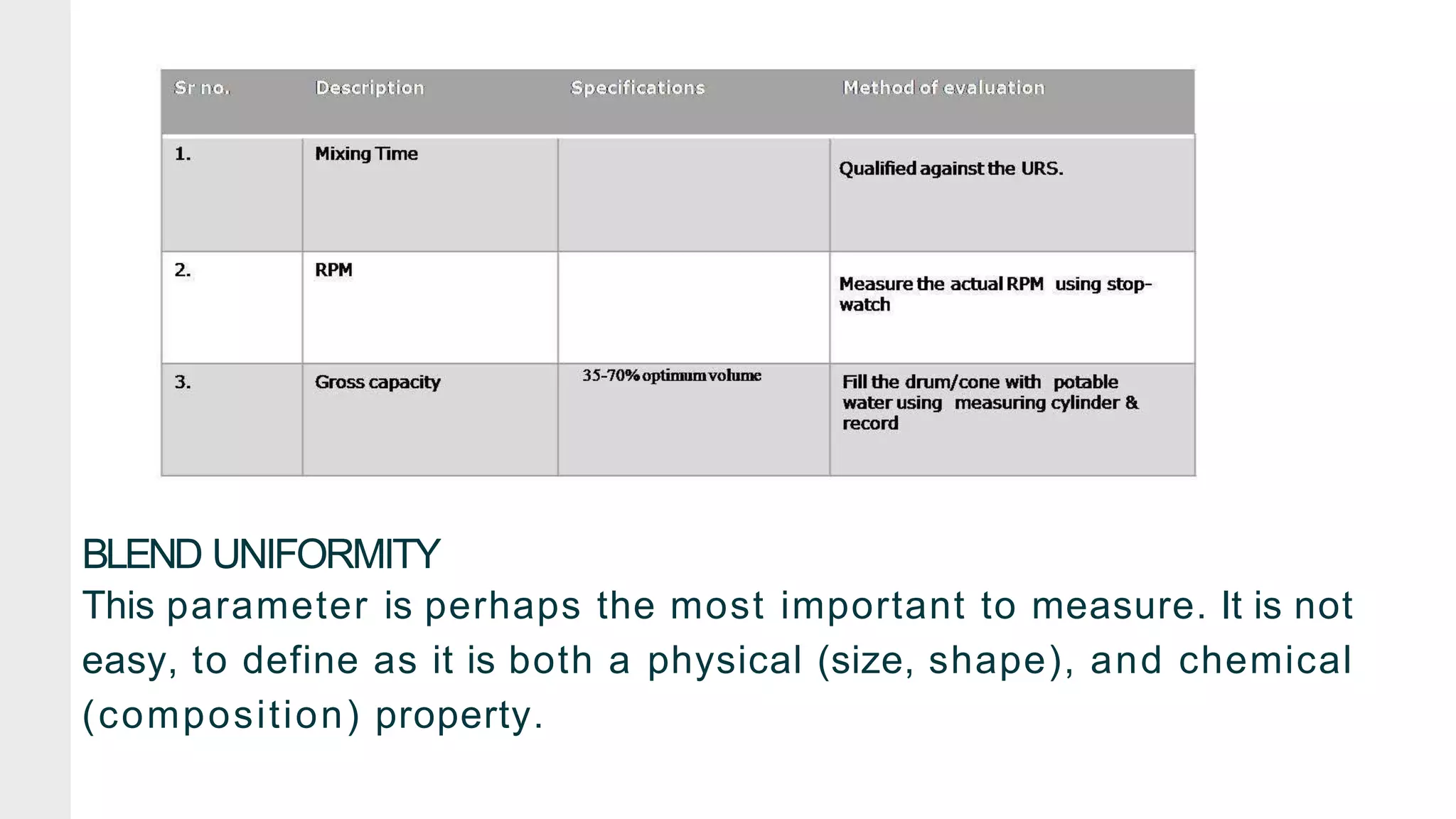
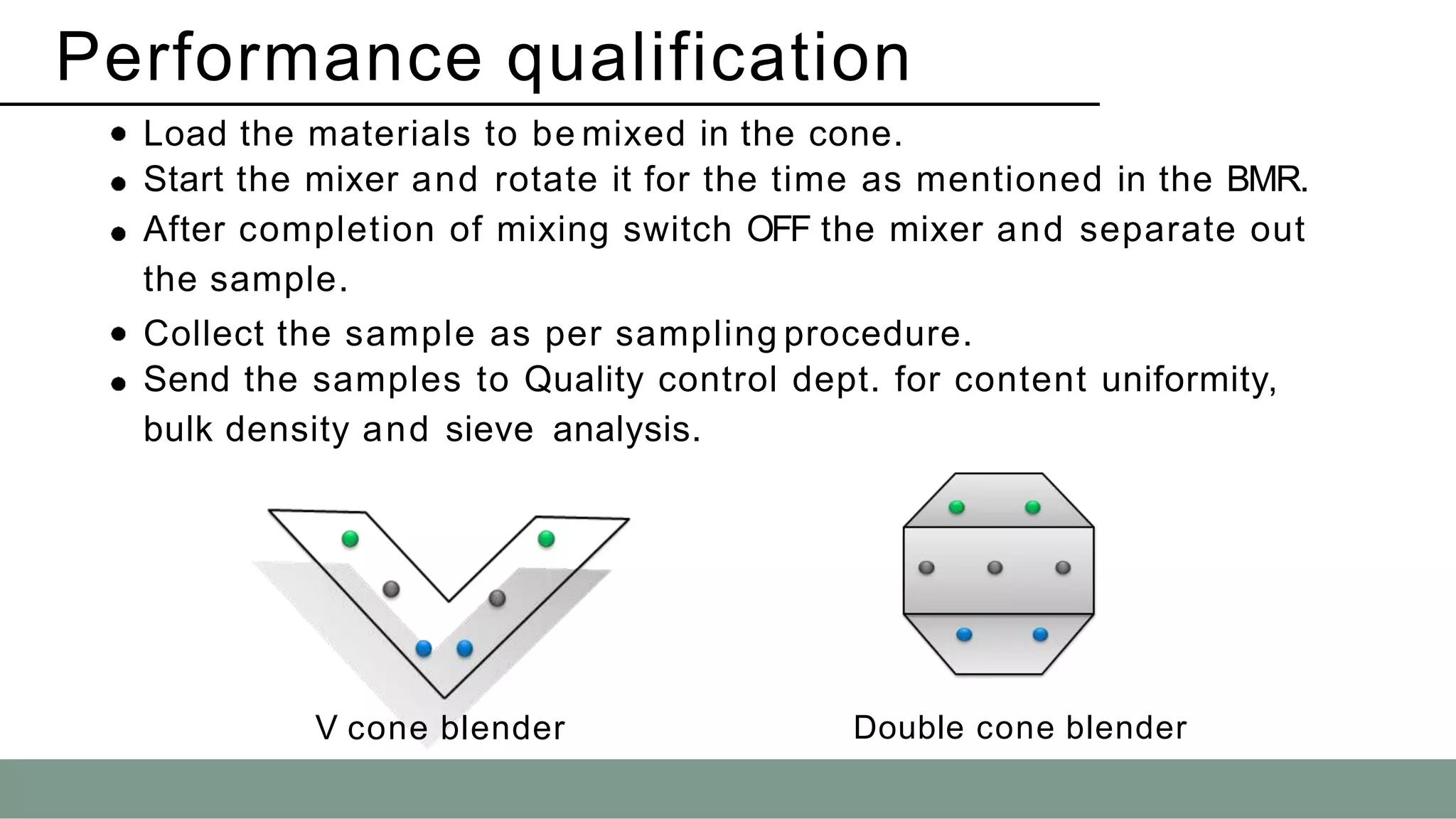
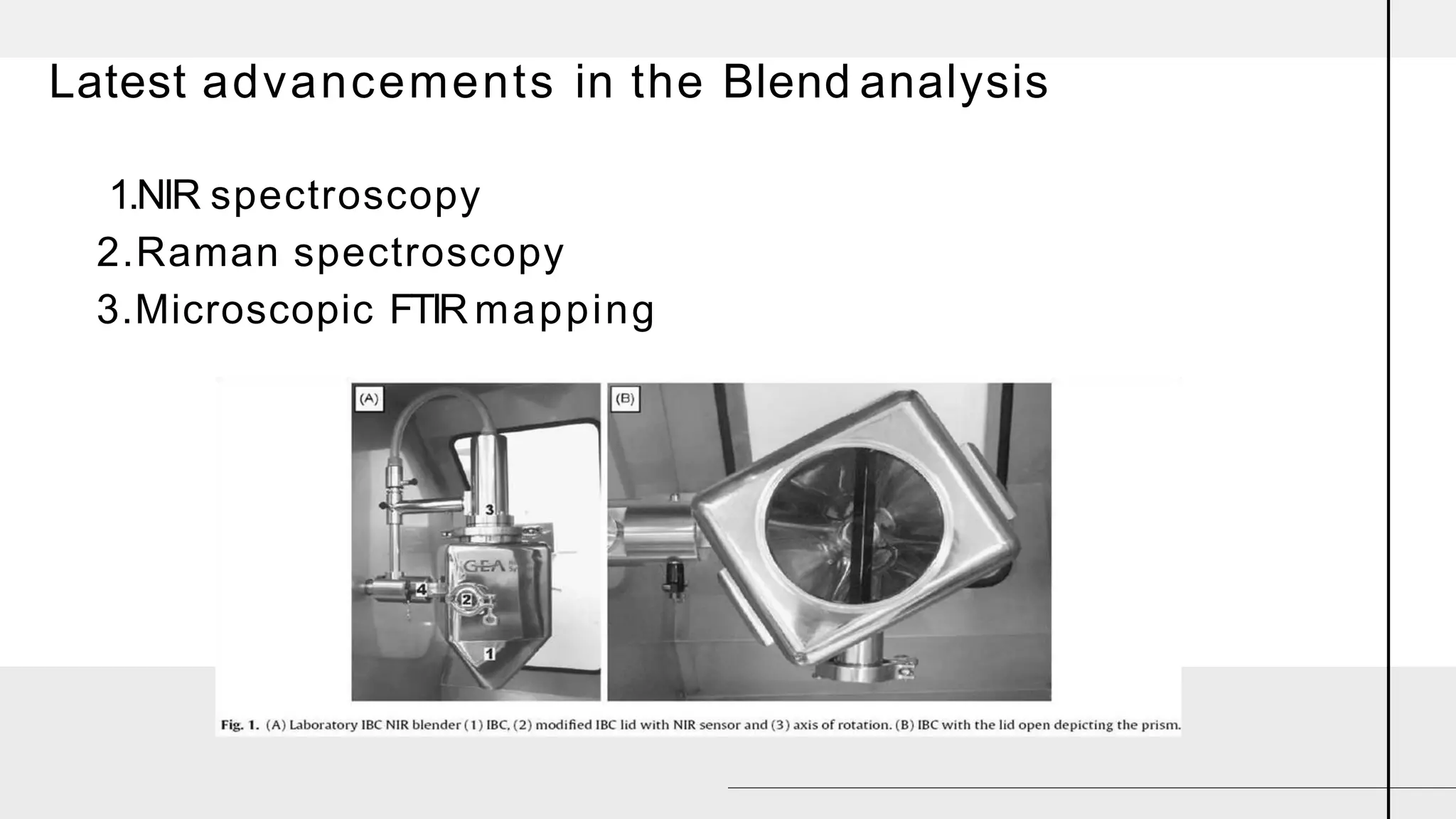
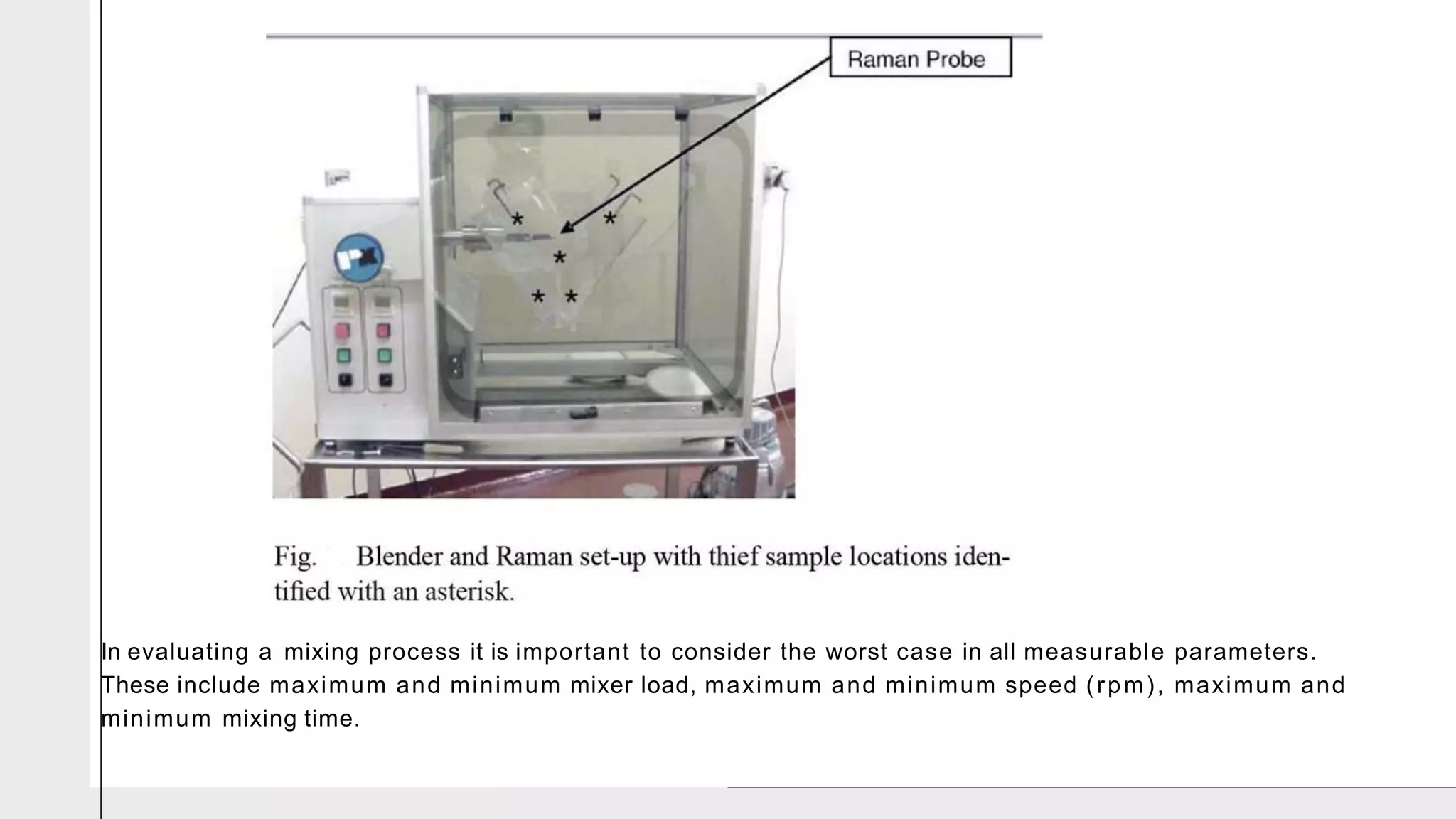
