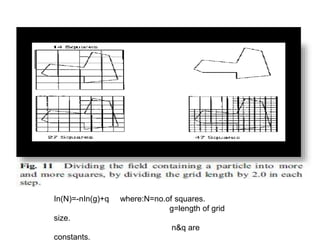
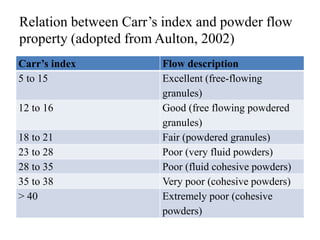
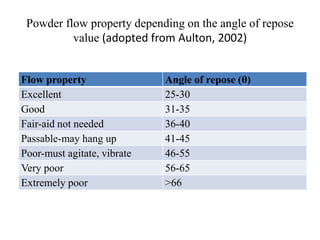
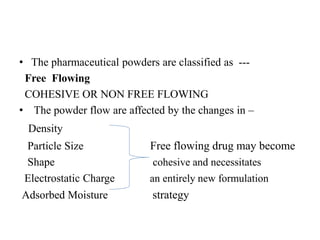
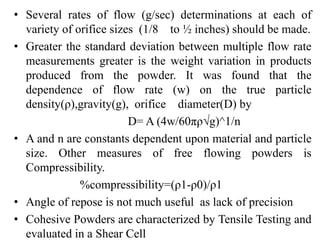
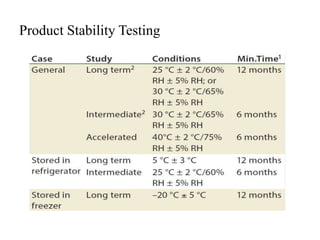
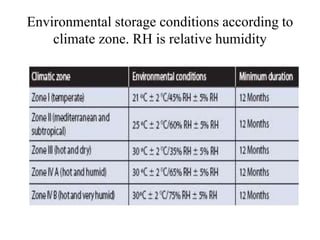
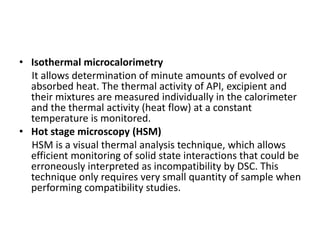
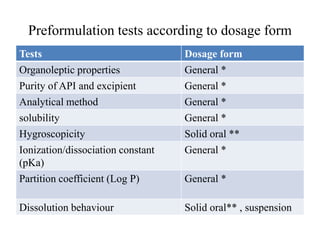
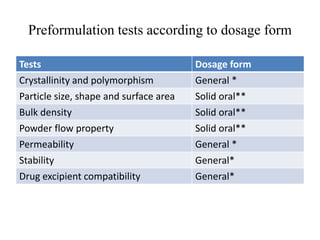
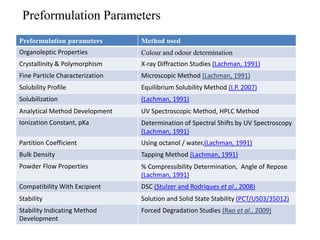
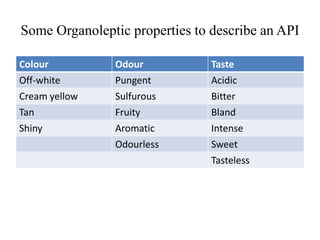
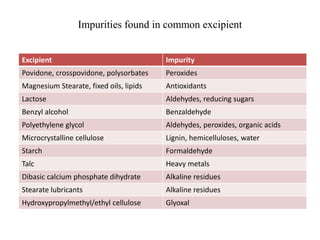
1. Preformulation testing involves characterizing key properties of drugs and excipients to develop safe, effective, and stable dosage forms. Tests include analyzing organoleptic properties, purity, solubility, hygroscopicity, and compatibility.
2. Analytical methods are important to quantify drugs during product development and stability testing. UV and HPLC methods are often used depending on the drug's chromophores.
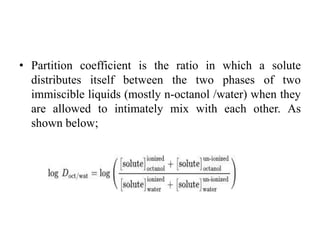
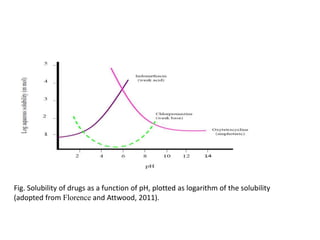
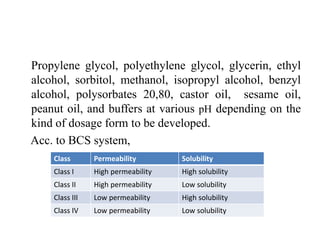
3. Solubility studies over the pH range of 1-8 are crucial because permeability and absorption depend on a drug's ionization state and solubility in different regions of the gastrointestinal tract.














![• Factors affecting absorption:
- pH at the site of absorption
- Ionization constant
- Lipid solubility of unionized species
“pH-partition theory”
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
• For acids:
pH = pKa + log [ionized form]/[unionized form]
• For bases:
pH = pKa + log [unionized form]/[ionized form]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/preformulationandproductdevelopment-181228033229/85/Preformulation-and-product-development-22-320.jpg)