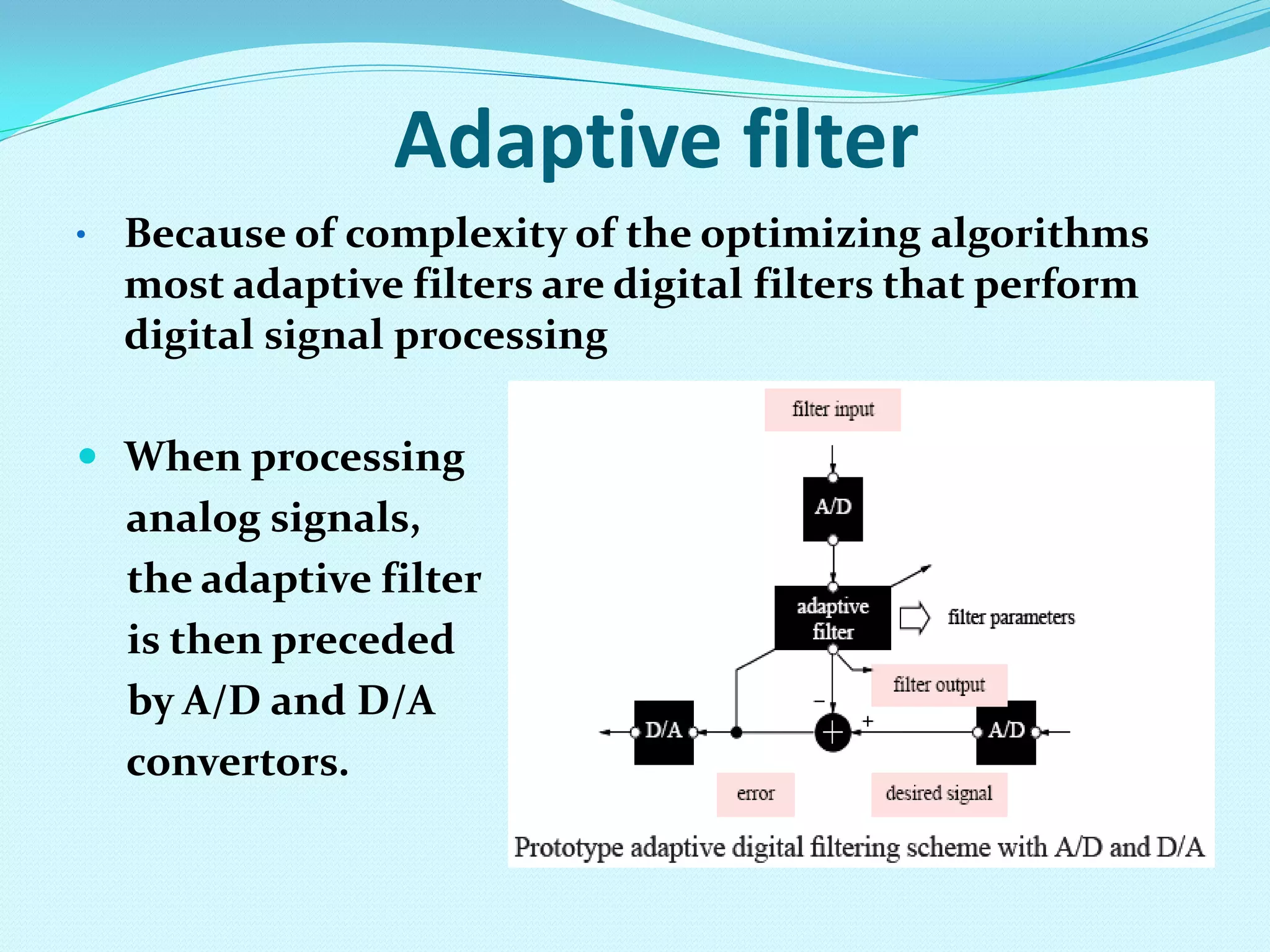
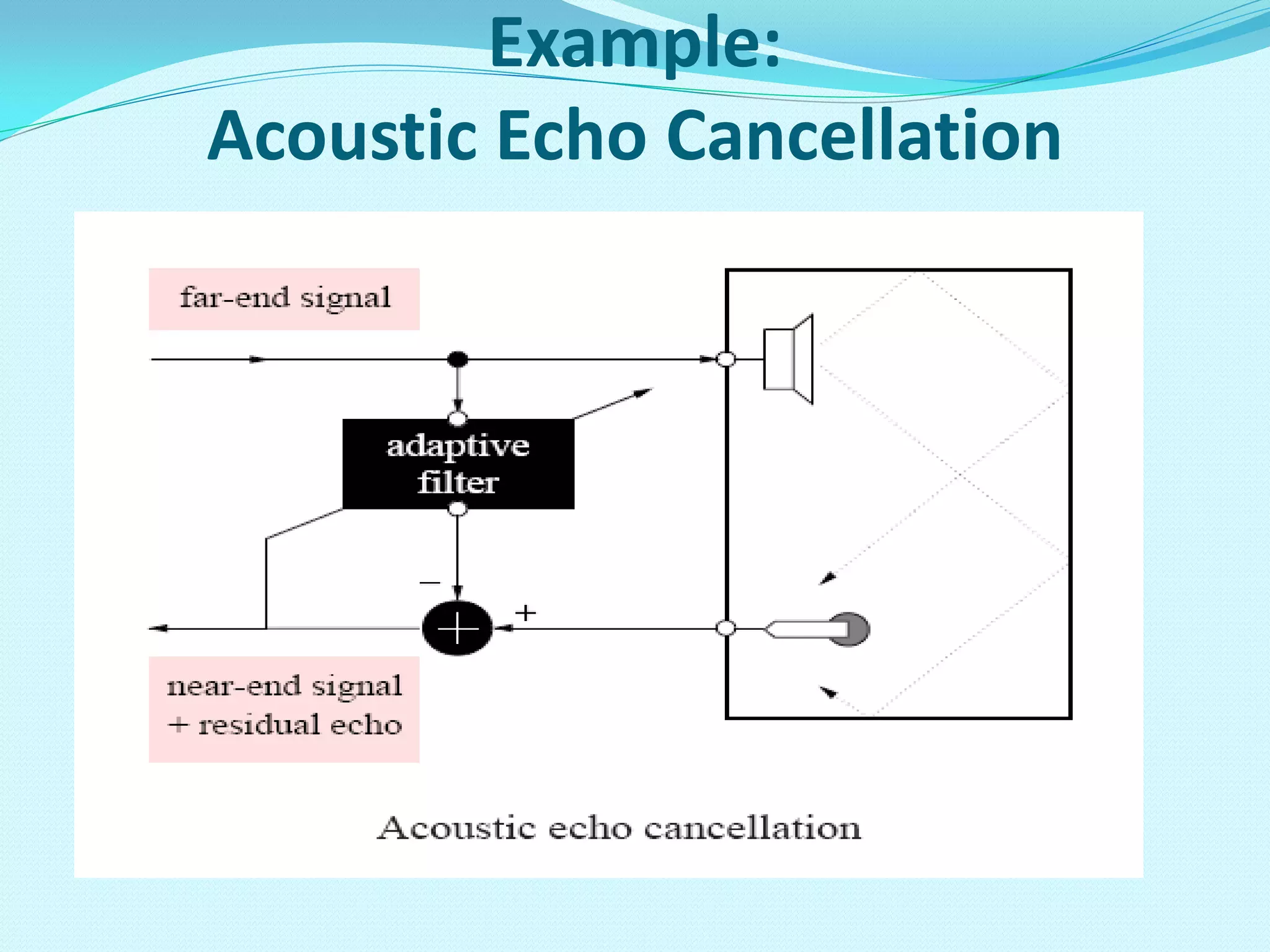
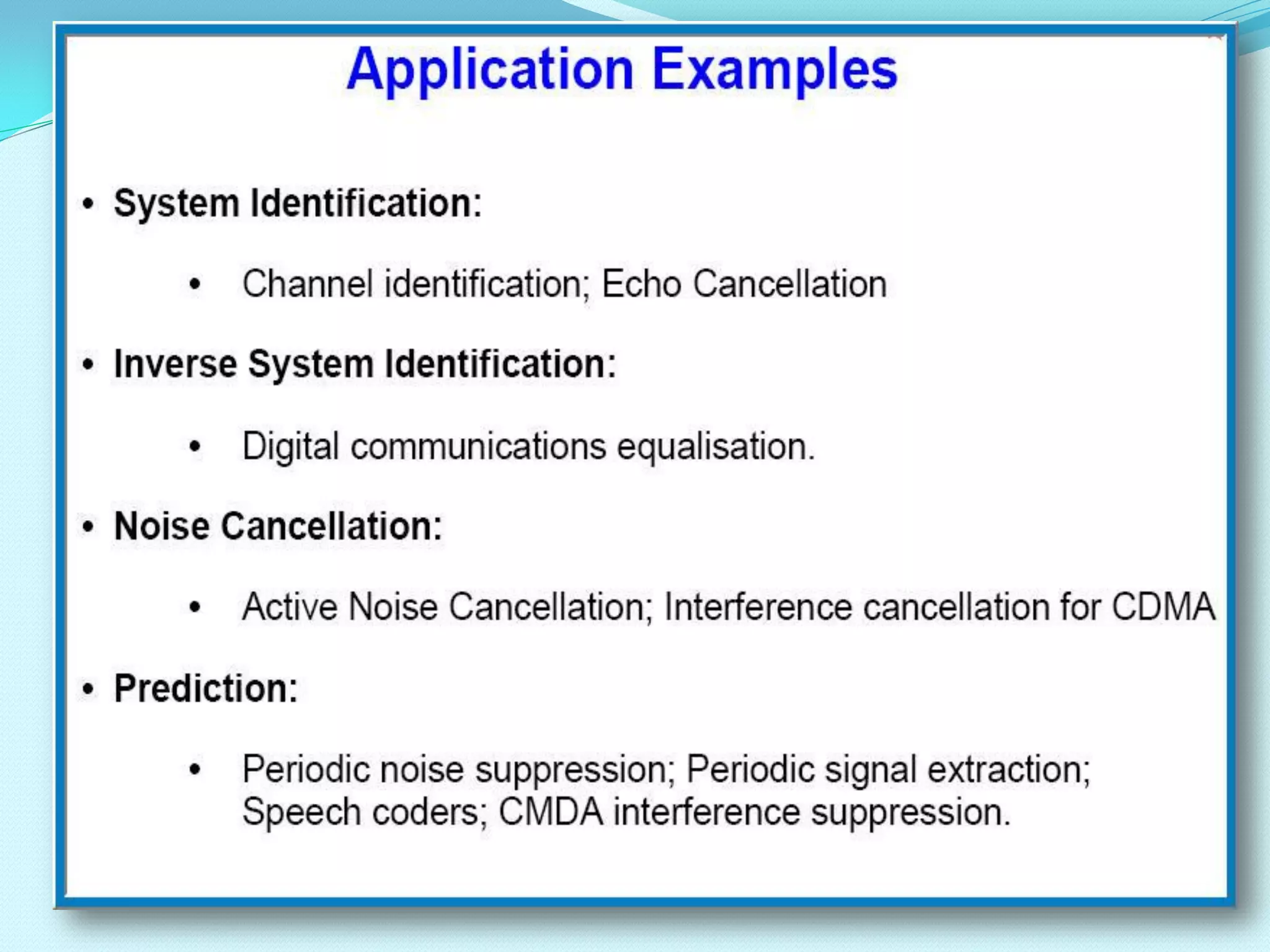
An adaptive filter is a filter that self-adjusts its transfer function according to an optimization algorithm driven by an error signal. It has two processes: a filtering process that produces an output in response to input, and an adaptation process that adjusts the filter parameters to changing environments based on the error signal. Adaptive filters are commonly implemented as digital FIR filters and are used for applications like system identification, acoustic echo cancellation, channel equalization, and noise cancellation.