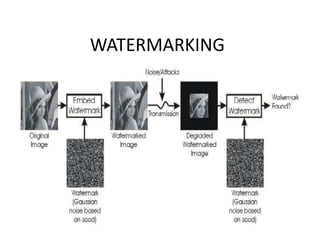
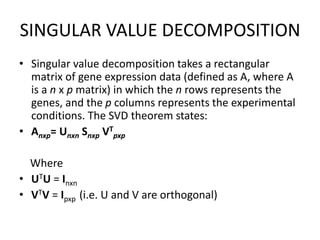
The document discusses a digital watermarking scheme utilizing discrete wavelet transform (DWT), discrete cosine transform (DCT), and singular value decomposition (SVD) to covertly embed ownership information in signals like audio and images. Key requirements for effective watermarking include fidelity, robustness against unauthorized modifications, and non-invertibility. The document elaborates on the technical aspects of DWT, DCT, and SVD, and addresses potential watermarking attacks.