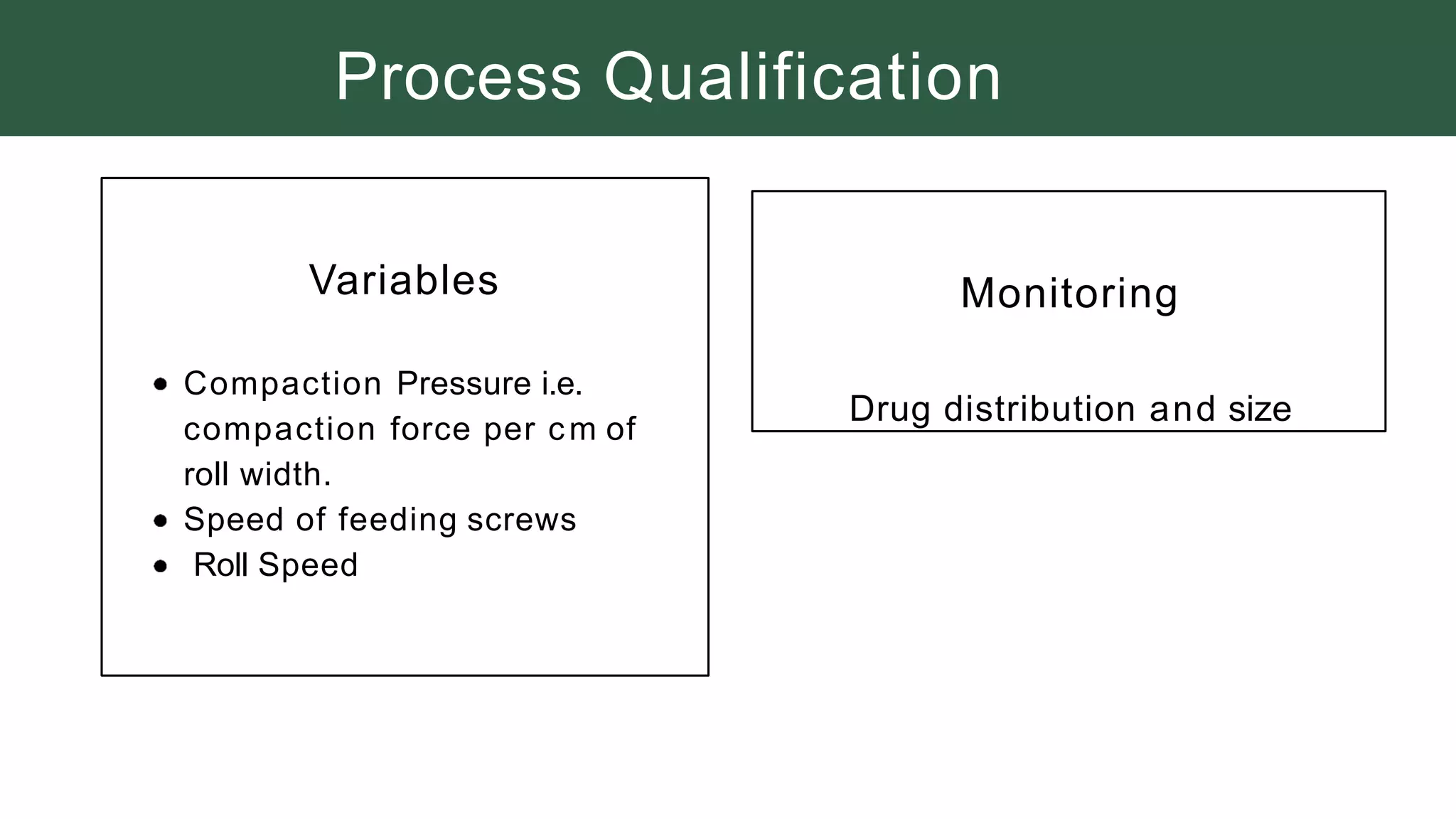
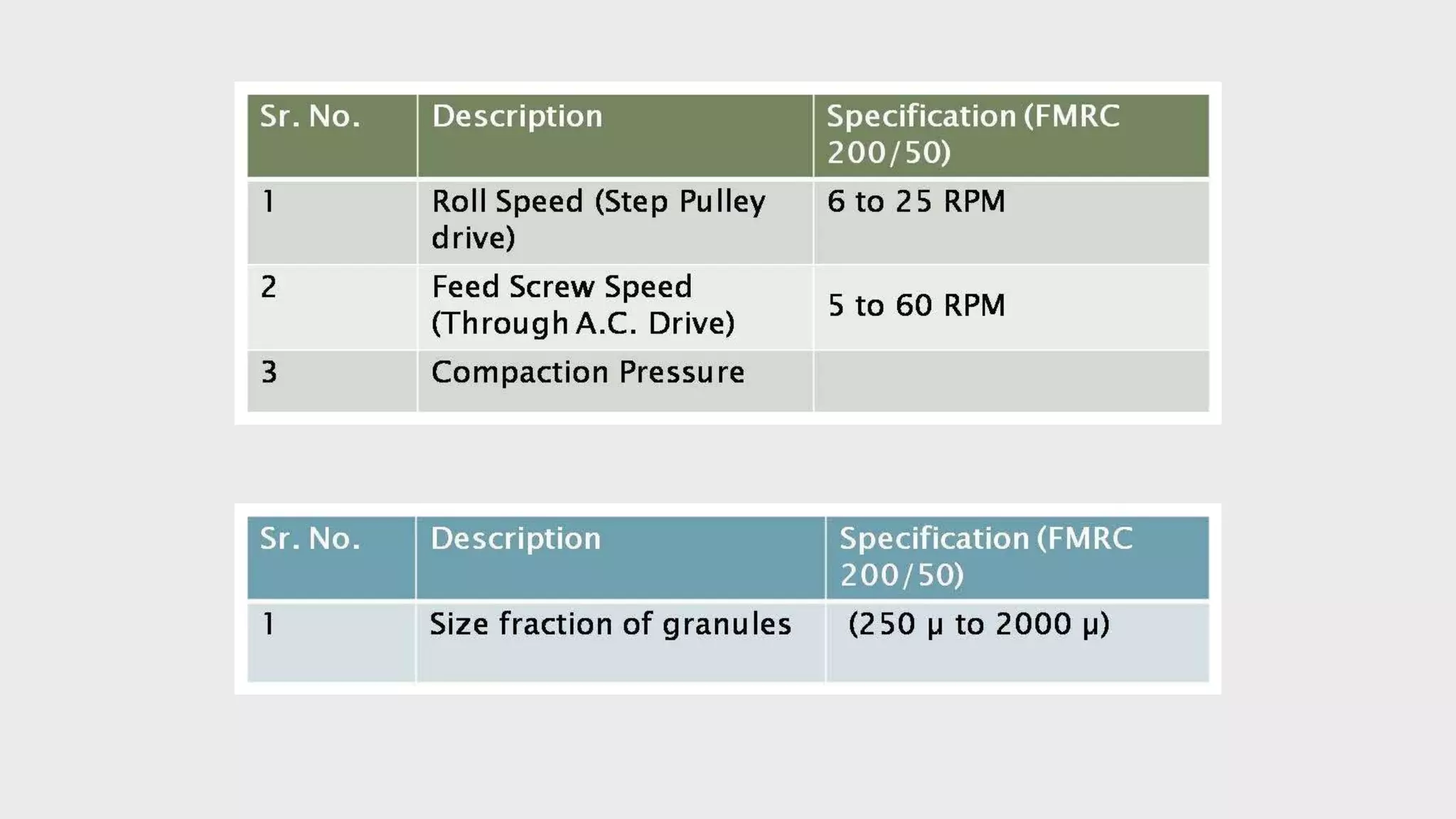
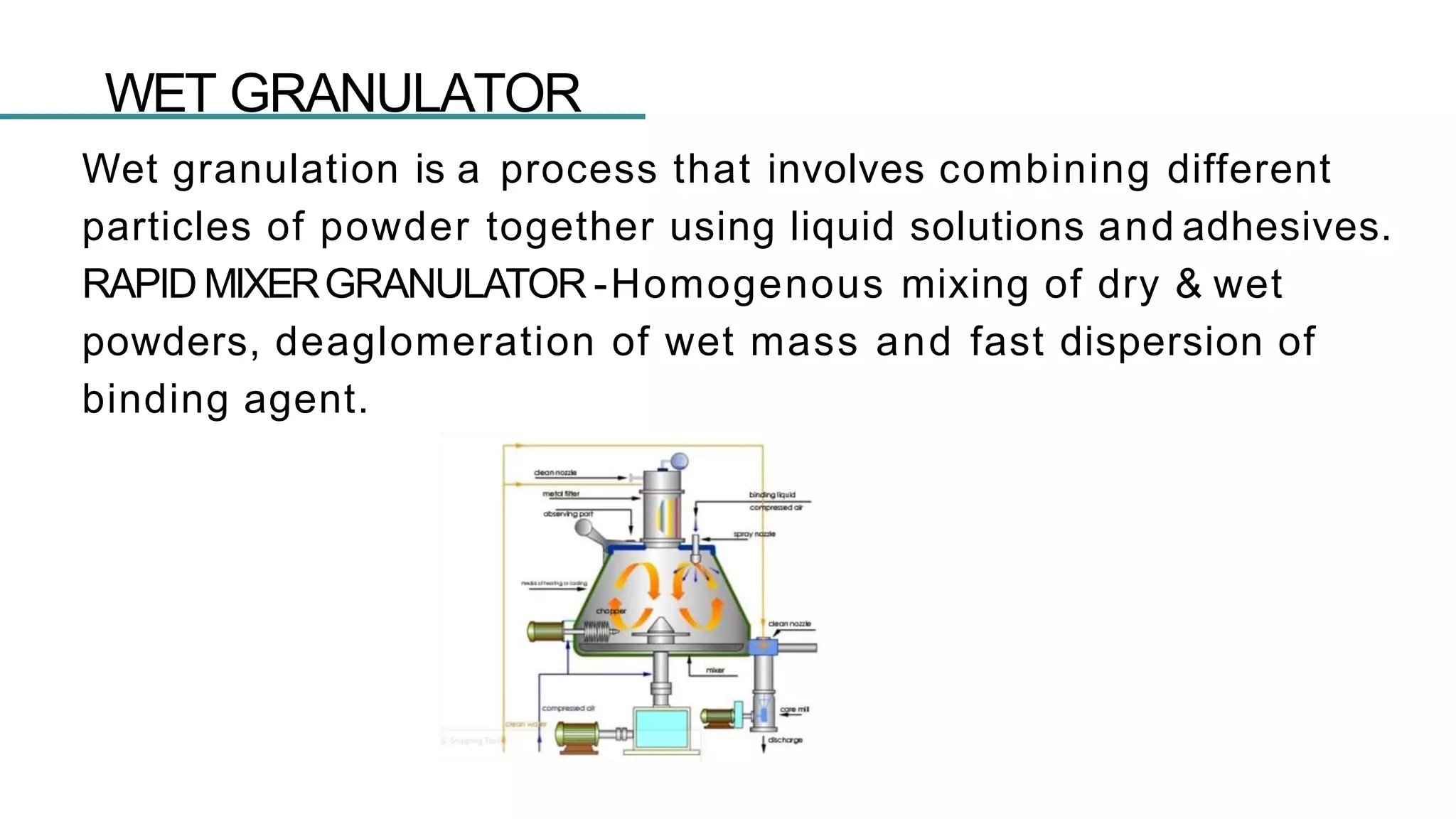
