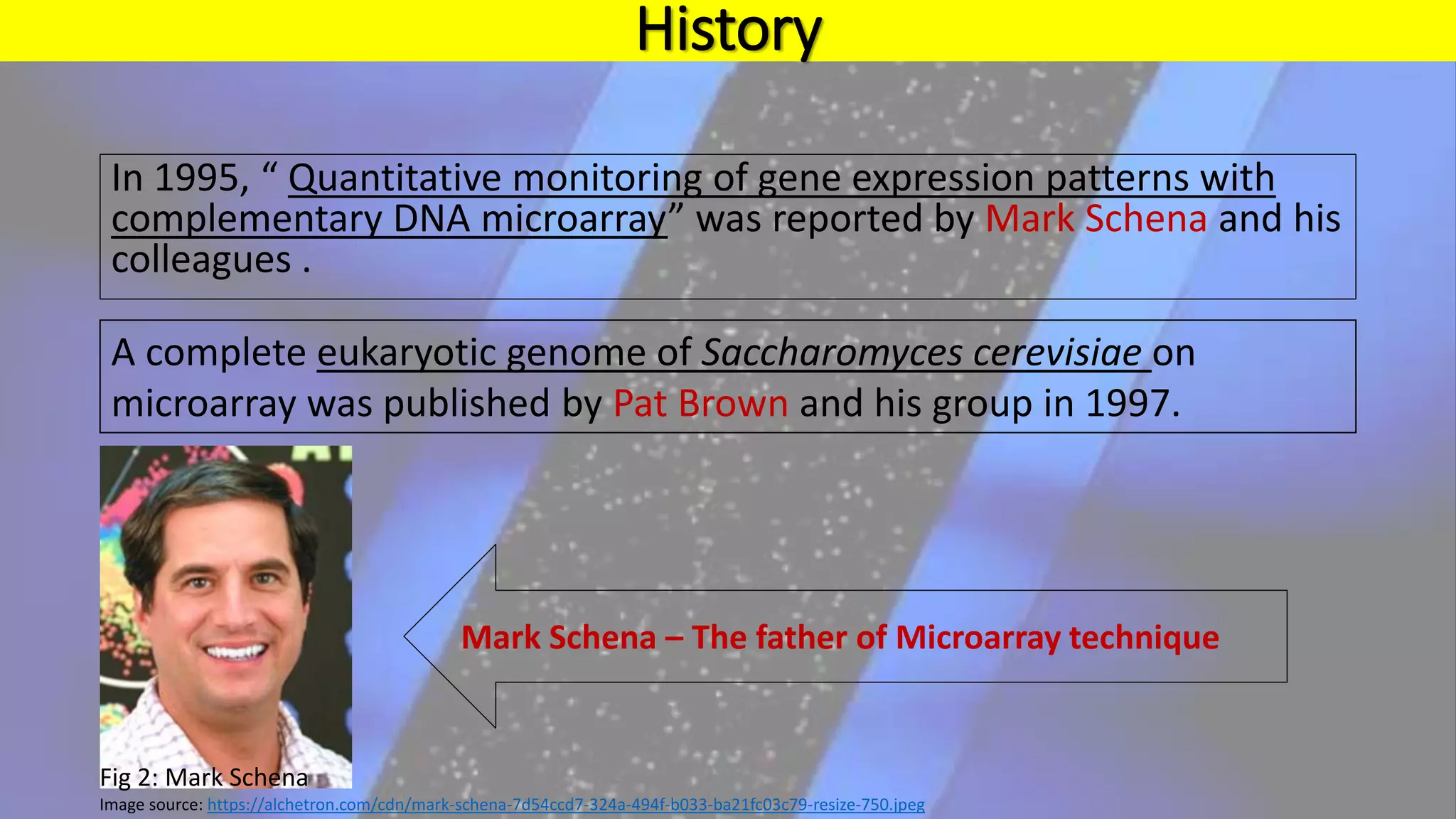
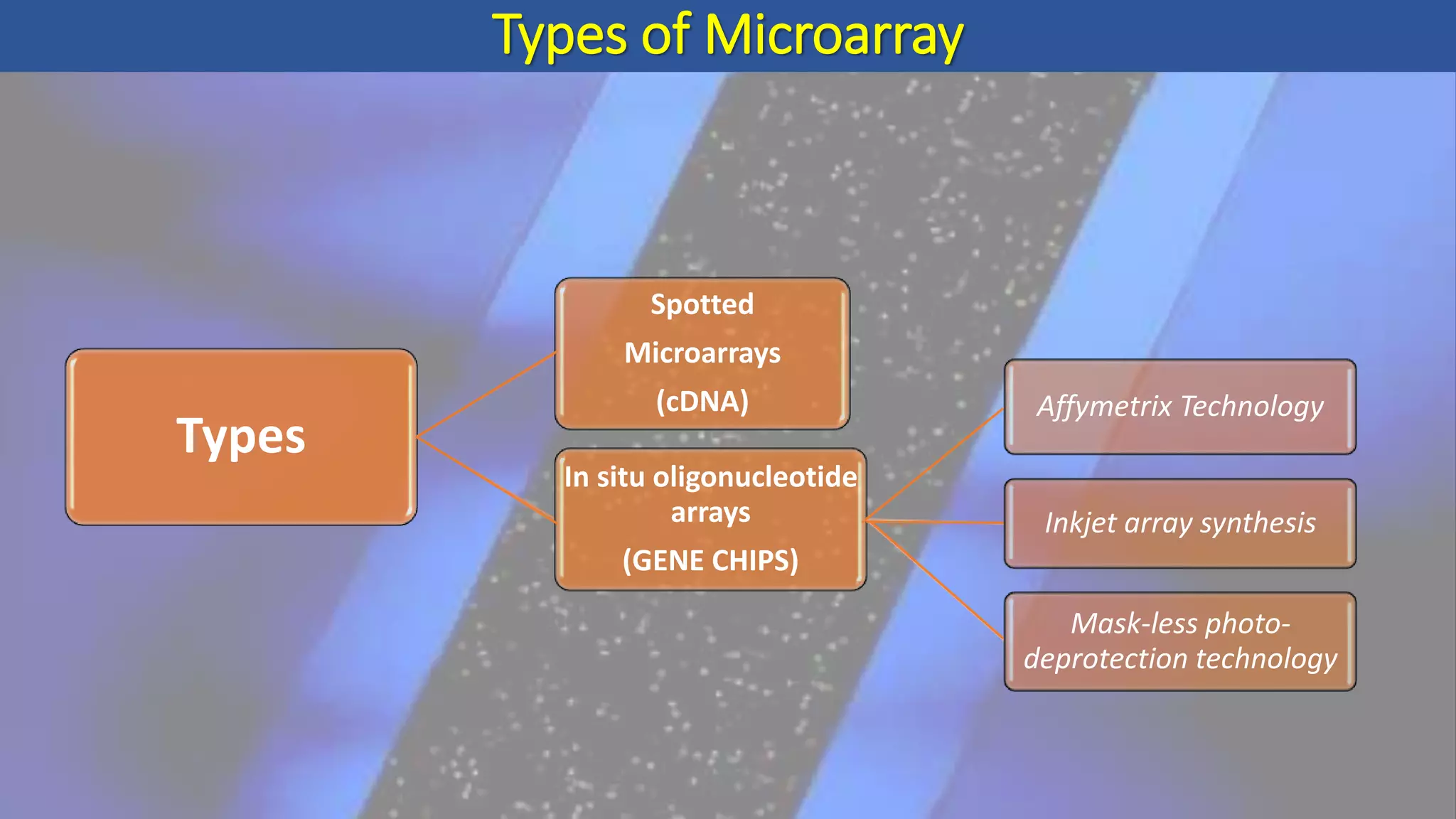
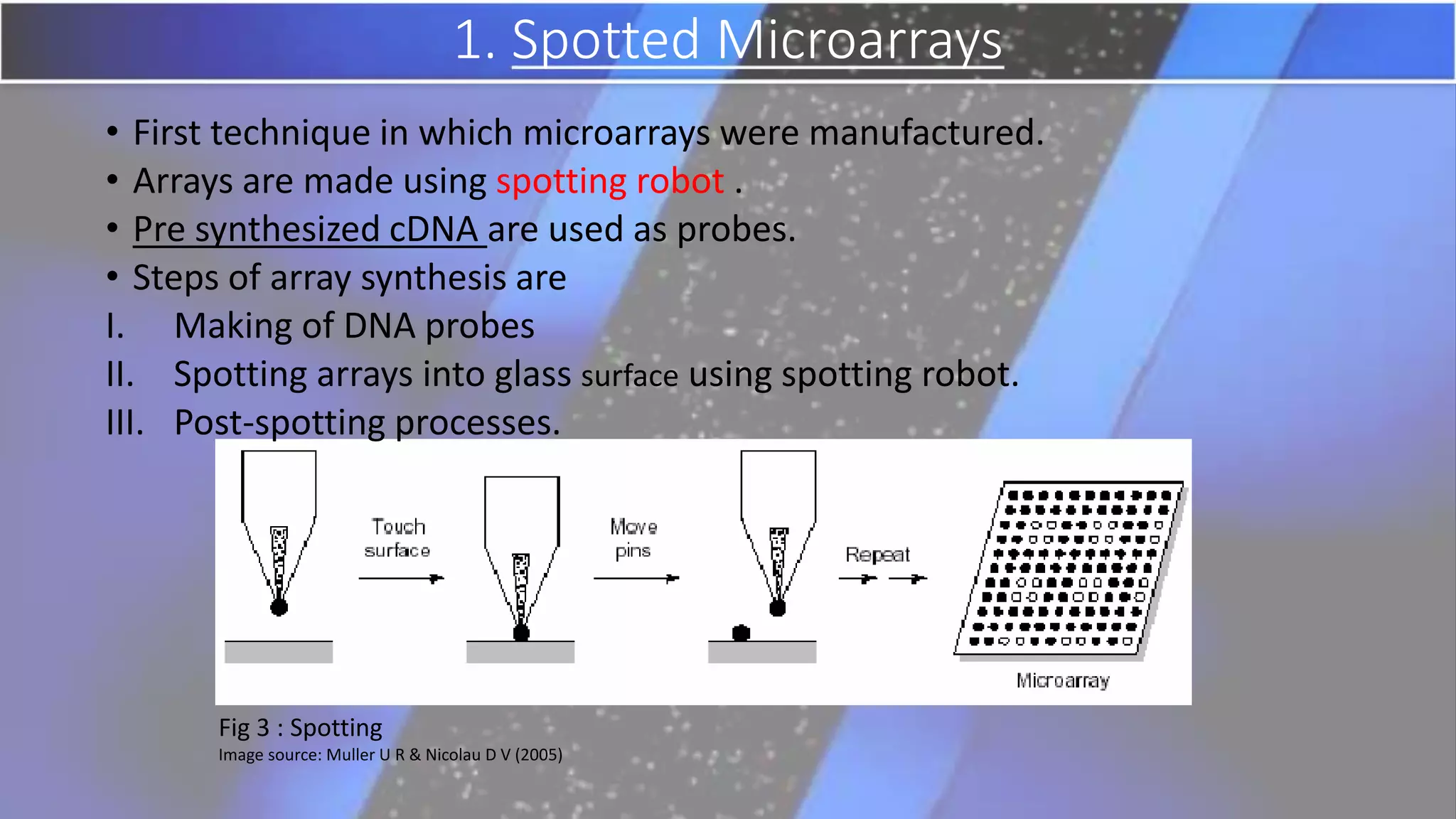
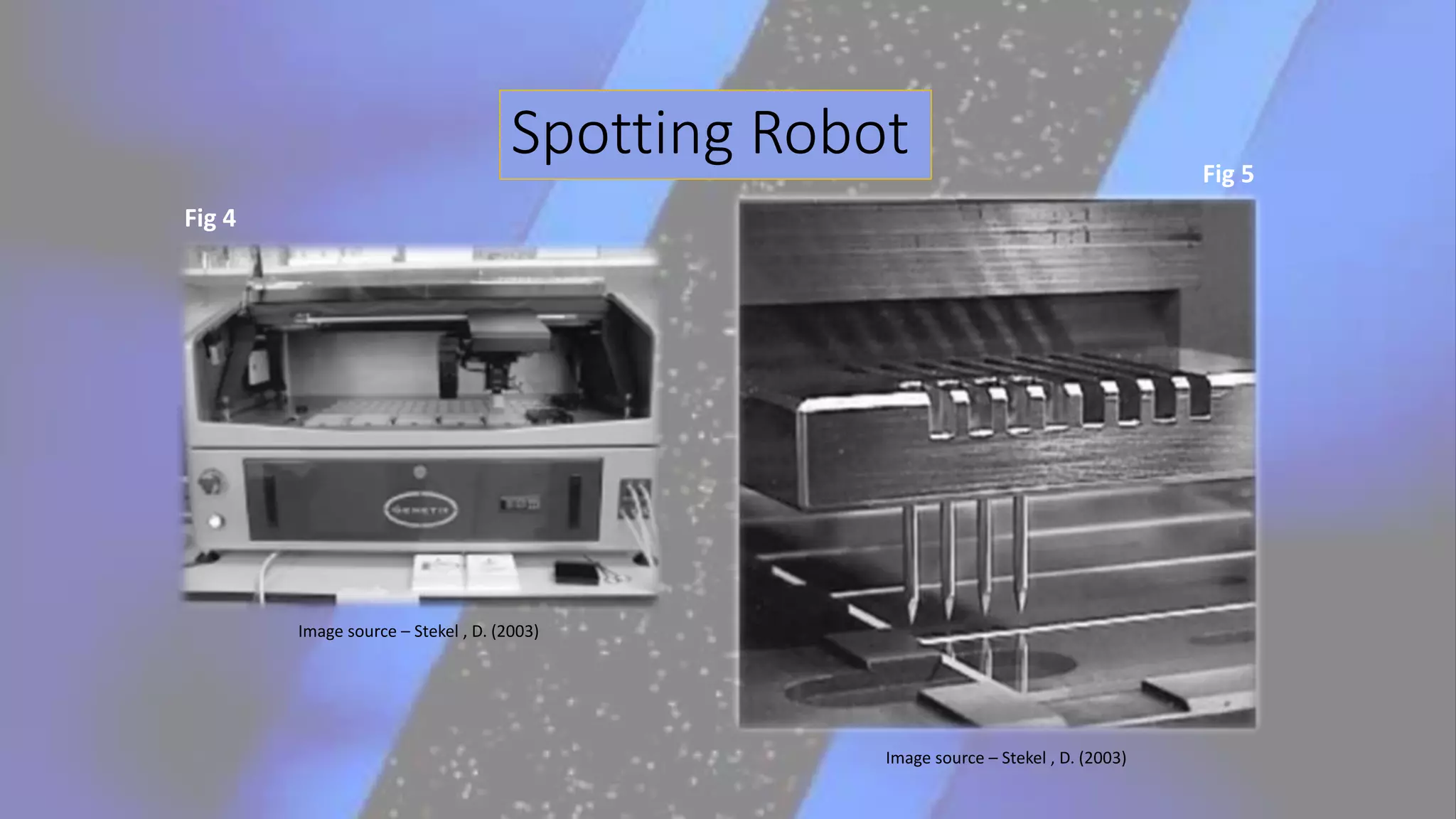
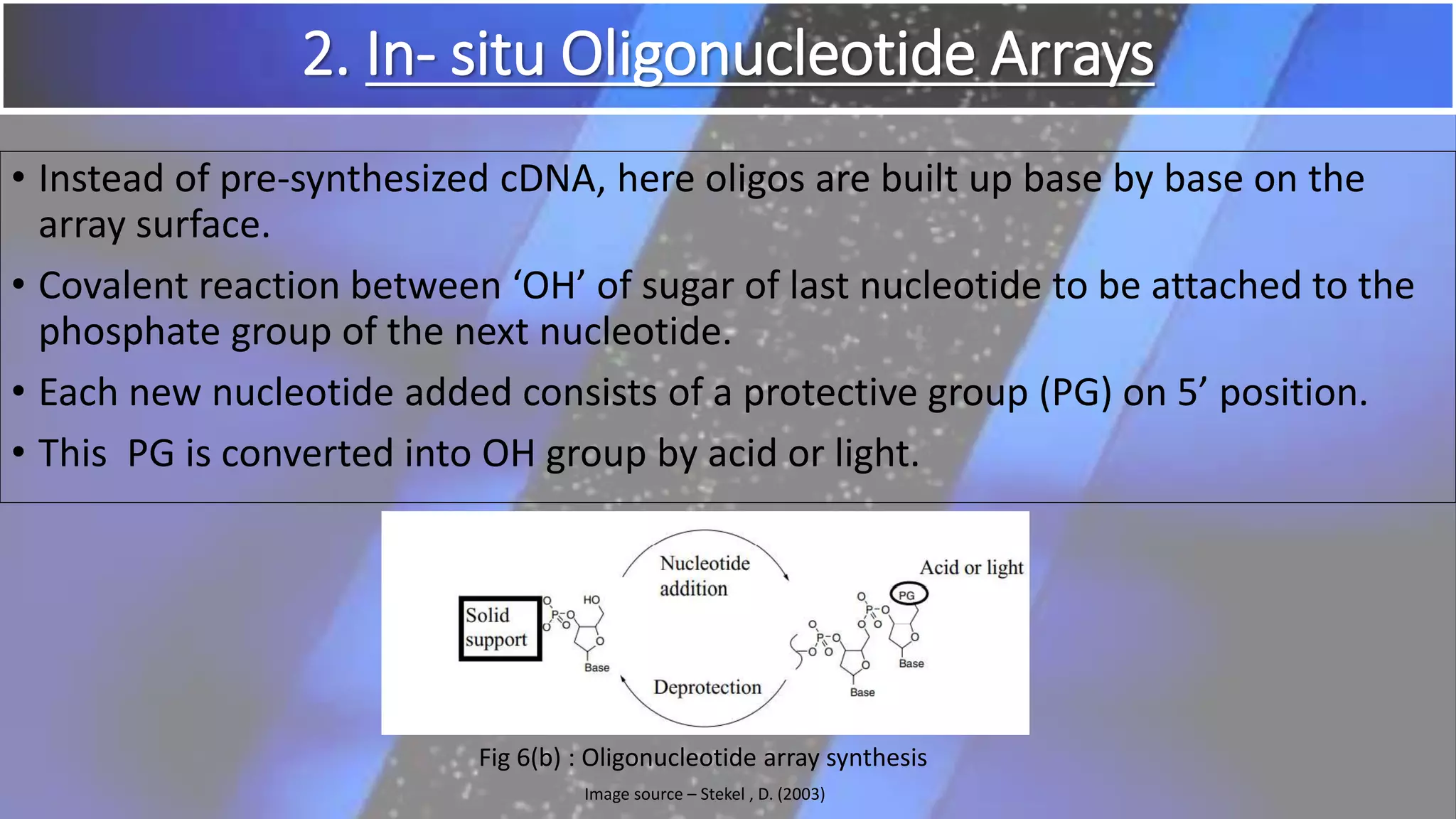
