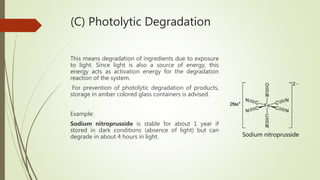
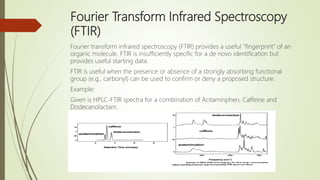
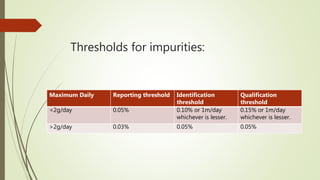
This document discusses degradation, degradants, and degradant characterization. It defines degradation as changes in a substance's properties due to environmental factors or formulation interactions. Degradants are products formed from degradation that can reduce potency or induce toxicity. Degradant characterization involves profiling degradants using analytical techniques like LC-MS, GC-MS, and LC-NMR to separate and identify degradants. Factors like temperature, moisture, light exposure, pH changes, and microbes can induce degradation.