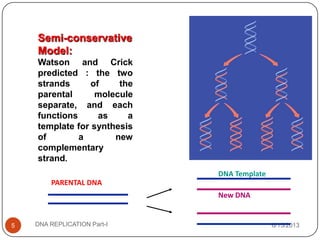
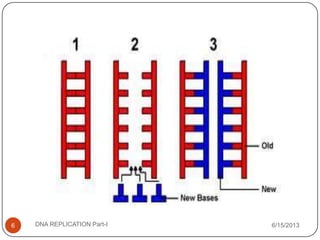
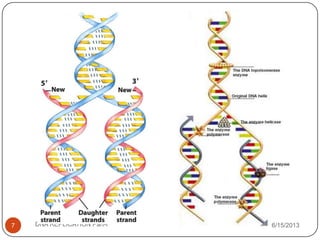
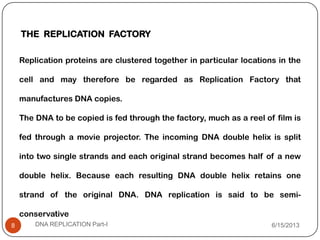
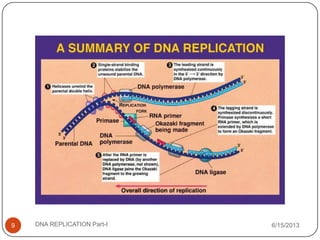
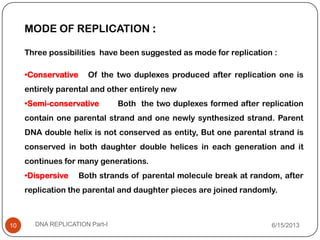
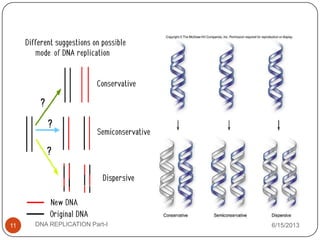
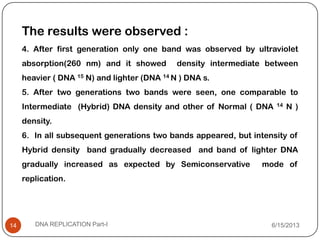
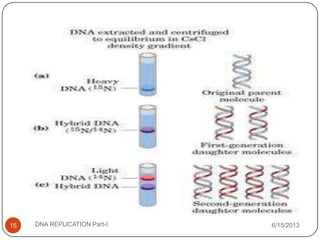
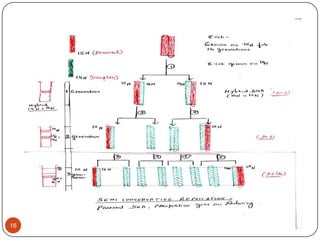
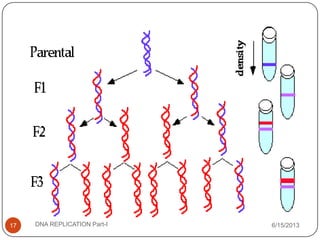
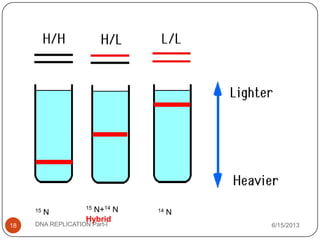
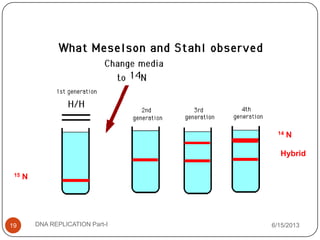
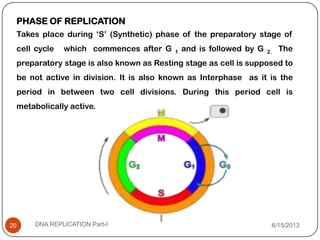
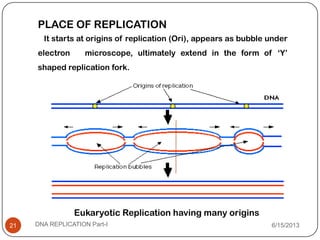
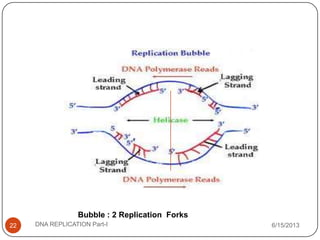
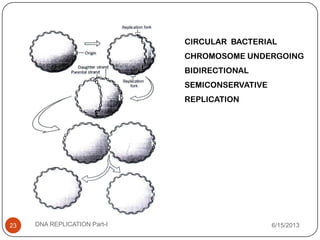
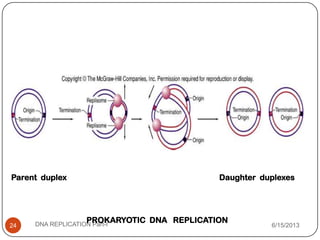
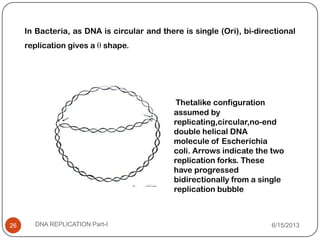
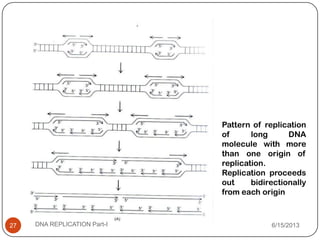
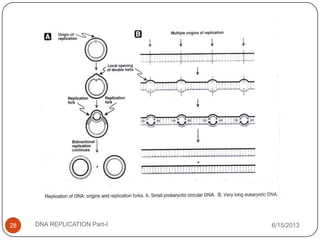
