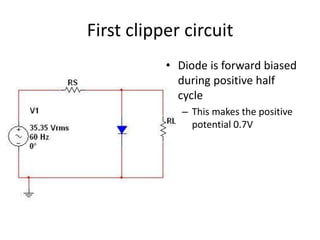
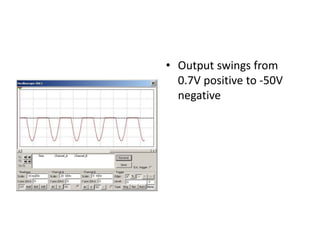
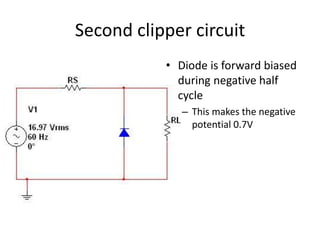
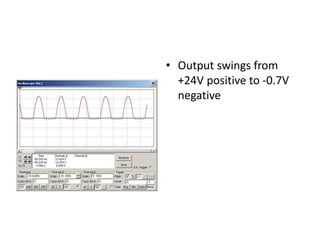
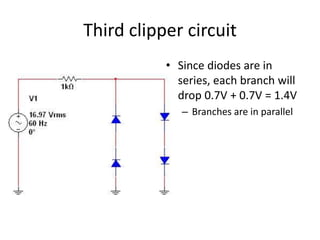
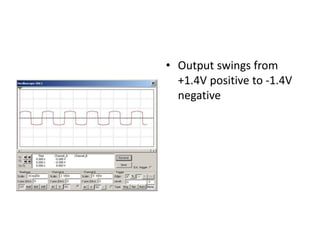
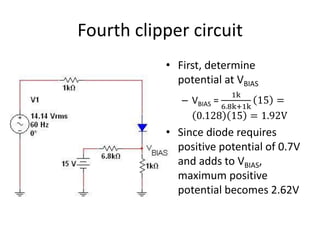
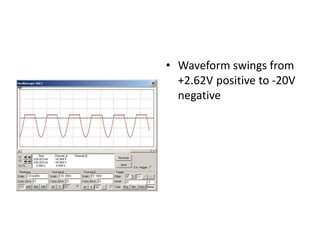
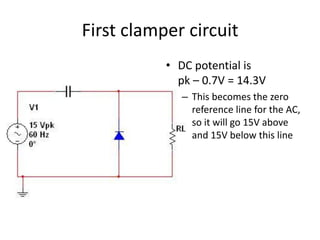
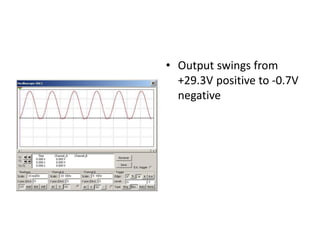
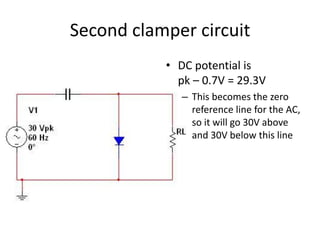
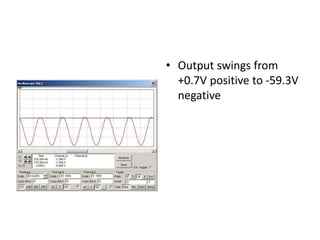
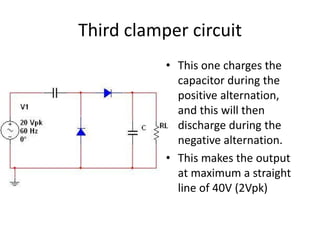
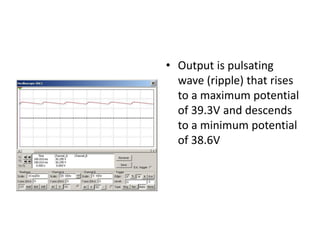
This document describes four different diode clipper circuits and three diode clamper circuits. The clipper circuits use diodes to clip portions of an input waveform, resulting in outputs that swing within narrowed positive and negative voltage ranges. The clamper circuits use diodes to set a reference voltage level, causing the output to oscillate symmetrically around this clamped level. Key aspects covered include how the diodes bias in different circuit configurations and the voltage ranges of the output waveforms for each circuit.