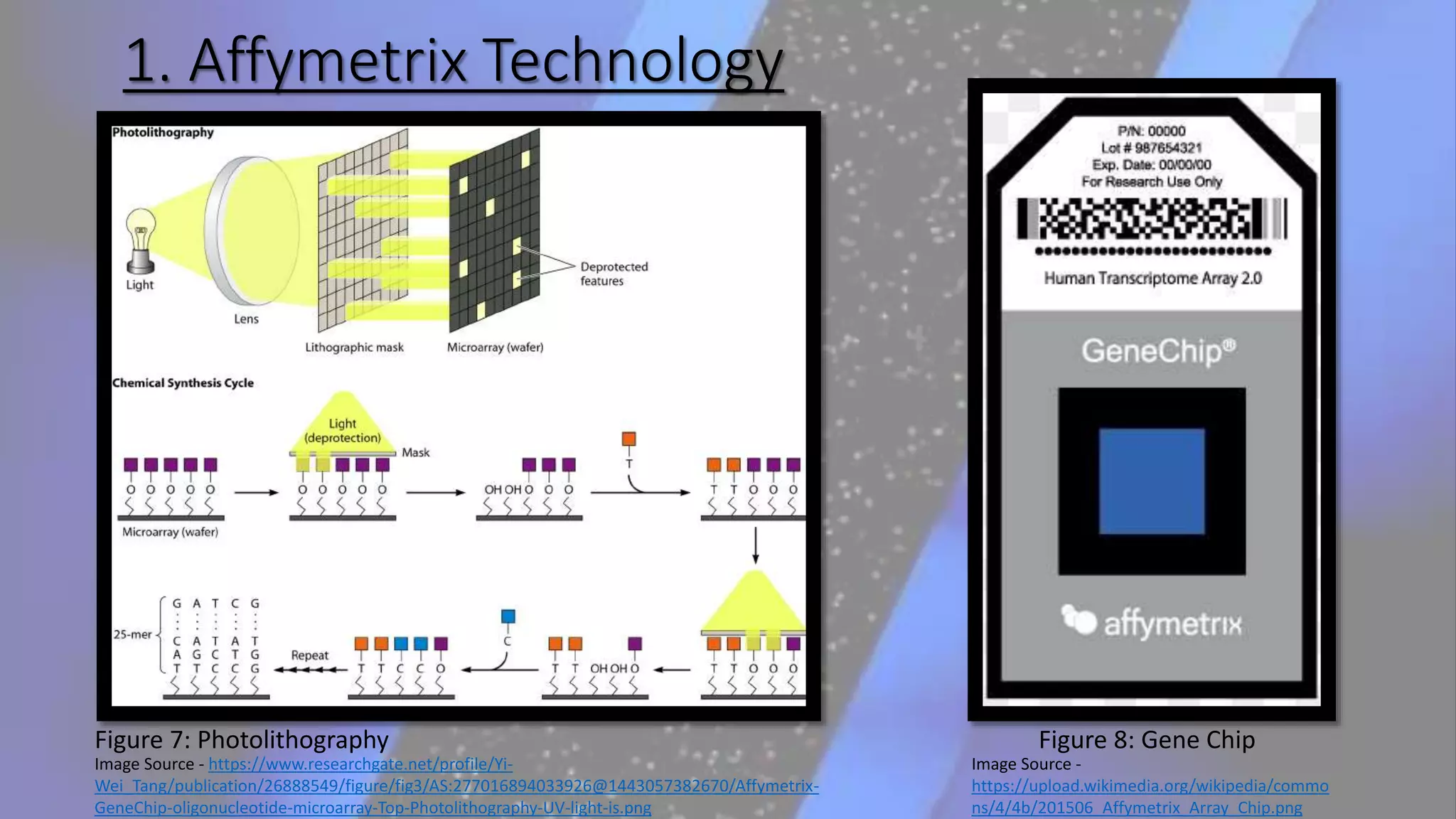
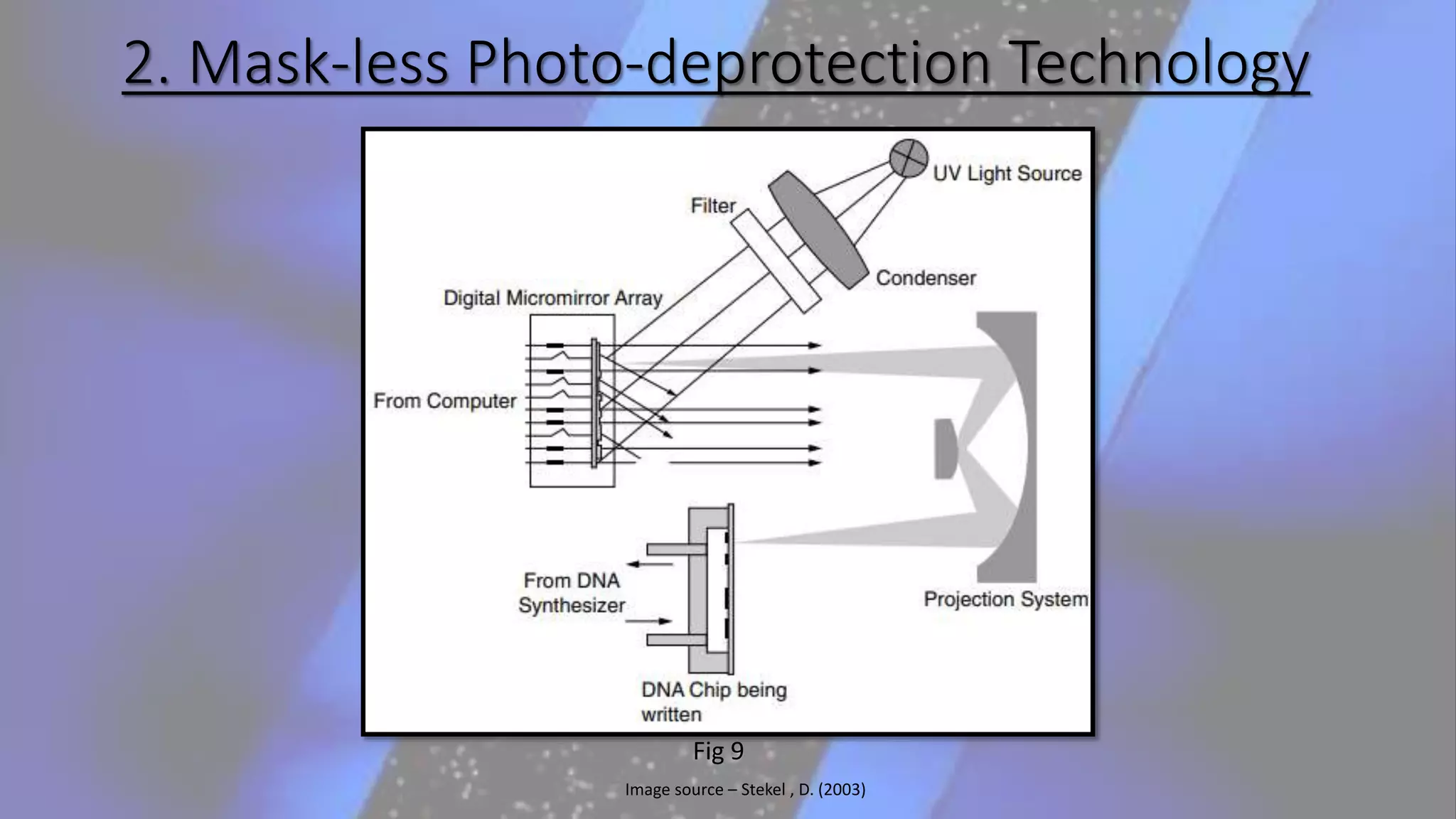
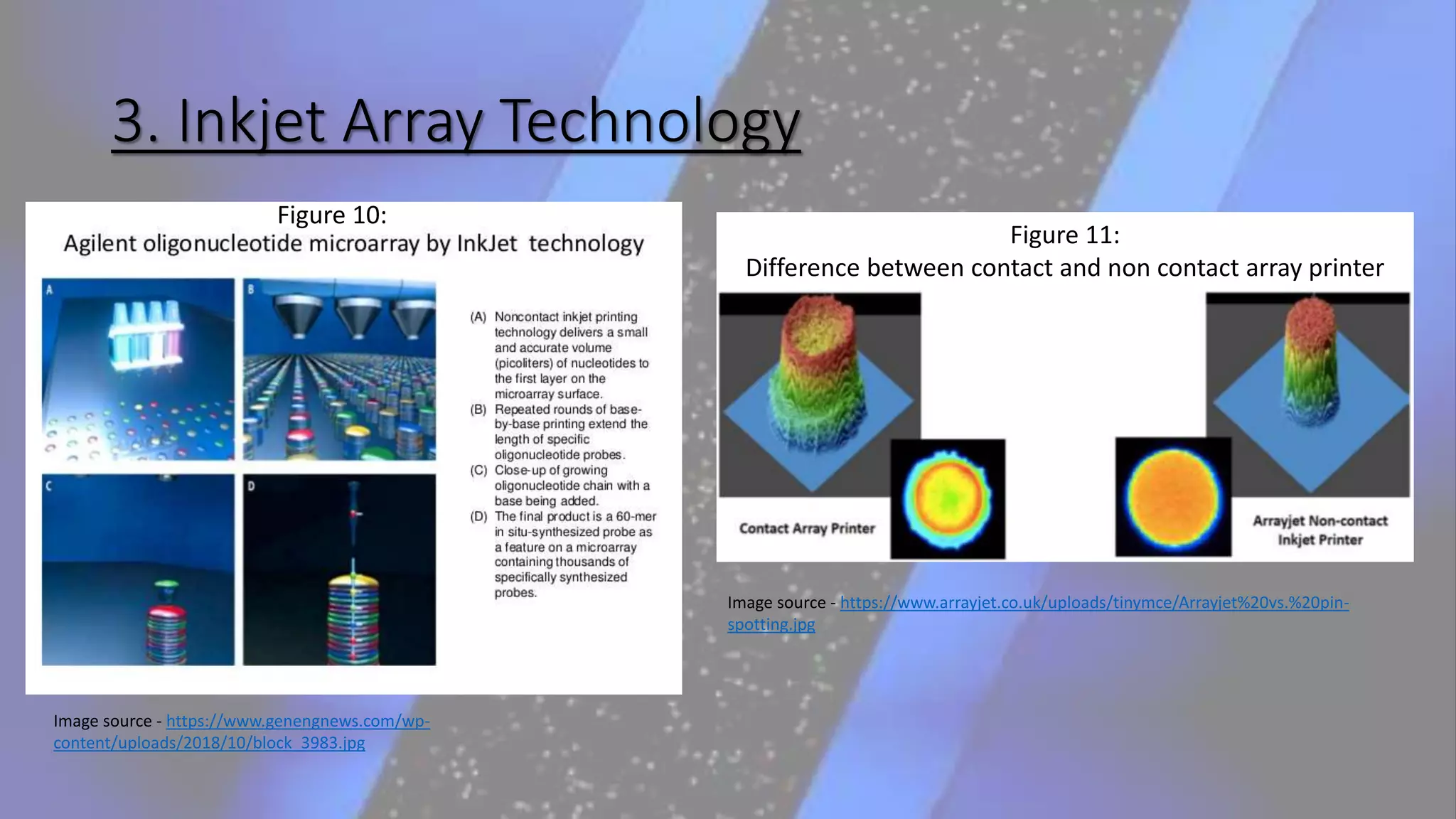
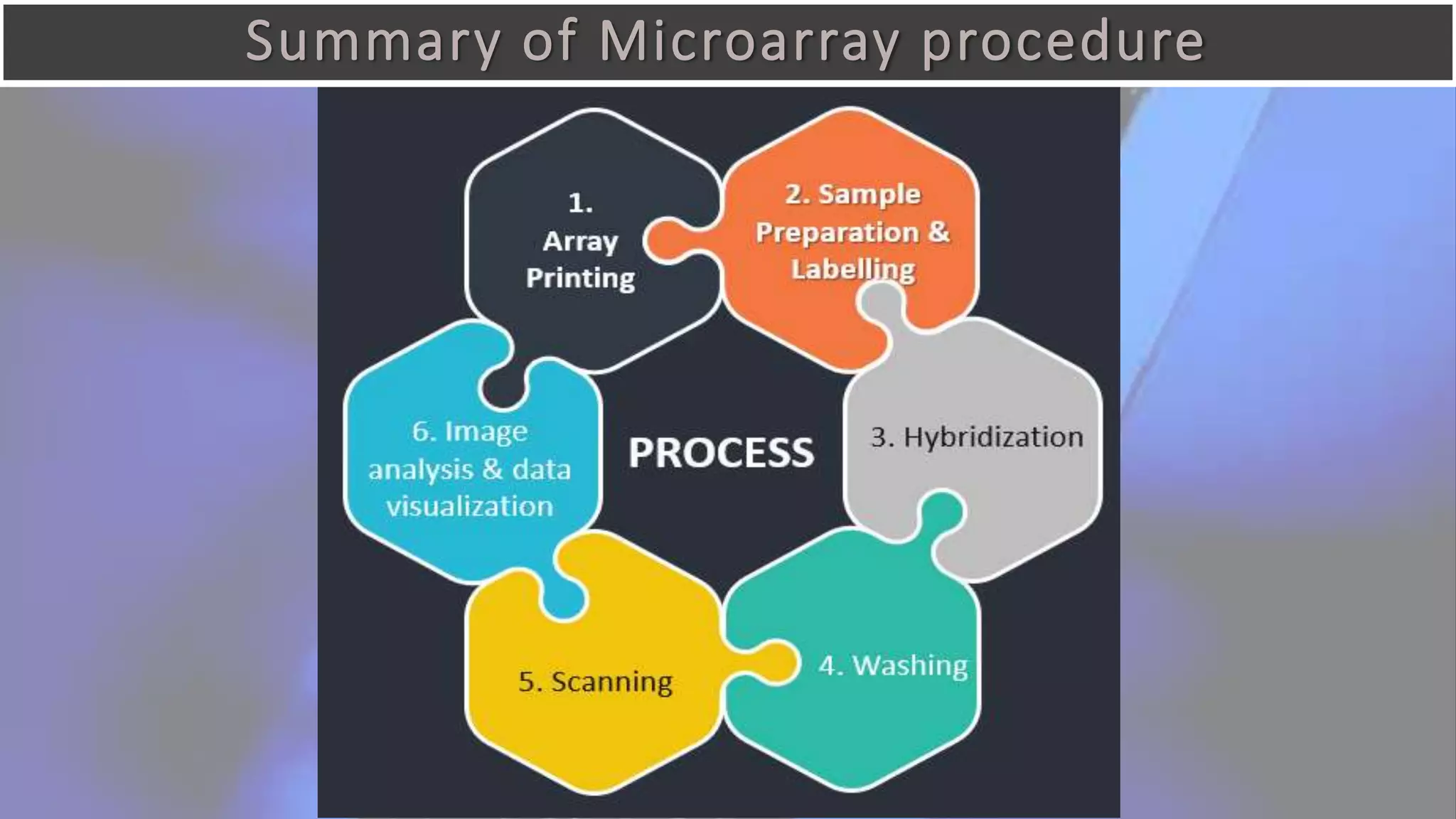
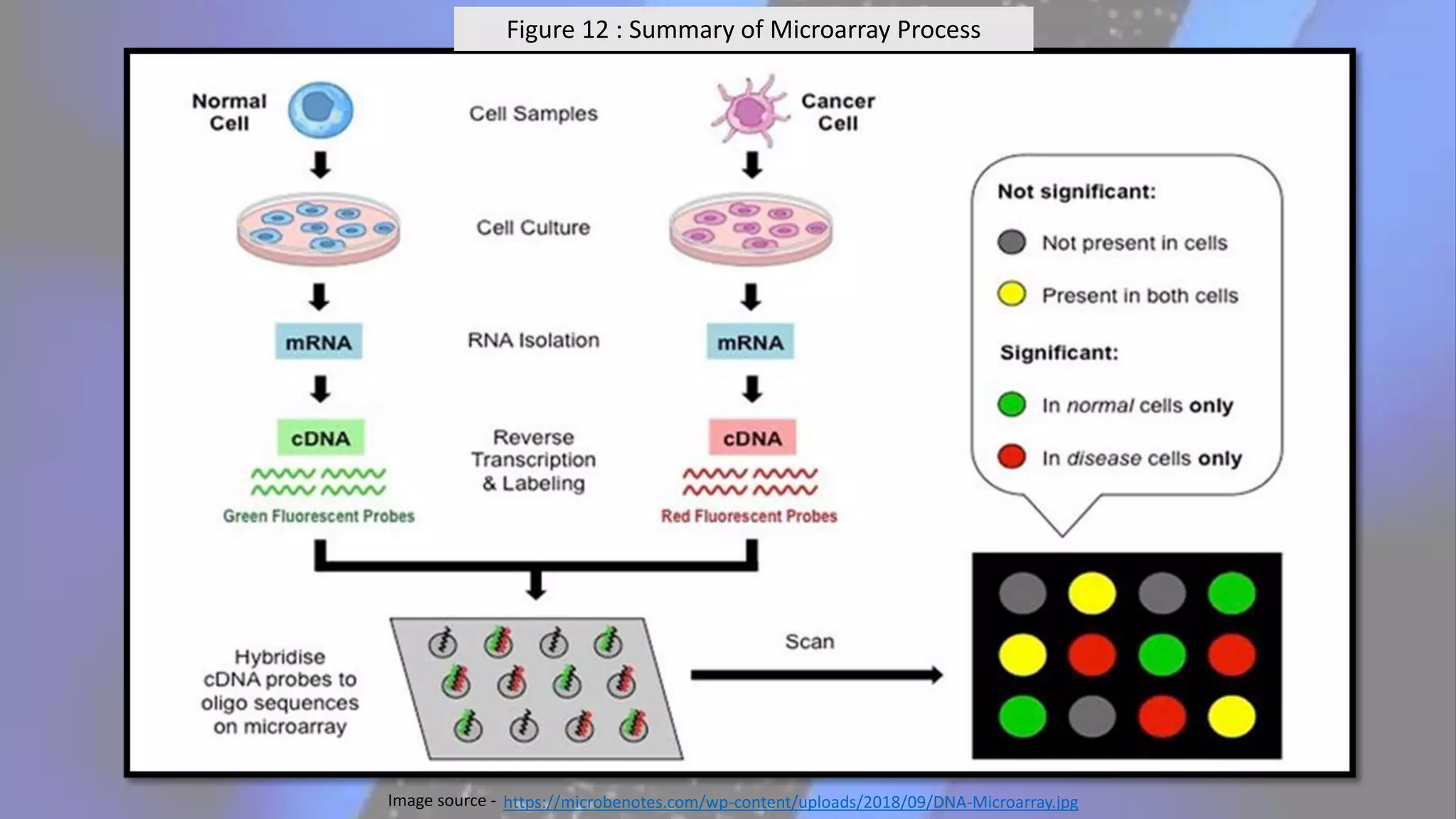
