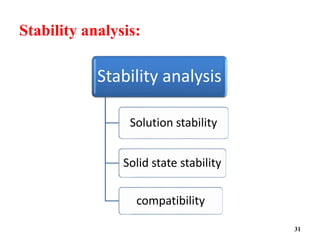
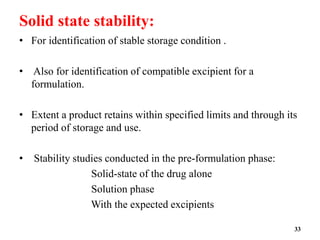
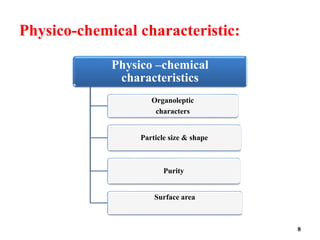
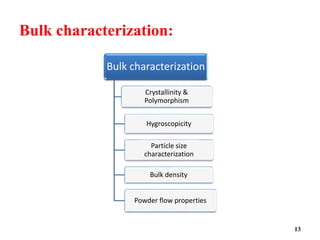
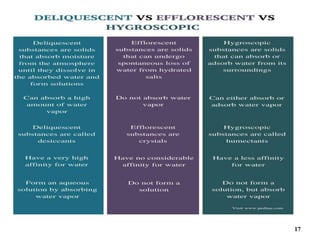
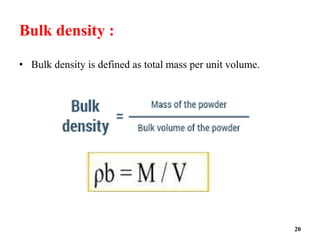
The document provides an overview of pre-formulation, which involves determining the physicochemical properties of a drug substance prior to developing a dosage form. It discusses the goals of pre-formulation to formulate an efficacious dosage form with good bioavailability. The protocol involves characterizing the physical, chemical, solubility, stability and compatibility properties of the drug. Key aspects covered include polymorphism, hygroscopicity, particle size, solubility, dissolution, stability in solution and solid state, and compatibility with excipients. The information guides subsequent formulation development.















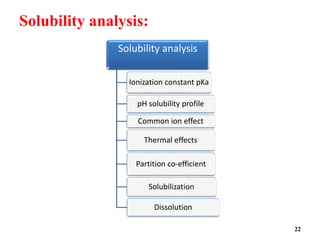


![pH solubility profile:
• The solubility of acidic or basic drug will show differences in
solubility with changes in pH.
• The solubility of an acidic or basic drug depends on the pKa of the
ionizing functional group and the intrinsic solubilities for both the
ionized and unionized forms.
• The relationship between solubility of the acidic drug and pH is
given by the equation
pH= pKa +log [Cs]/[Ca]
Where pKa =negative logarithm of the ionization constant of the acid .
[Cs]= molar concentration of the salt form in water
[Ca ] = molar concentration of free acid in water
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pre-formulationprotocol-190602082512/85/Pre-formulation-protocol-25-320.jpg)