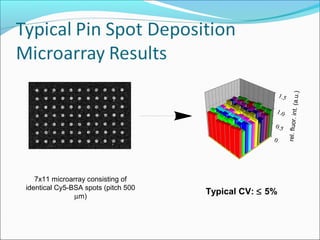
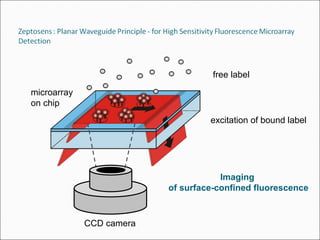
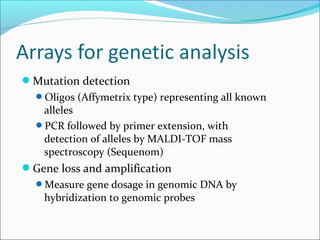
This document discusses the history and technologies of DNA microarrays. It begins with the early techniques of DNA hybridization from the 1960s-1970s that led to the development of microarrays. The key aspects of microarrays are that they allow analysis of hundreds or thousands of DNA probes simultaneously attached to a solid surface using robotics and informatics. Major technologies include cDNA probes on nylon or glass and oligonucleotides synthesized on glass slides. Principal uses are for genome-scale analysis of gene expression, genetic variations, and mutations.