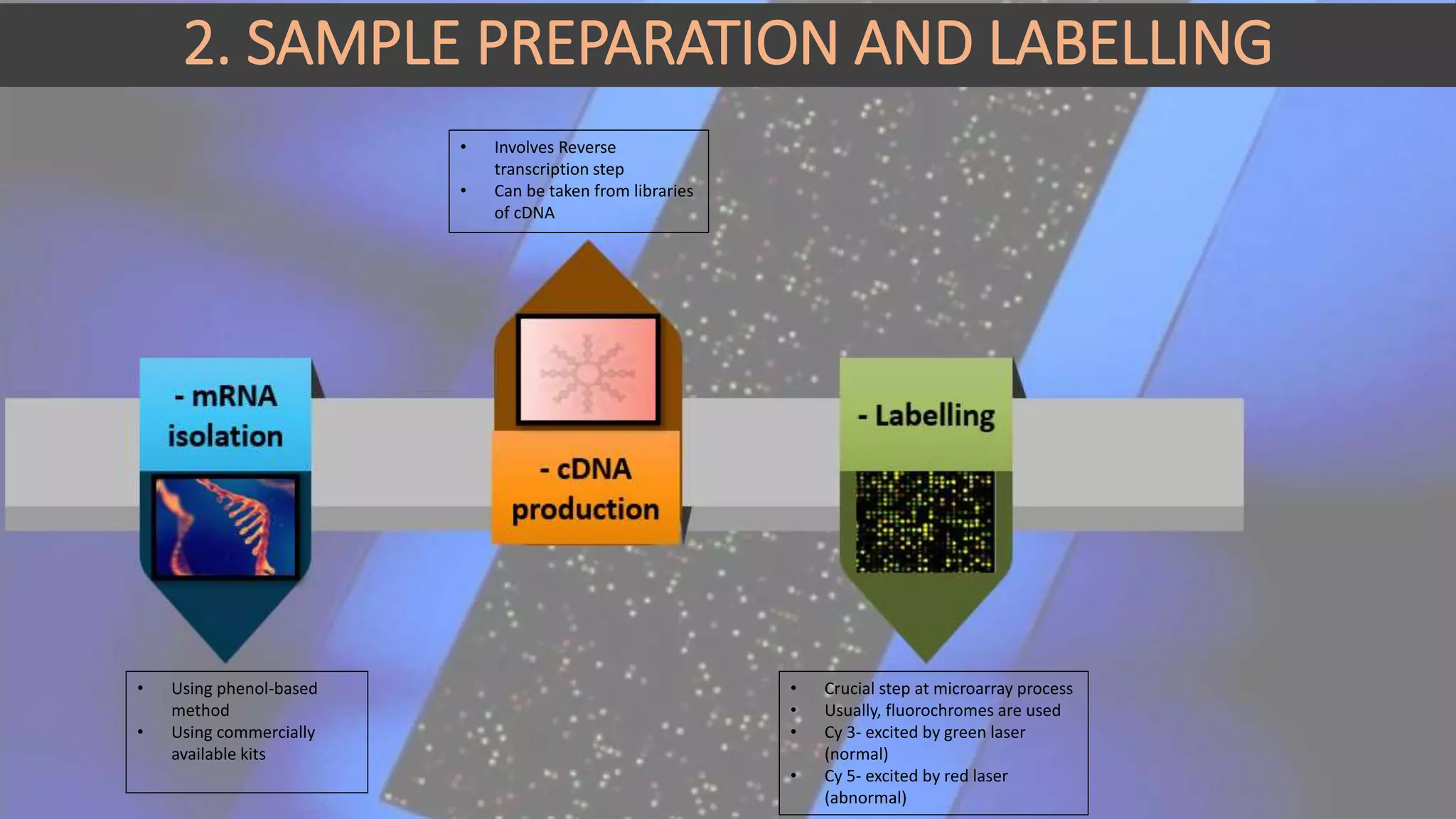
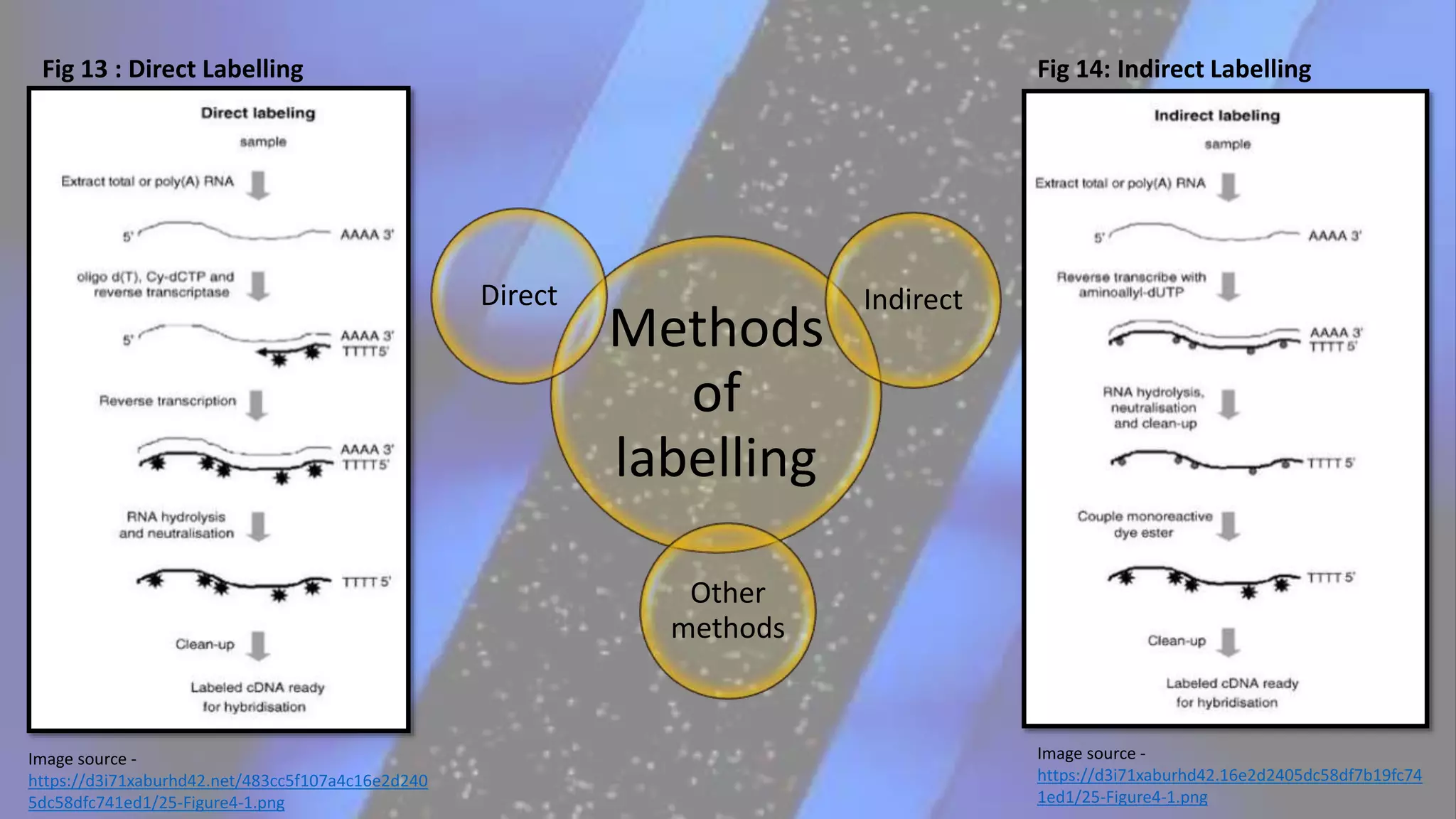
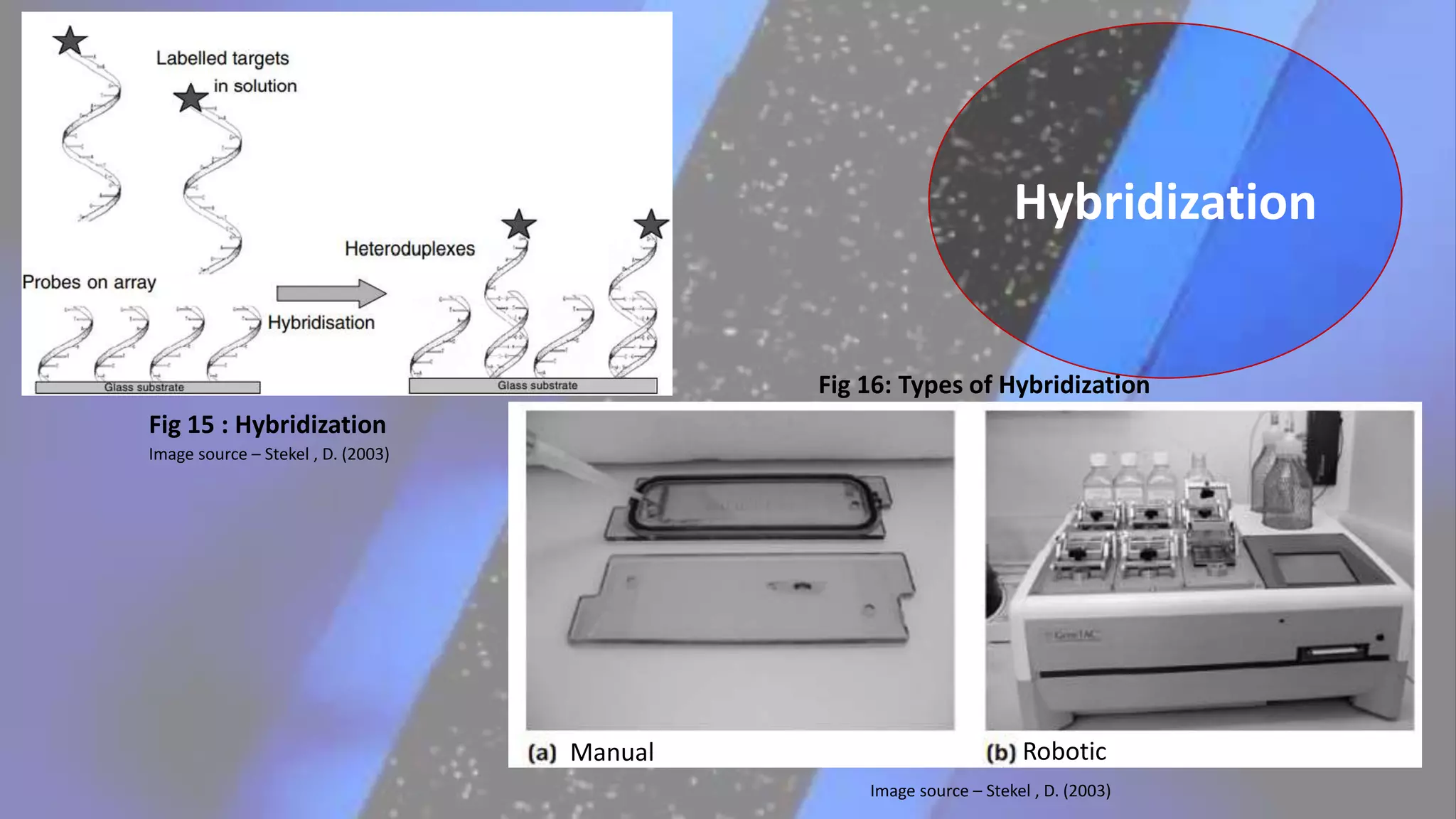
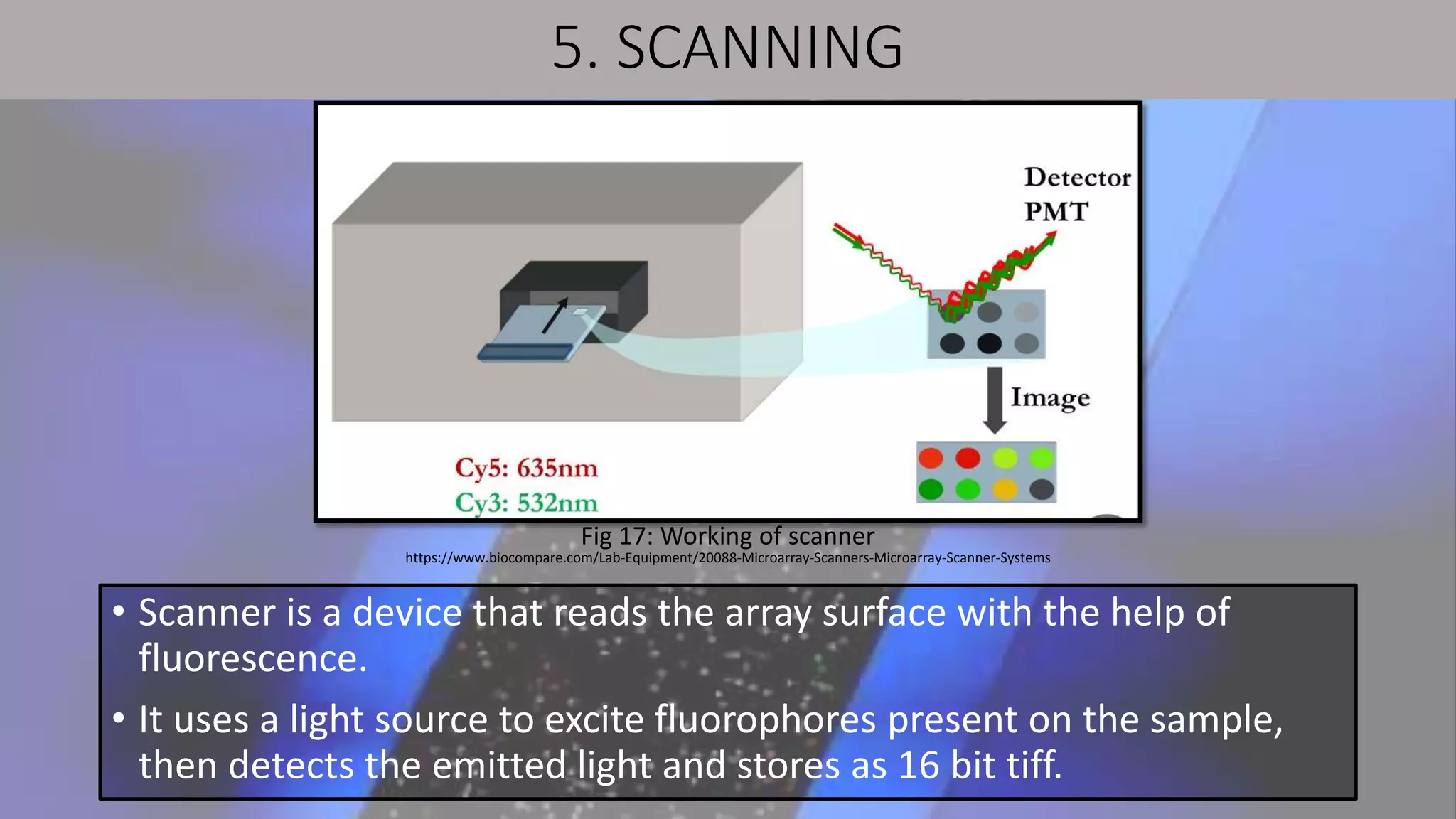
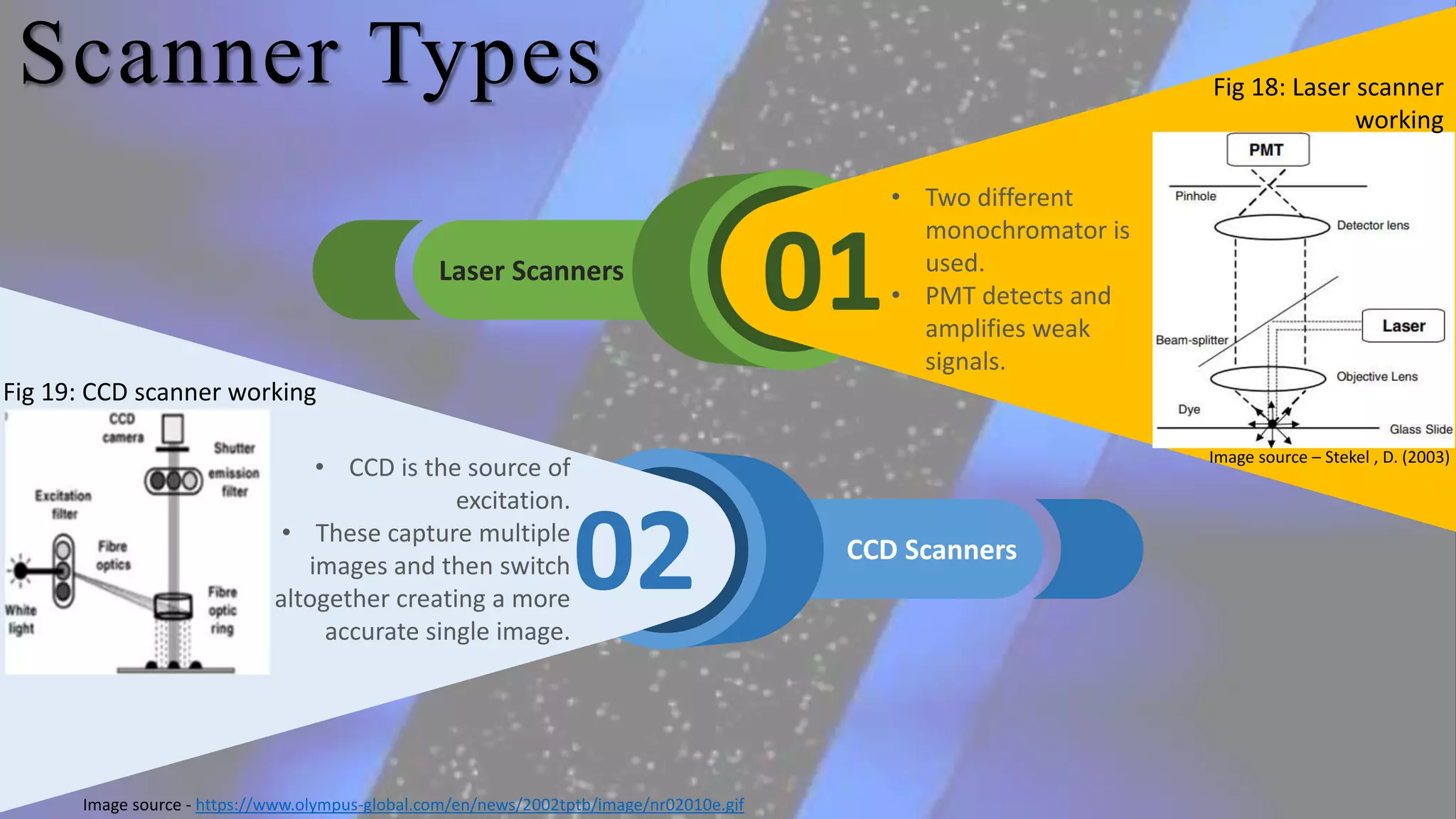