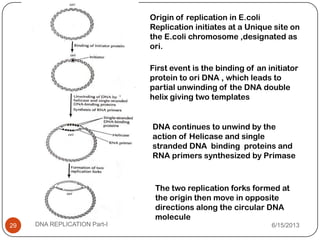
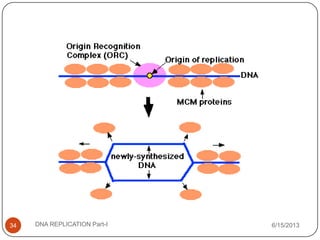
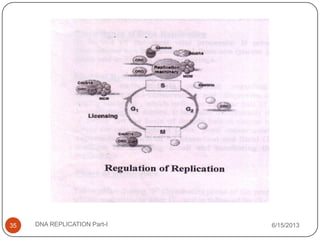
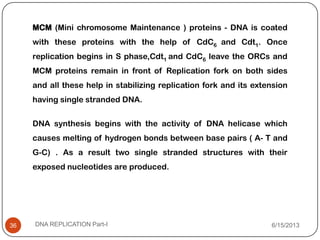
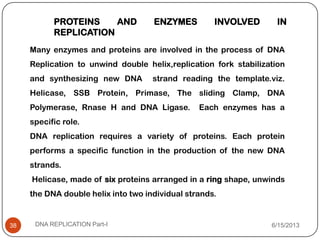
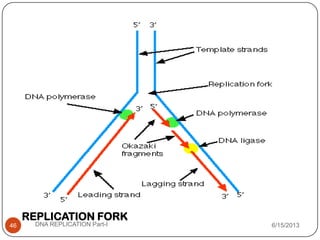
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle and involves unwinding the DNA double helix, creating RNA primers, and synthesizing new DNA strands using existing strands as templates in the 5' to 3' direction. The replication factory contains many replication proteins that cluster together to duplicate DNA. Experimental evidence from Meselson-Stahl experiments supported the semi-conservative mode of replication, in which each new DNA molecule contains one original and one new strand. Replication initiates at specific origins of replication and proceeds bidirectionally.