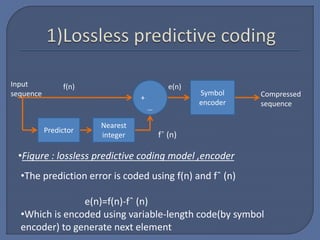
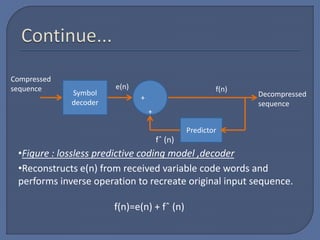
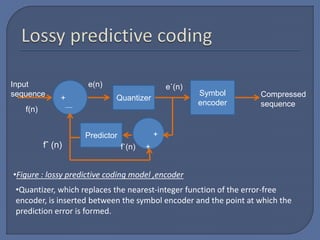
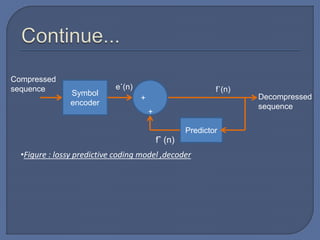
This document discusses predictive coding, which achieves data compression by predicting pixel values and encoding only prediction errors. It describes lossless predictive coding, which exactly reconstructs data, and lossy predictive coding, which introduces errors. Lossy predictive coding inserts quantization after prediction error calculation, mapping errors to a limited range to control compression and distortion. Common predictive coding techniques include linear prediction of pixels from neighboring values and delta modulation.