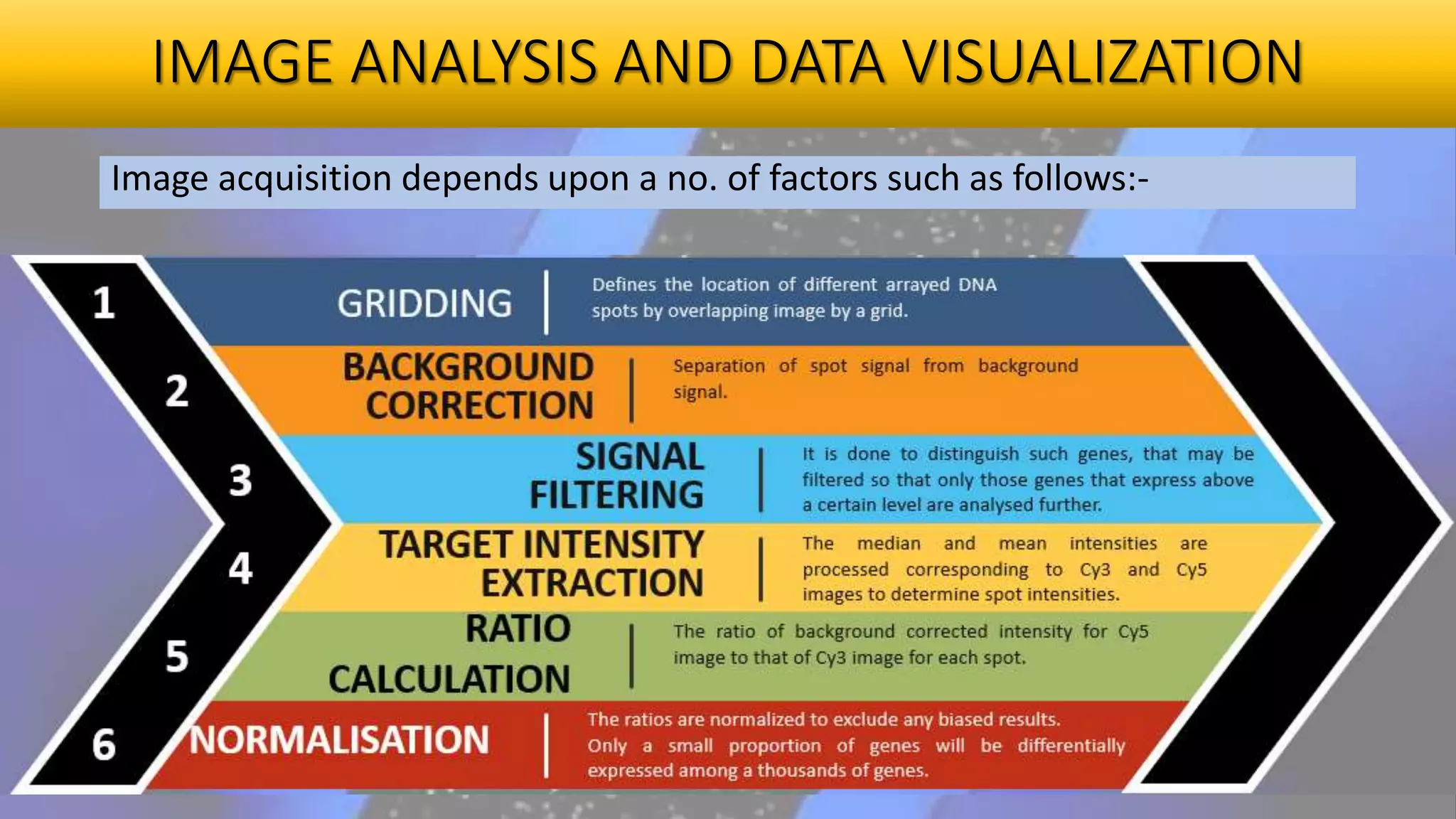
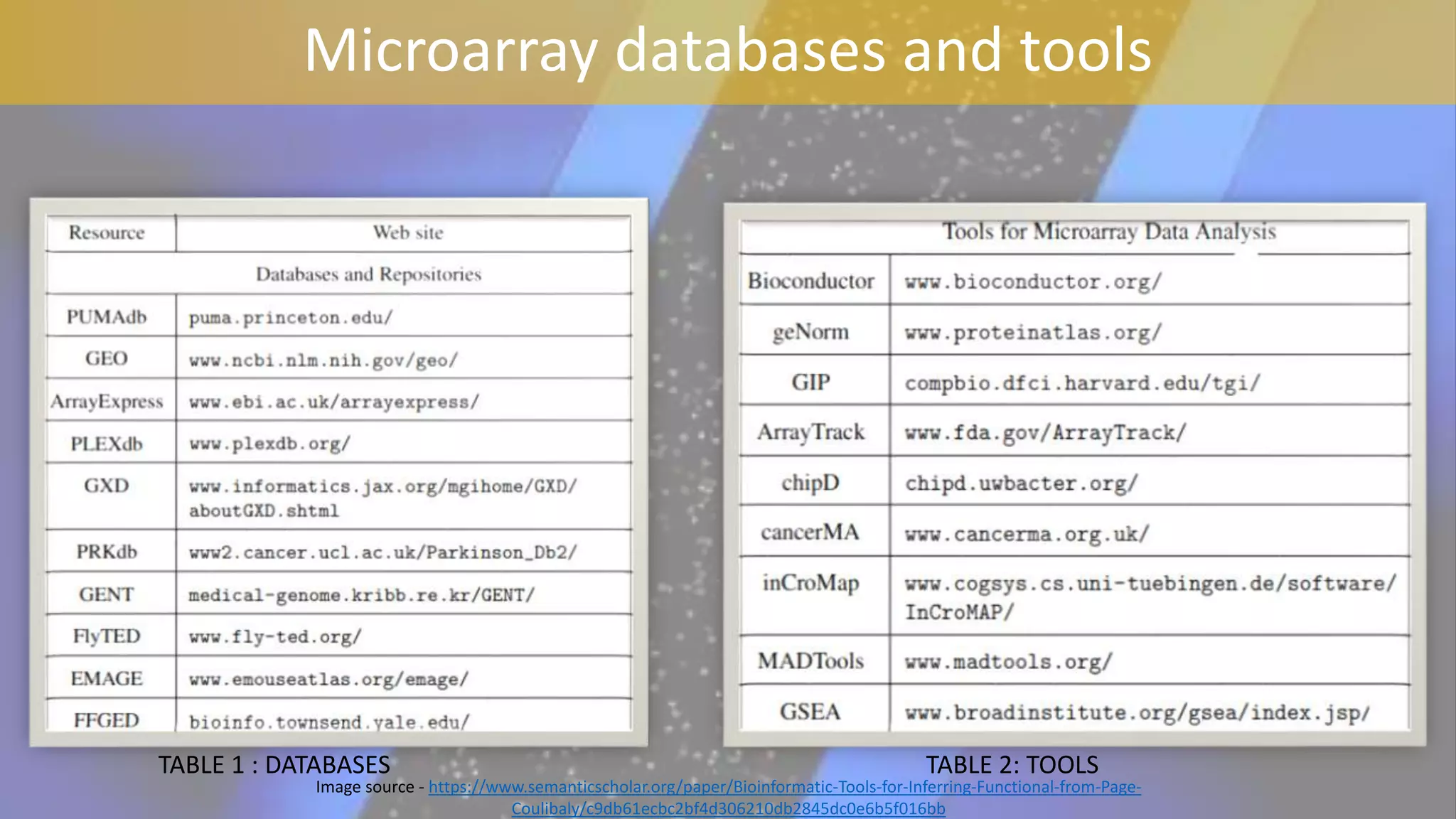
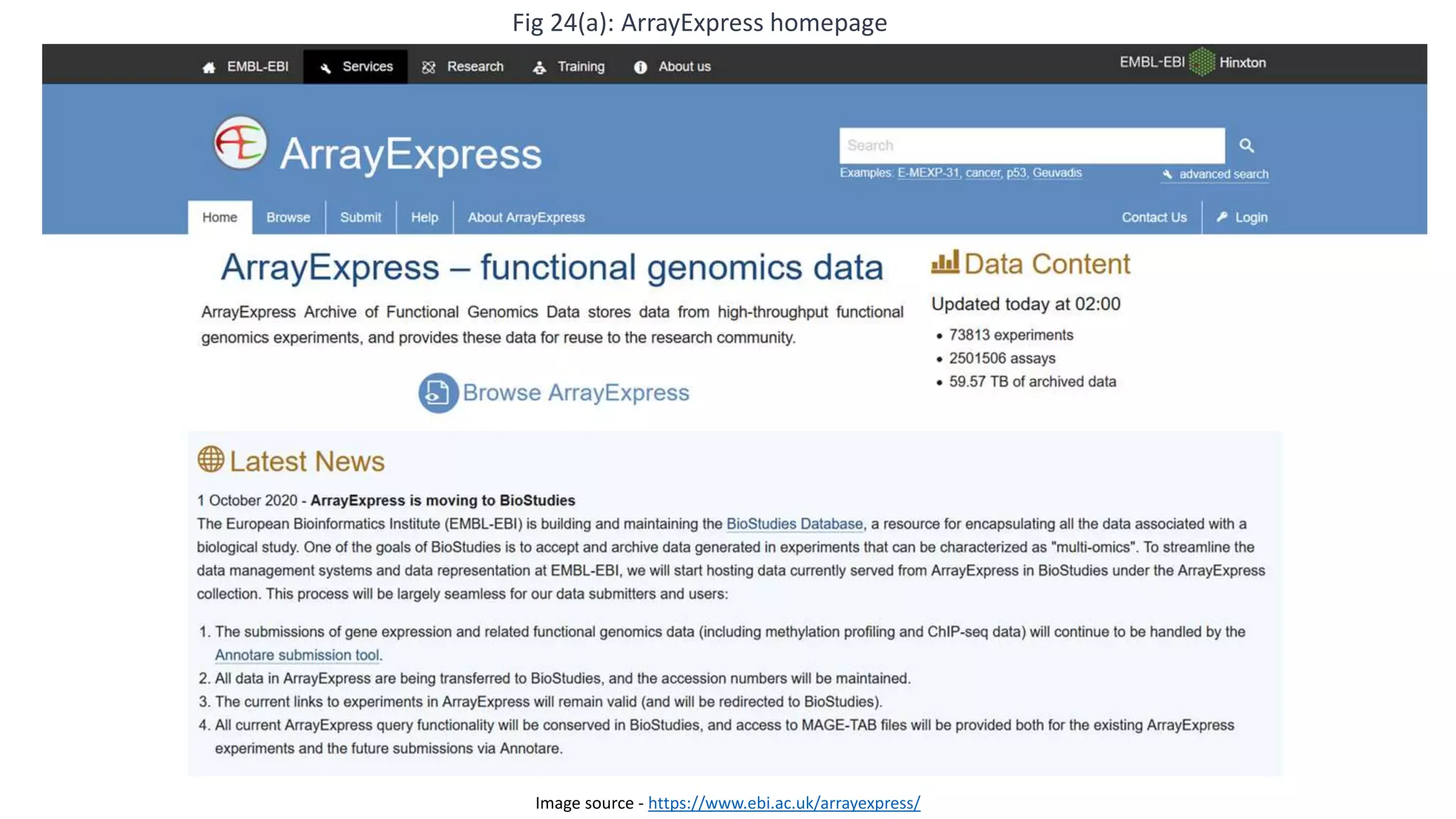
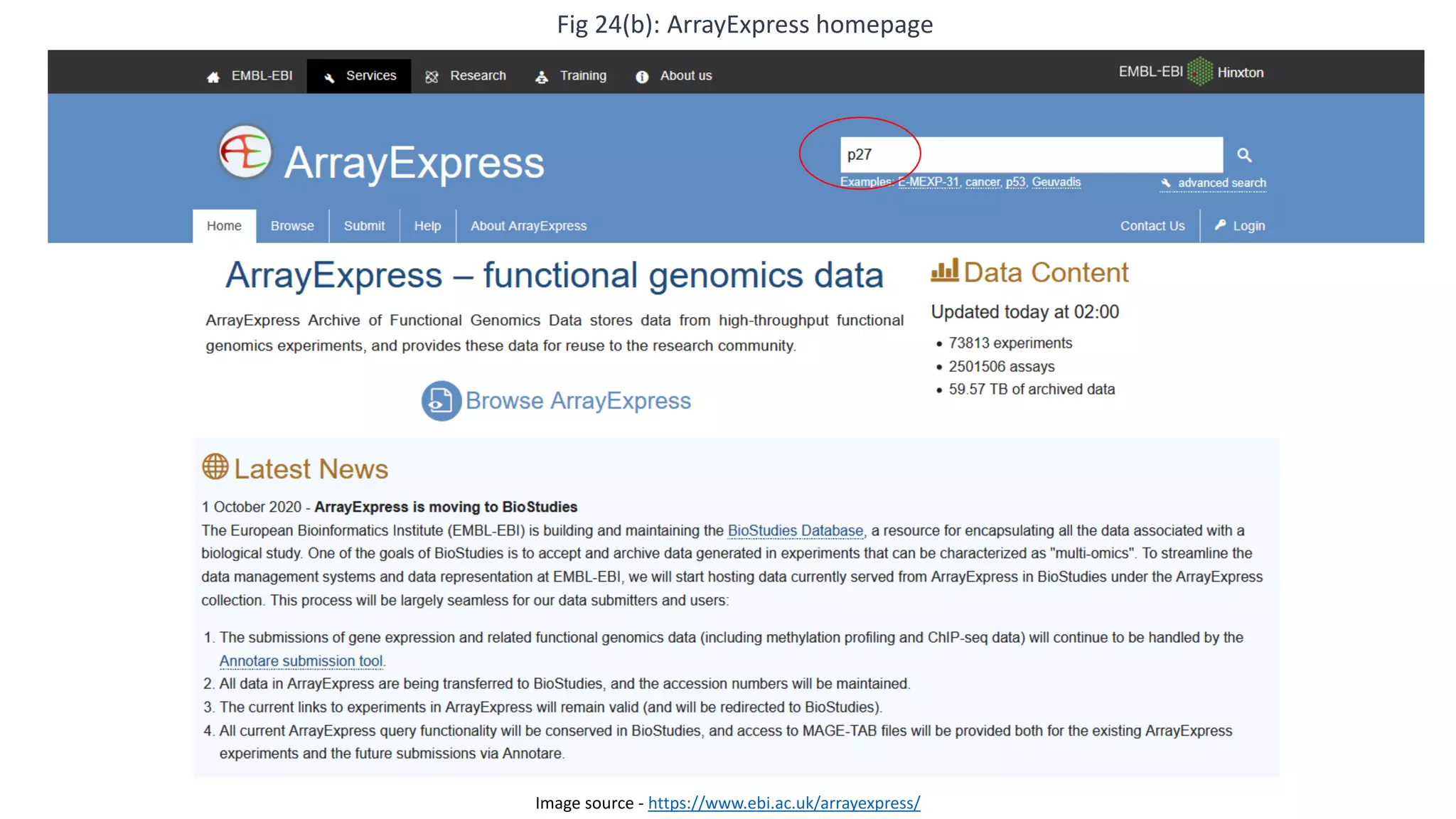
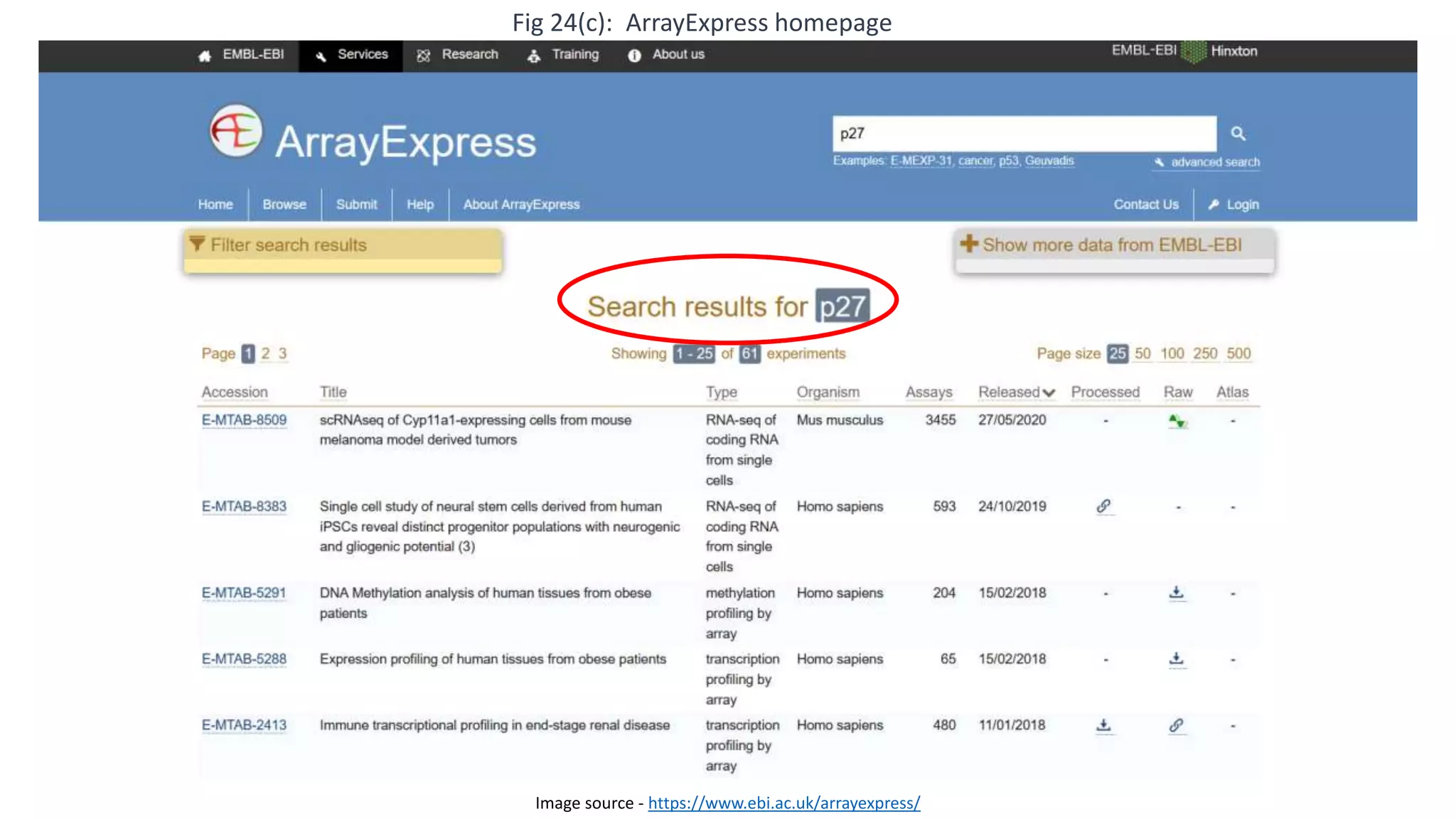
