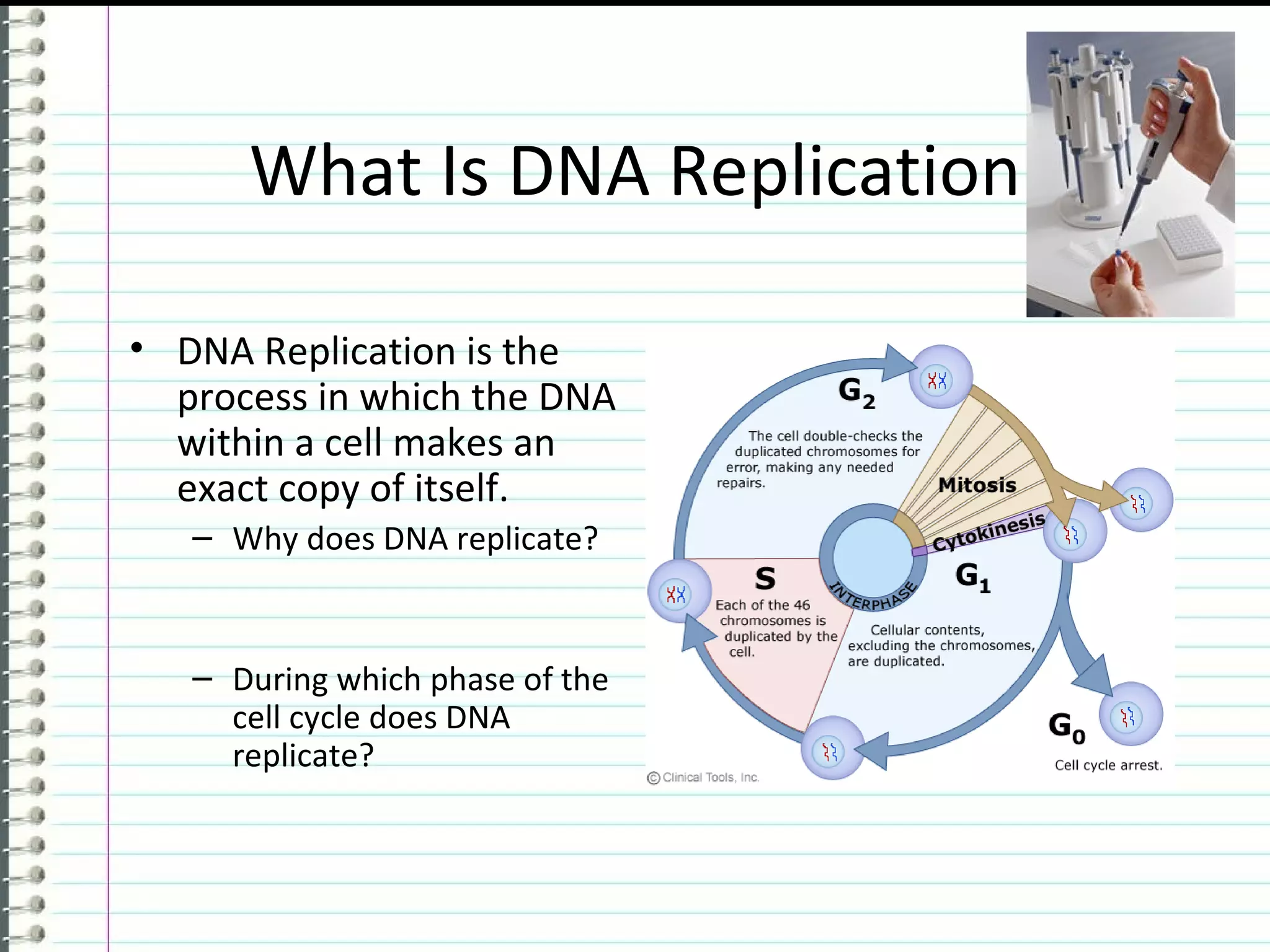
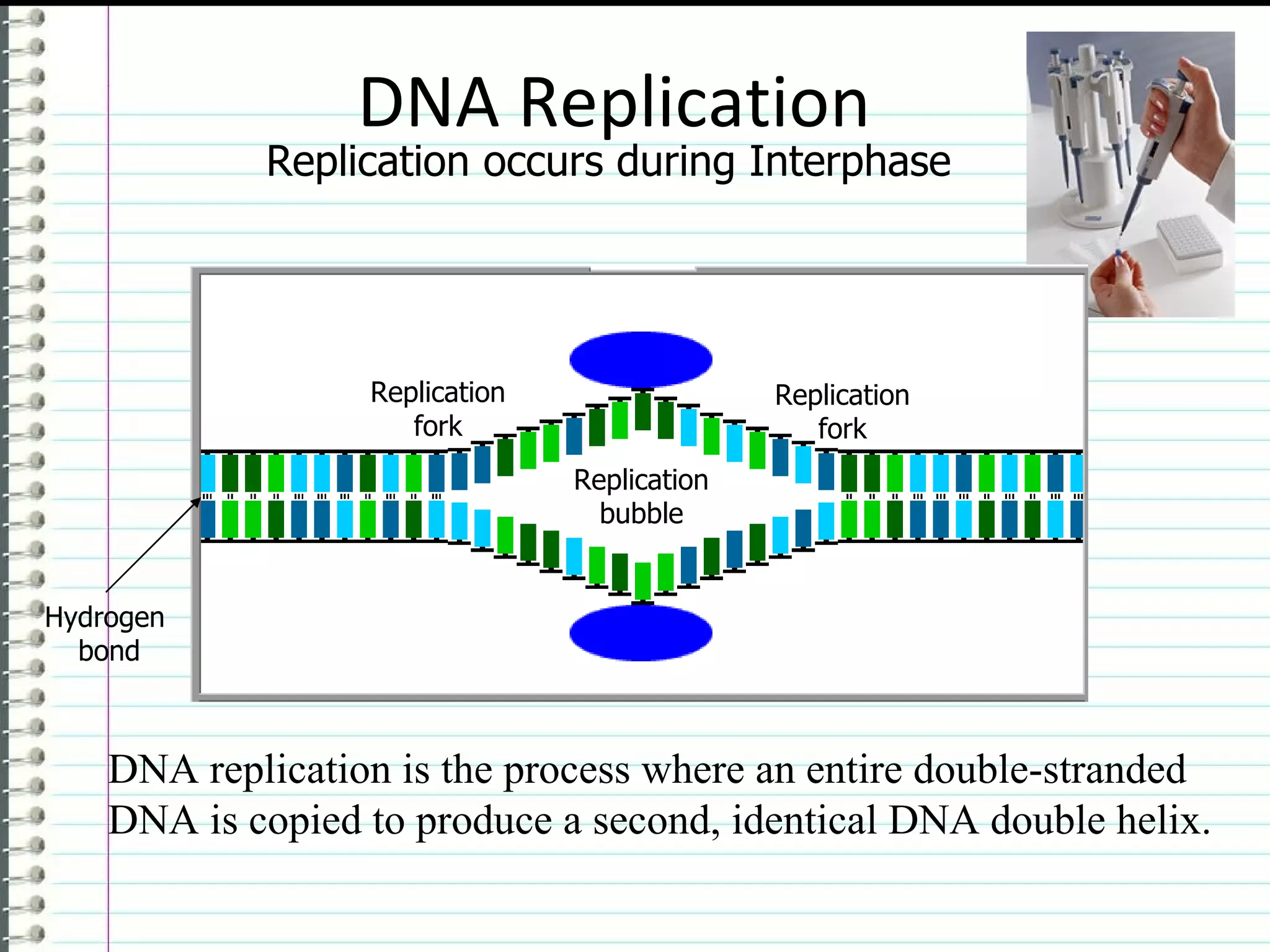
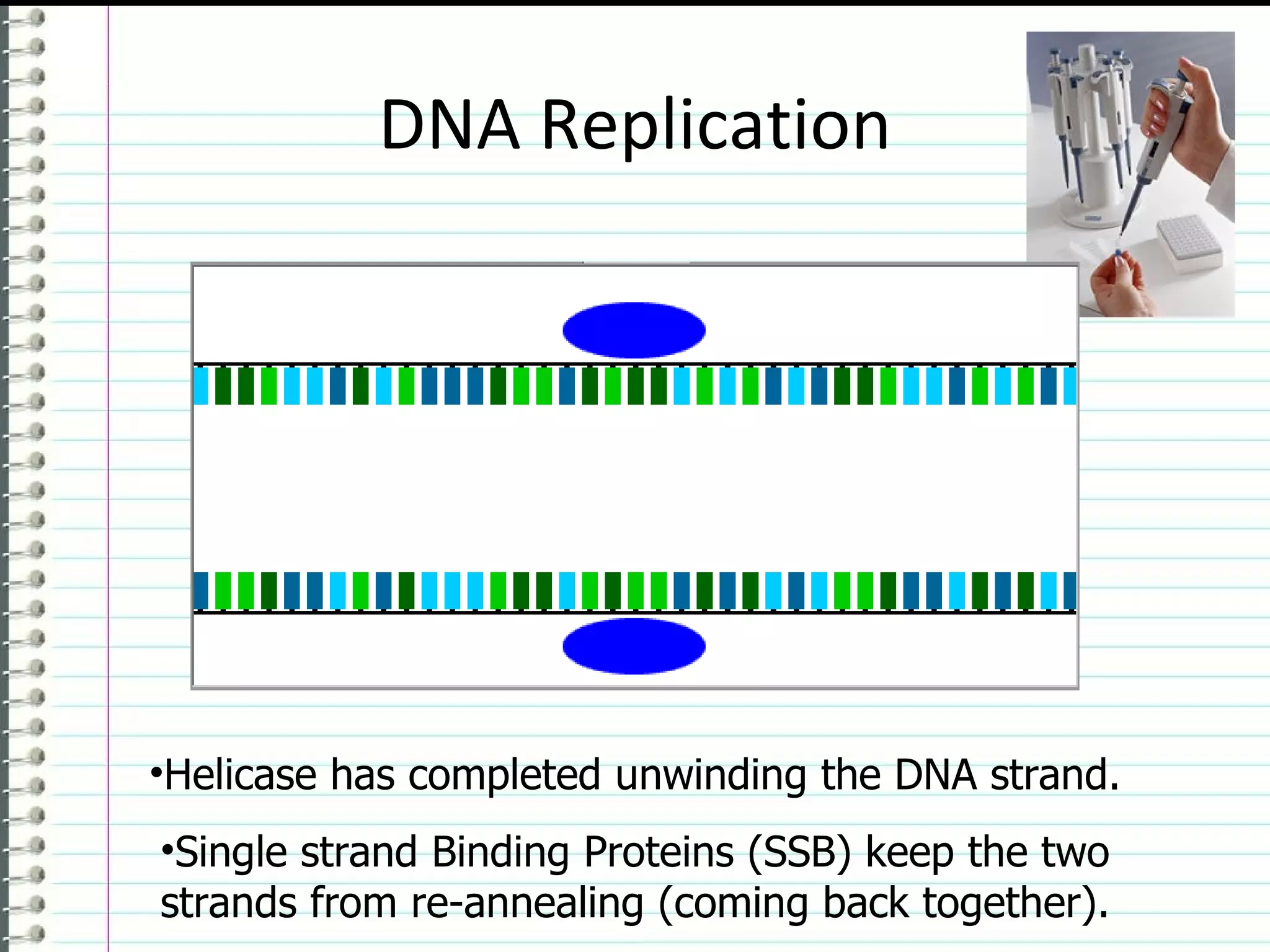
DNA replication is the process where a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical copies. It occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle. The DNA double helix unwinds and each strand serves as a template for new partner strands. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to each new strand, building them from the 5' to 3' direction. The leading strand is synthesized continuously while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in fragments called Okazaki fragments that are later joined together. This semiconservative process results in two double-stranded DNA molecules that are identical to the original DNA.