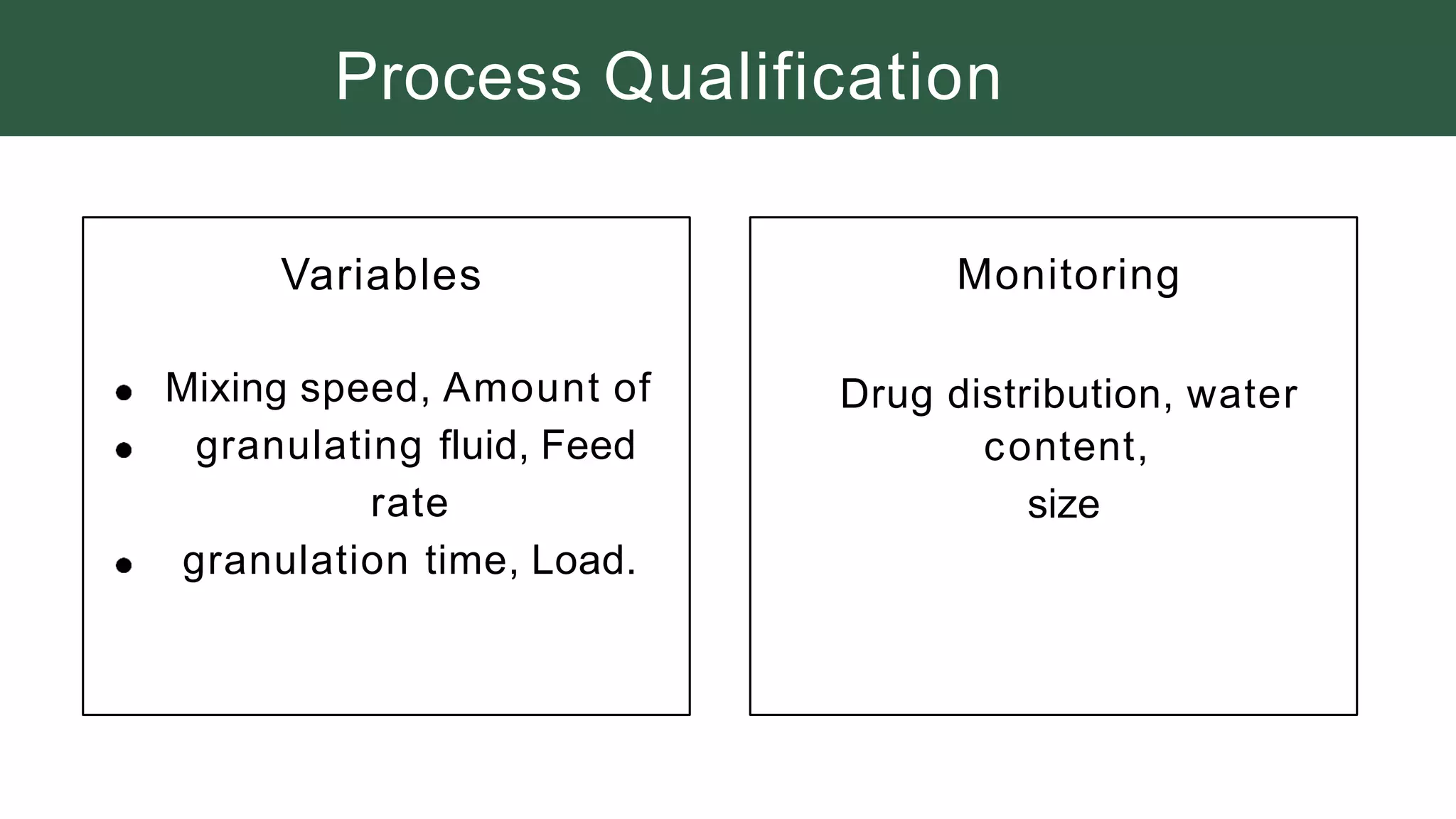
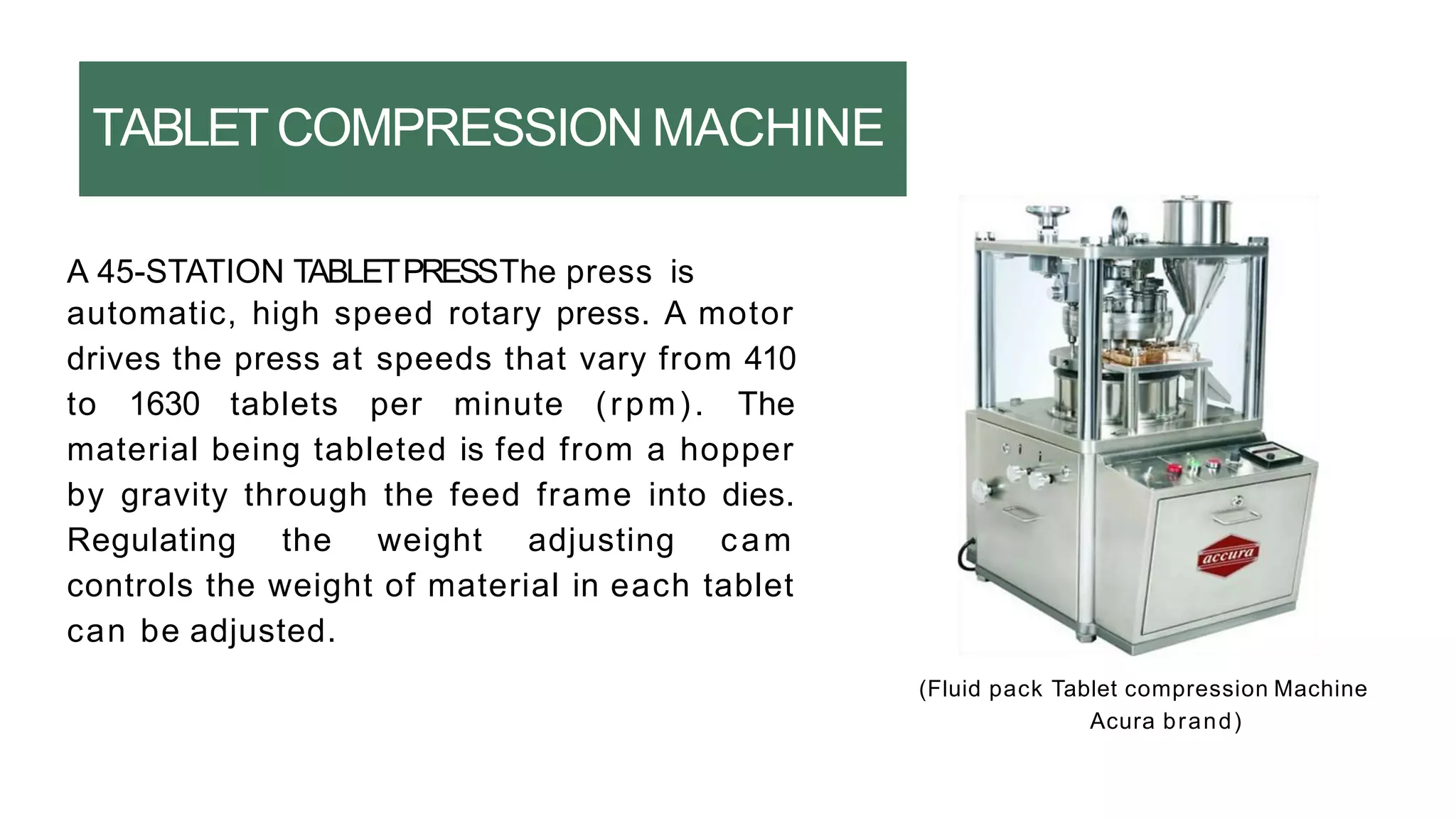
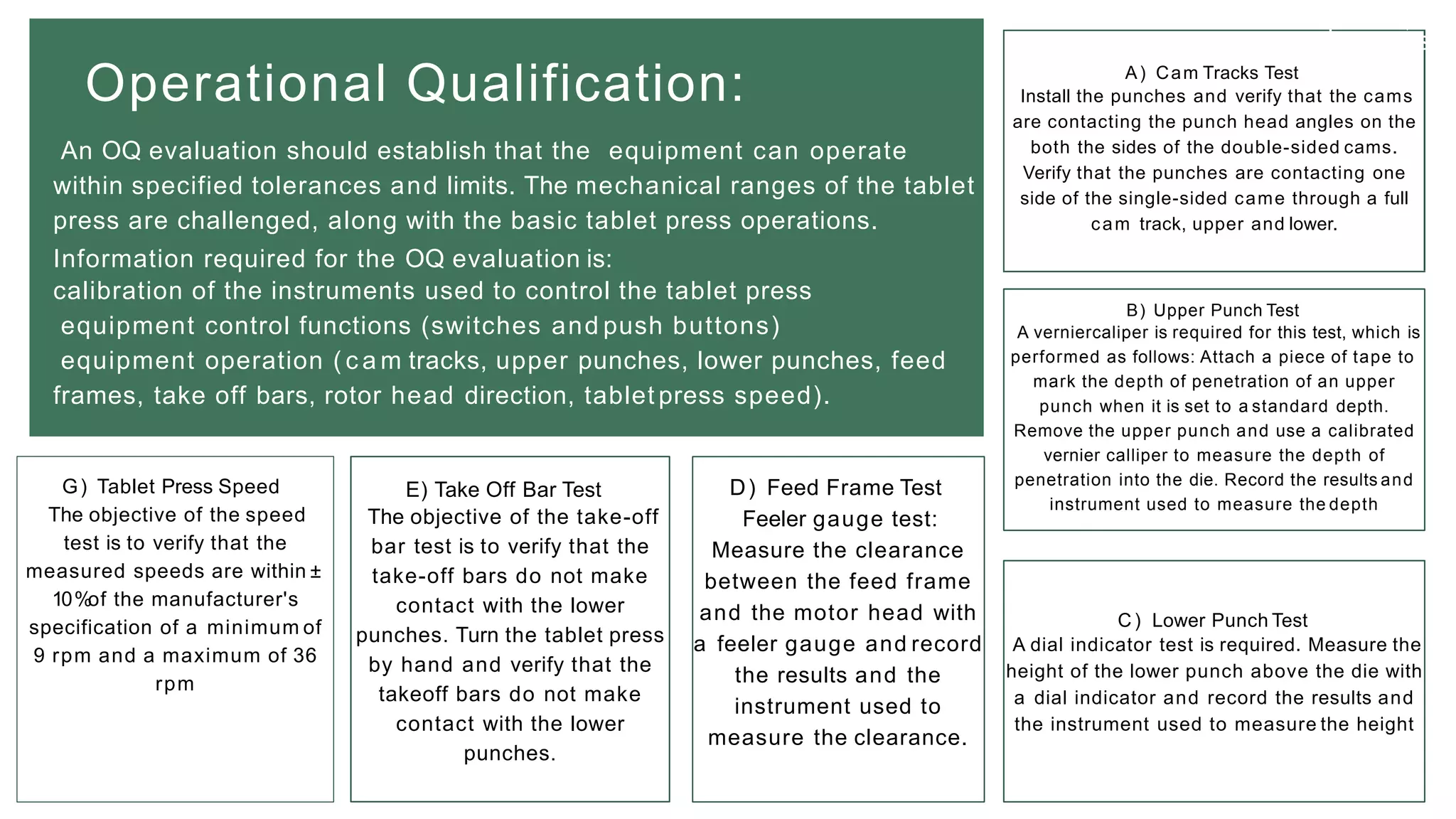
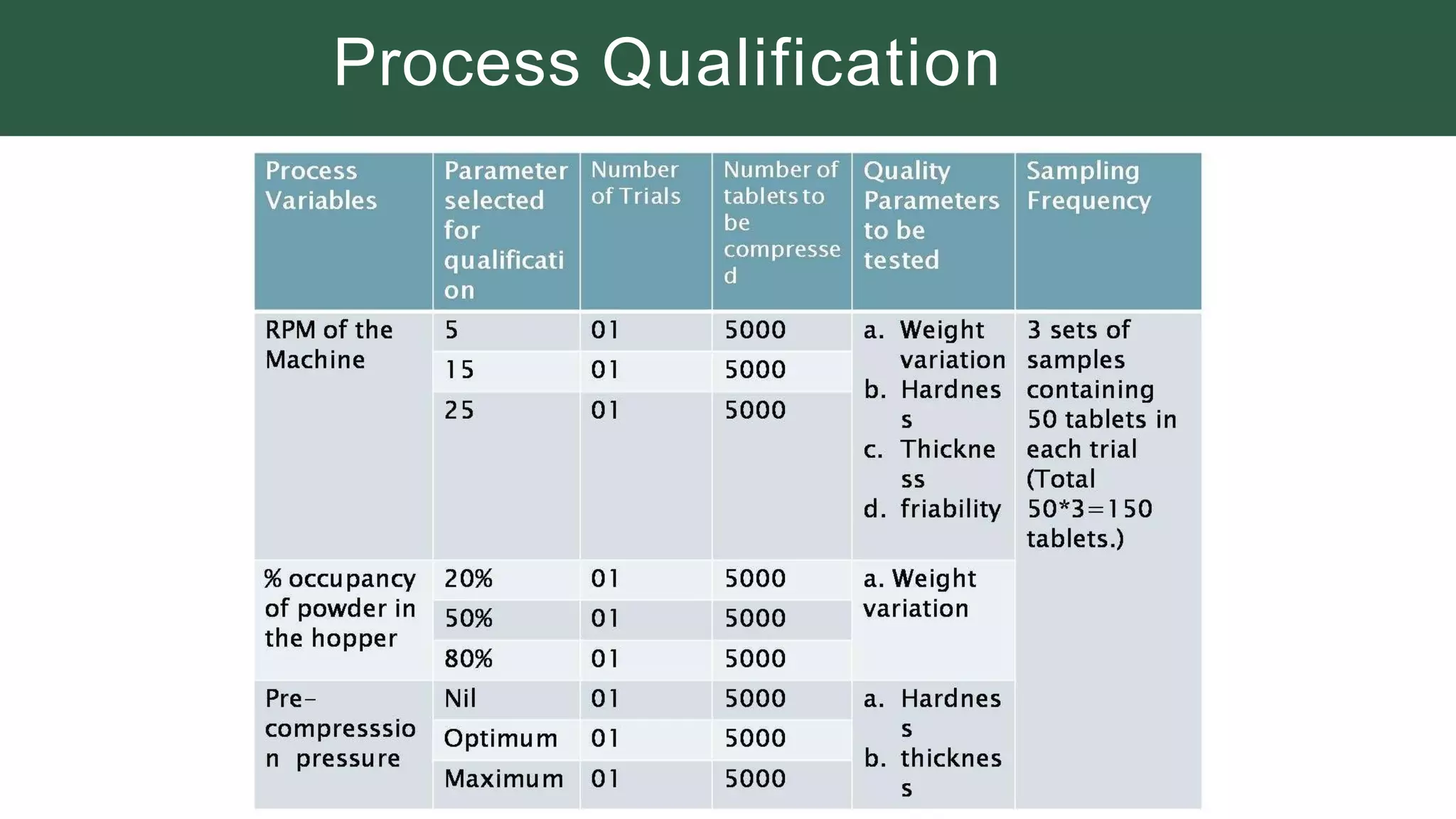