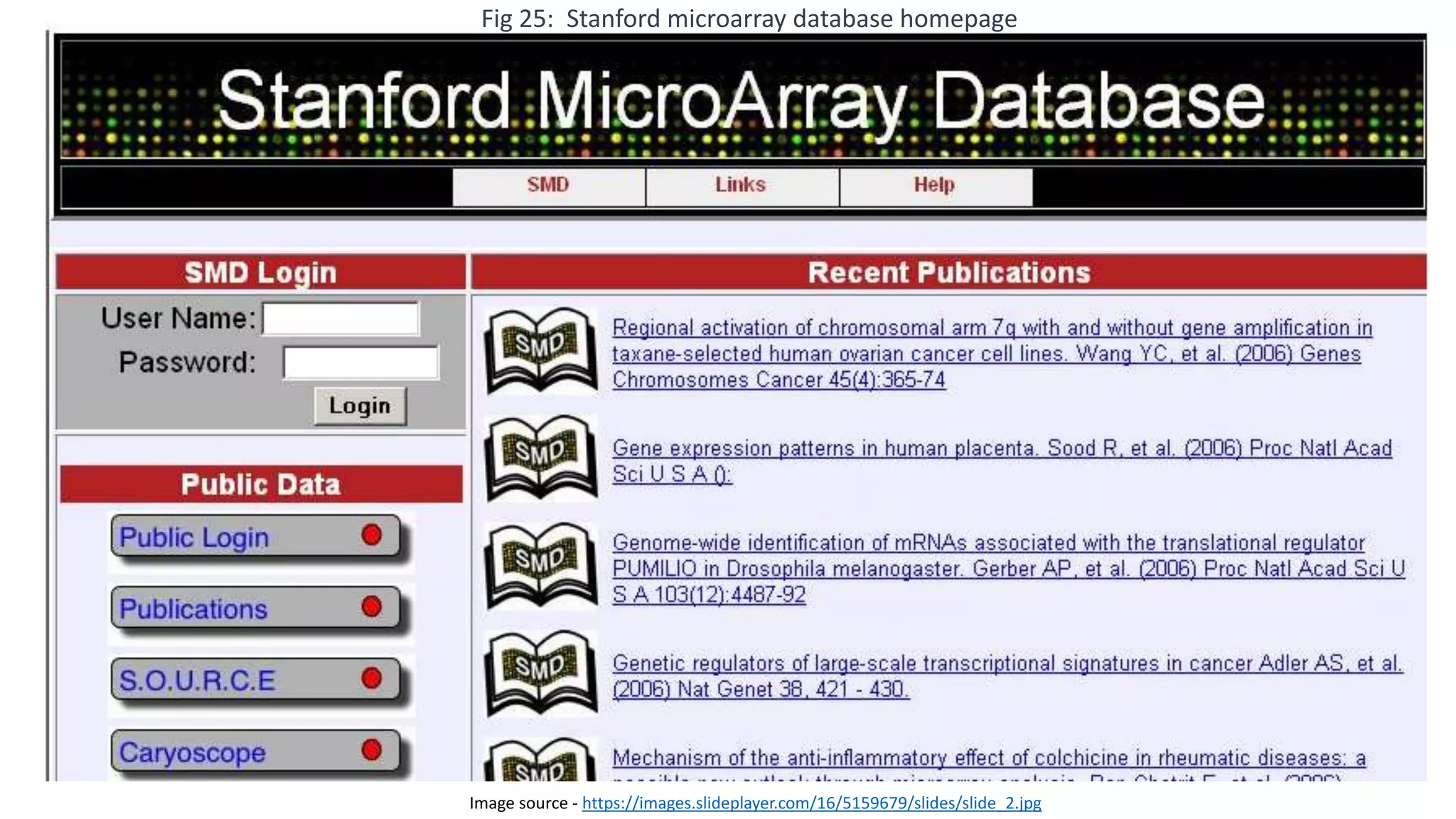
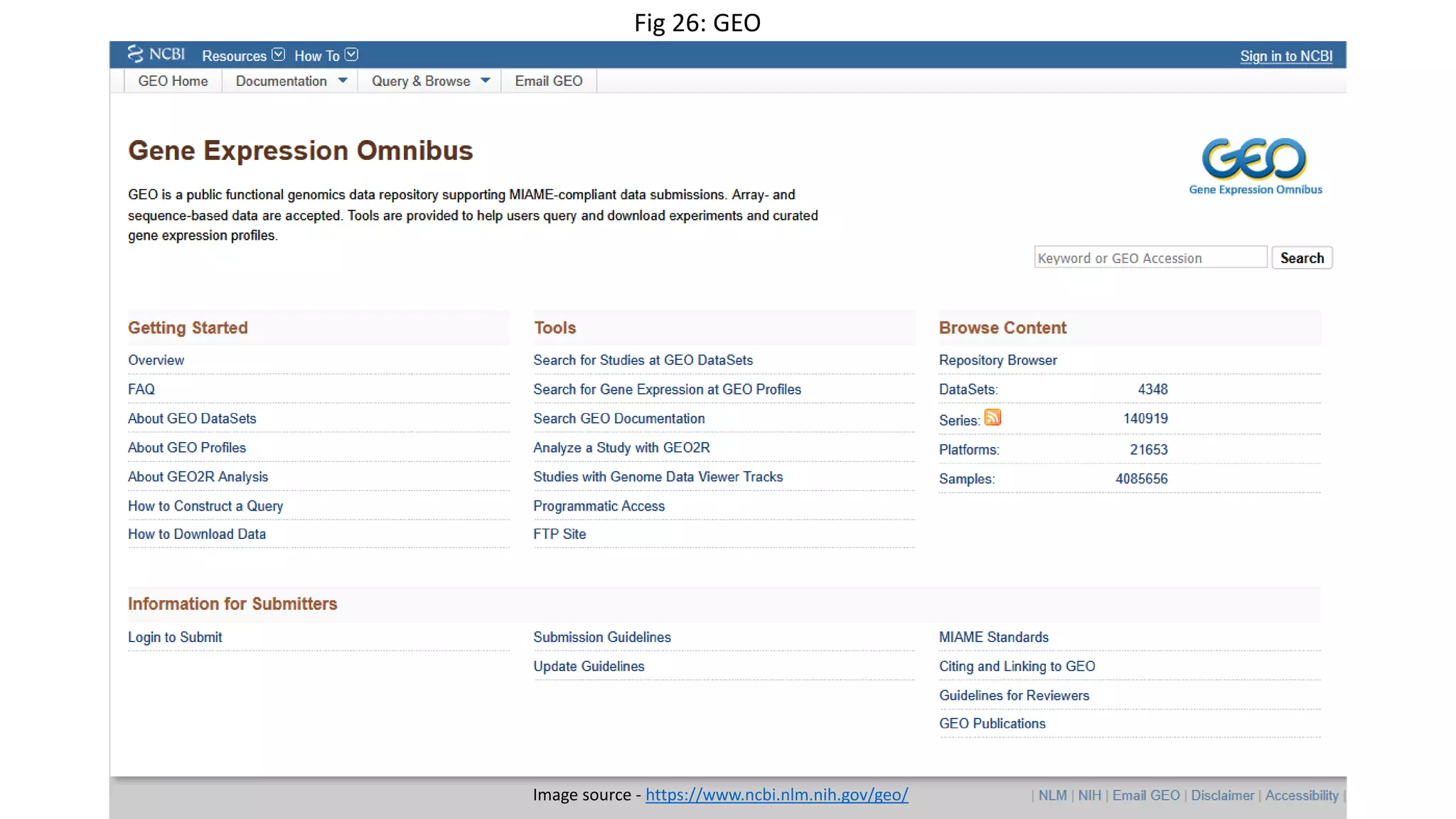
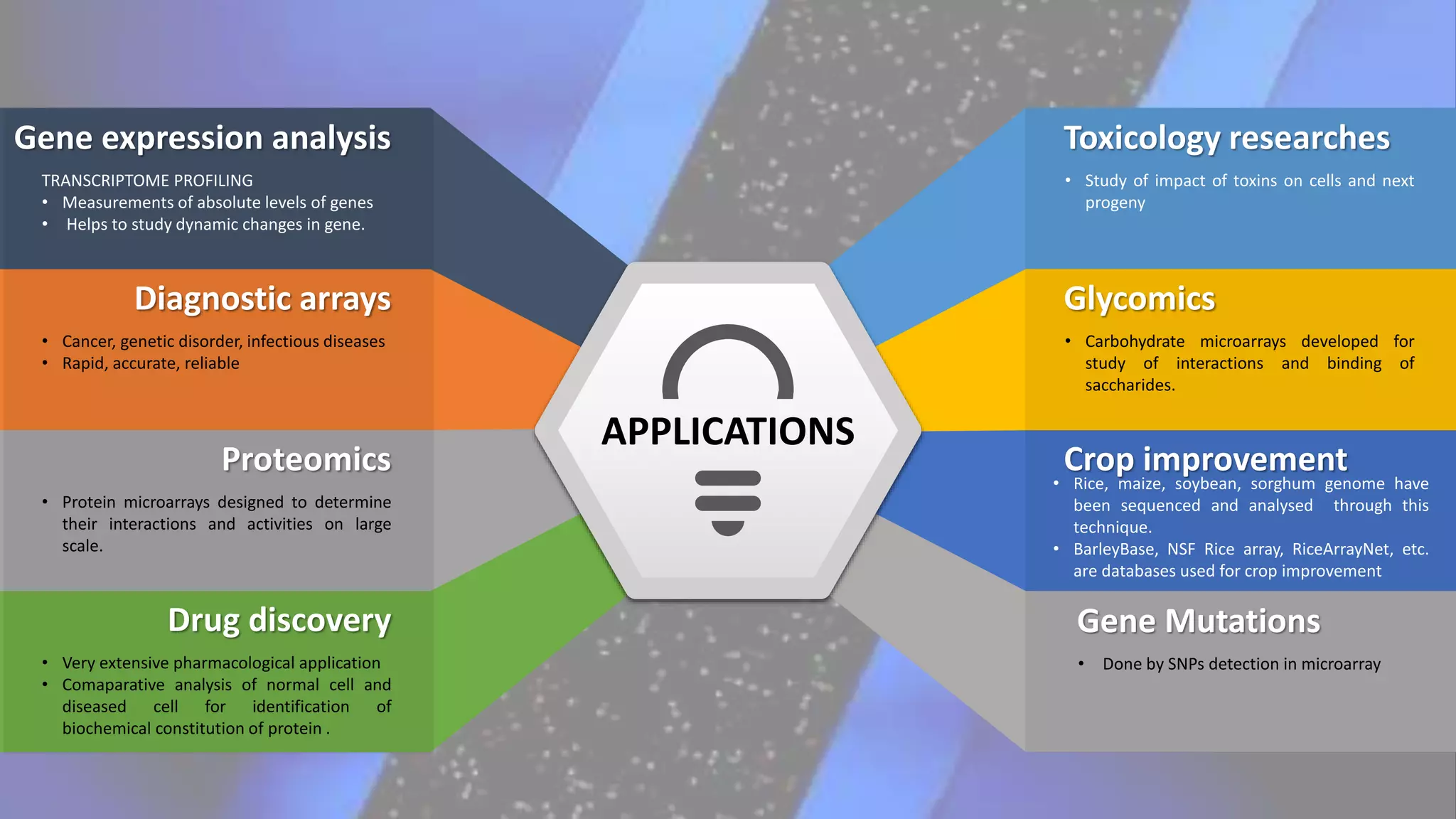
Microarray is a technique that arranges biological molecules like DNA on a solid surface to investigate a large number of genes simultaneously. It originated in 1995 when DNA microarrays were first reported for monitoring gene expression patterns. There are different types of microarrays like spotted and in-situ synthesized oligonucleotide arrays. The basic steps of a microarray experiment include array printing, sample preparation/labeling, hybridization, washing, scanning and data analysis. It has various applications in gene expression analysis, disease diagnosis, drug discovery and more. Though expensive, microarrays allow fast, high-throughput analysis of thousands of genes.