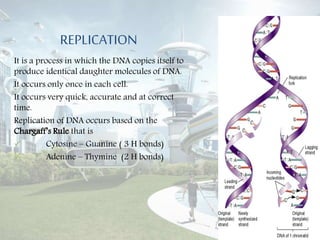
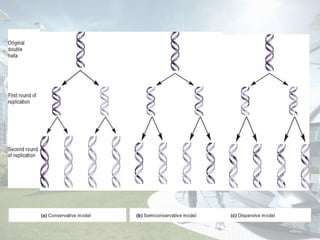
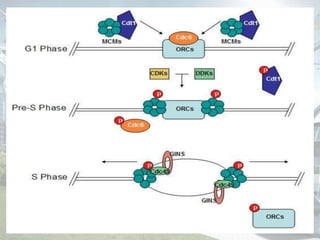
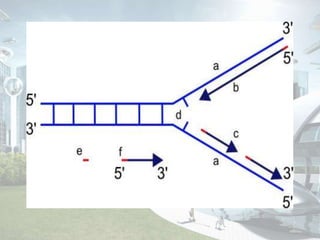
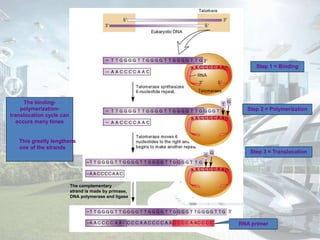
DNA replication is the process by which DNA copies itself to produce identical daughter molecules. It occurs through a semi-conservative process in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In eukaryotes, replication is a complex multi-stage process involving initiation, formation of a pre-replication complex, conversion to an initiation complex, elongation via leading and lagging strand synthesis, and termination. Key proteins involved include ORC, Cdc6, Cdt1, MCM complexes, Cdc45, GINS, DNA polymerases, primase, ligase and topoisomerases. Replication occurs with high fidelity and is tightly regulated to prevent re-replication.