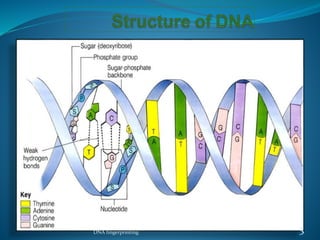
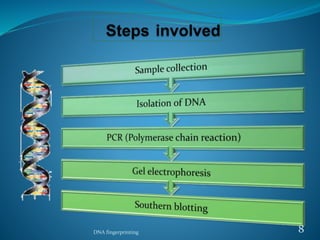
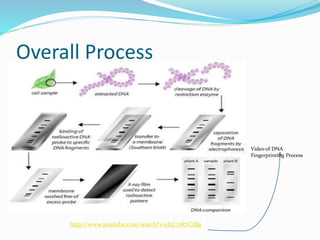
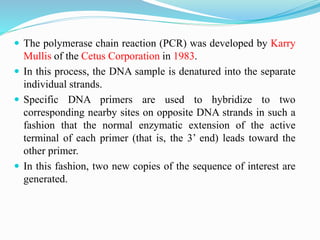
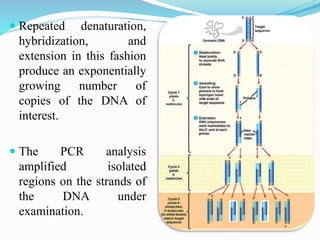
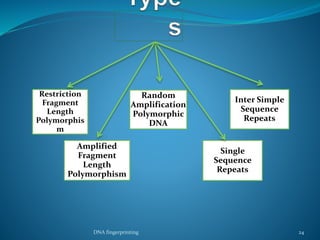
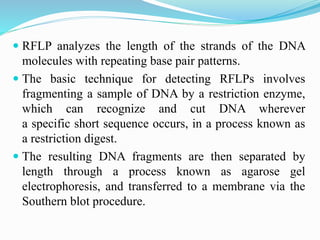
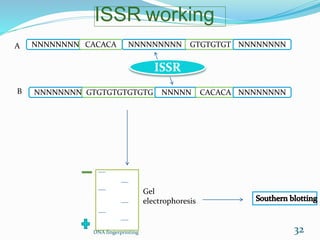
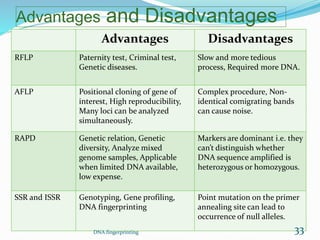
DNA fingerprinting is a technique used for identification by extracting and analyzing the base pair pattern of an individual's DNA. It involves isolating DNA from a sample, cutting the DNA into fragments using restriction enzymes, and comparing the fragment patterns on a gel to identify individuals. The main applications of DNA fingerprinting are in solving criminal cases by matching DNA evidence to suspects, diagnosing inherited diseases, and determining biological relationships in areas like paternity testing.























![[1] DNA Fingerprinting in Plants and Fungi by Kurt Weising, Hilde Nybom,
Markus Pfenninger, Kirsten Wolff, Wieland Meyer
[2] Jeffreys AJ, Wilson V and Thein SL Hypervariable ‘ minisatellite ' regions in
human DNA. Nature 1985 314: 67-73.
[3] SAMPLING TECHNIQUES FOR GENETIC ANALYSIS, Tapir specialist group.
[4] DNA Amplification & PCR, New England Biolabs.inc
[5] Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP), probe, NCBI.
[6] Ovidiu Paun and Peter Schönswetter, Amplified Fragment Length
Polymorphism (AFLP) - an invaluable fingerprinting technique for genomic,
transcriptomic and epigenetic studies, PMC 2012 Dec 3.
[7] Penner GA, Bush A, Wise R, Kim W, Domier L, Kasha K, Laroche A, Scoles
G, Molnar SJ, Fedak G., Reproducibility of random amplified polymorphic DNA
(RAPD) analysis among laboratories, NCBI.
[8] Afaf I. Shehata, Haila A. Al- Ghethar, Ali A. Al- Homaidan, Application of
simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for molecular diversity and
heterozygosity analysis in maize inbred lines, Saudi Journal of Biological
Sciences Volume 16, Issue 2, October 2009, Pages 57–62, science direct
DNA fingerprinting 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationdnafp-170430160716/85/DNA-Fingerprinting-42-320.jpg)
