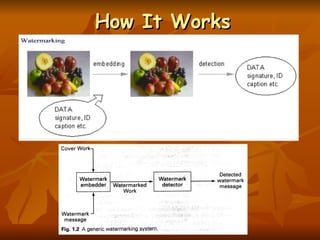
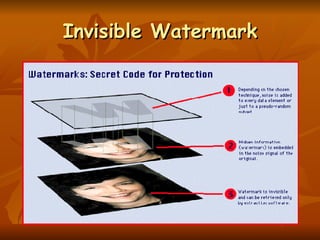
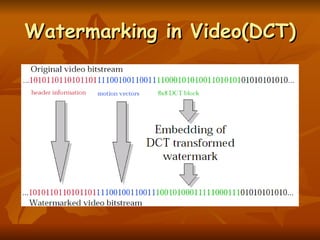
Digital watermarking allows users to embed special patterns or data into digital content like images, audio, and video without changing the perceptual quality. Watermarking helps protect copyright ownership by embedding information directly into the media itself through small changes to the content data. Watermarks can be invisible, inseparable from the content after processing, and do not change the file size. Watermarks are classified based on human perception (visible or invisible), robustness (fragile, semi-fragile, or robust), and the type of document (text, image, audio, or video). Frequency domain techniques like discrete cosine transformation are commonly used to embed watermarks in images and videos.