The document discusses several topics related to international trade and globalization including:
- Trade agreements and organizations that work to reduce trade barriers like the EU, NAFTA, WTO, and GATT.
- Factors that influence a country's economy and income distribution like industrial structure, government policies, and political stability.
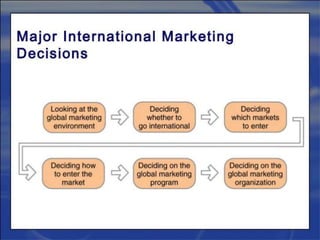
- Considerations for developing a marketing strategy in foreign markets like objectives, country selection, entry methods, and adapting products and communications to other cultures.
- The stages of internationalization a company may go through from exporting to becoming a global organization.