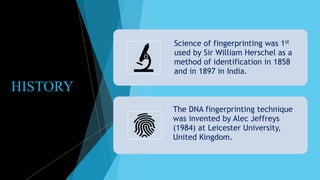
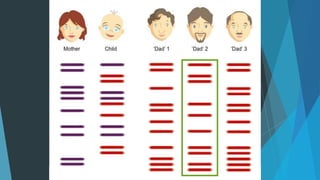
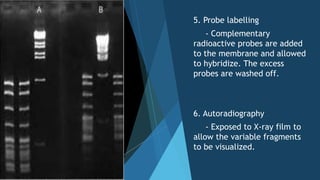
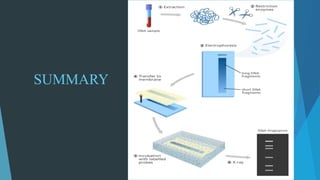
DNA fingerprinting is a technique that analyzes variations in repetitive DNA sequences to generate unique individual profiles. It was invented in 1984 by Alec Jeffreys and involves extracting DNA from samples, cutting the DNA with restriction enzymes, separating fragments via gel electrophoresis, and comparing band patterns on autoradiographs. DNA fingerprinting can be used for forensic identification, paternity testing, and studying human lineages and inherited disorders.







![REFERENCES
Barh, D. and Azevedo, V. (2017) Omics Technologies and Bio-Engineering, pp. 591-625.
Bioscience Times (2018) DNA Fingerprinting- Principle, Methods, Applications [Online]. Available at:
https://www.biosciencetimes.com/molecular-biology/dna-fingerprinting/276/ (Accessed: 28 August
2019).
Kofanova, O. A., Mathieson, W., Thomas, G. A. and Betsou F. (2014) ‘DNA Fingerprinting: A Quality
Control Case Study for Human Biospecimen Authentication’, Biopreservation and Biobank, 12(2), pp.
151–153 [Online]. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3995361/ (Accessed:
27 August 2019).
Roewer, L., (2013) ‘DNA fingerprinting in forensics: past, present, future’, Investigative Genetics, 4(22)
[Online]. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3831584/ (Accessed: 28 August
2019).
Sciencing (2019) What are Specific Biotechnology Applications for DNA Fingerprinting? [Online].
Available at: https://sciencing.com/specific-biotechnology-applications-dna-fingerprinting-23975.html
(Accessed: 28 August 2019).
Your Article Library (2019) DNA Fingerprinting: Principles and Techniques of DNA Fingerprinting
[Online]. Available at: http://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/dna/dna-fingerprinting-principles-and-
techniques-of-dna-fingerprinting/12211 (Accessed: 28 August 2019).
Yourgenome.org. (2016) What is a DNA fingerprint? [Online] Available at:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group8dnafingerprintingbatch17-200121160515/85/DNA-fingerprinting-12-320.jpg)
