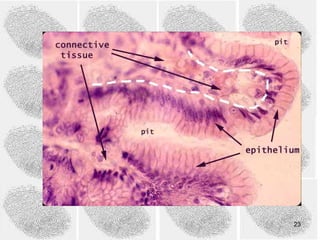
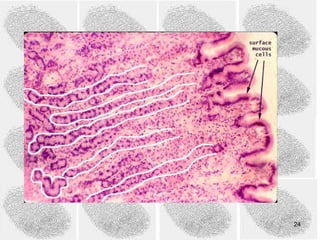
1) DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals by their unique DNA patterns. It analyzes Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs) in DNA, which vary between people.
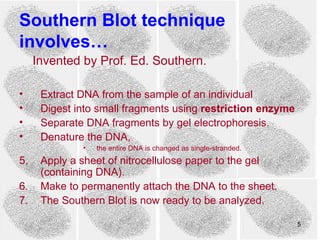
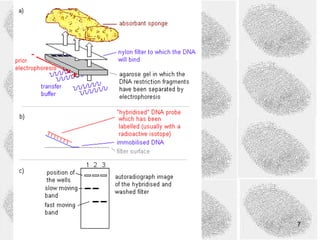
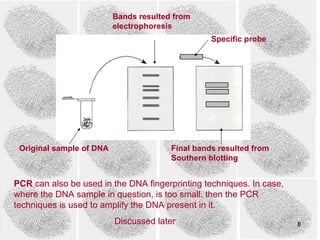
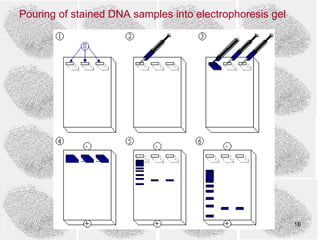
2) The Southern blot technique is used to detect and analyze VNTRs. It involves extracting DNA from a sample, cutting it, separating fragments by size, and probing for specific VNTRs.
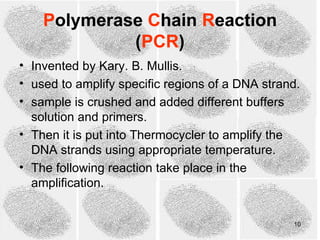
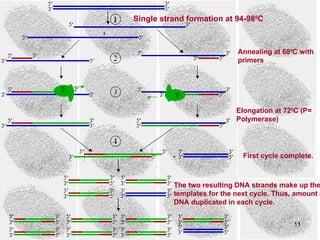
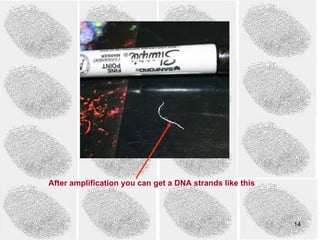
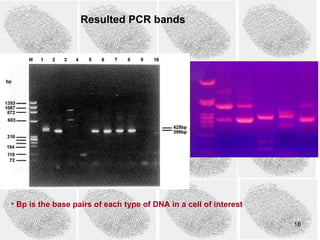
3) PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is used to amplify small DNA samples. It heats and cools DNA in cycles to make billions of copies of specific DNA regions for analysis.