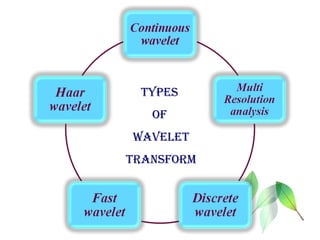
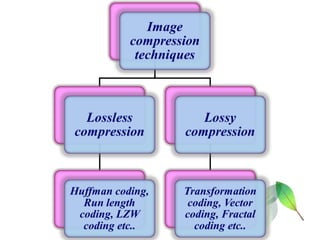
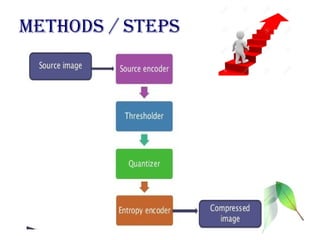
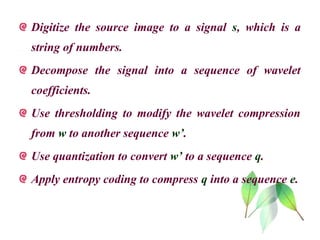
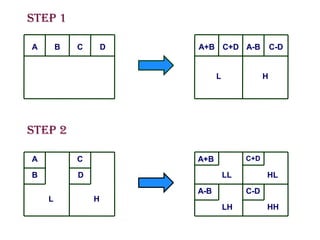
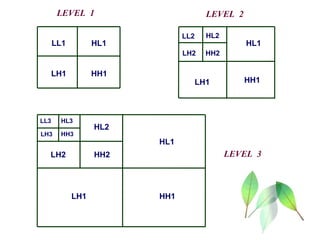
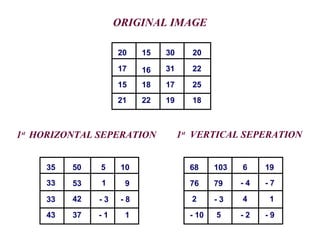
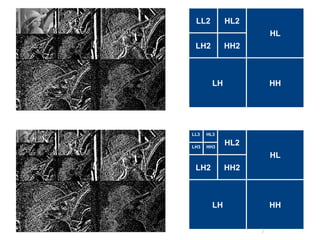
The document discusses wavelet transform as a technique for image compression, highlighting its historical development and methodology. It explains the advantages of using wavelets, such as better compression ratios and the ability to maintain image quality without introducing blocking artifacts. Additionally, it explores various applications of wavelet transforms across different fields, affirming their effectiveness and significance in digital image processing.