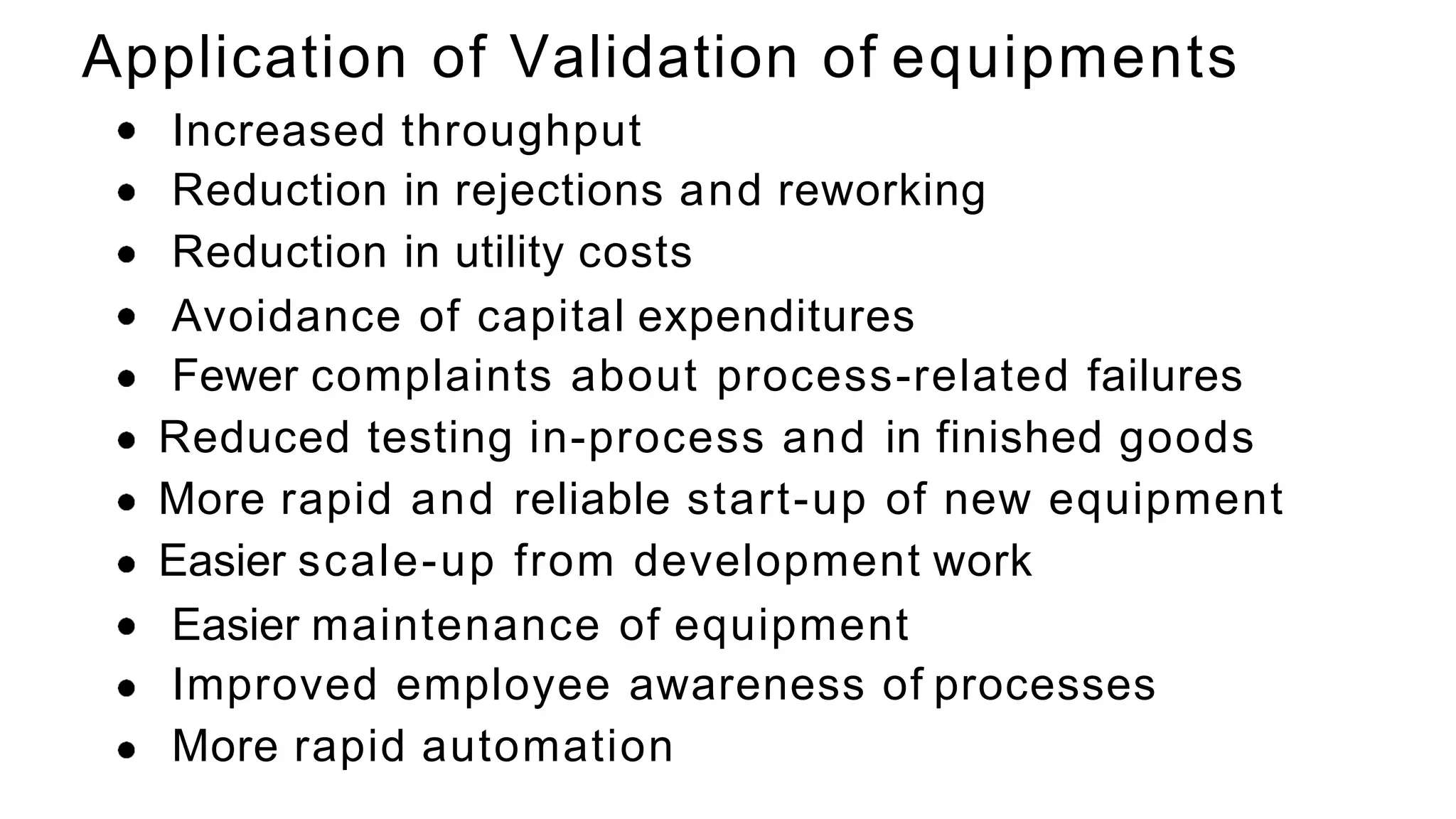
The document summarizes the validation process for common pharmaceutical equipment used in powder blending, granulation, and tablet compression. It discusses the validation of cone blenders, mixers, granulators, and tablet compression machines. The validation process involves design qualification, installation qualification, operational qualification, and performance qualification to ensure equipment is properly designed, installed, operated, and performs as intended. Key aspects that are validated include design criteria, utilities, cleaning procedures, operating parameters, and finished product quality attributes. Validation helps improve safety, reproducibility, and compliance for pharmaceutical manufacturing.