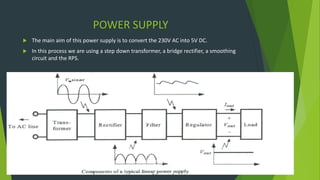
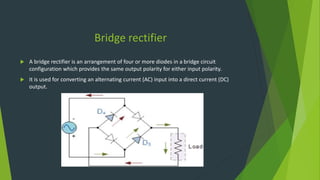
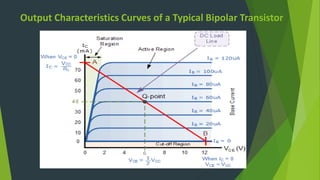
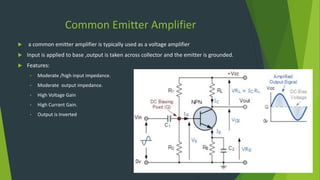
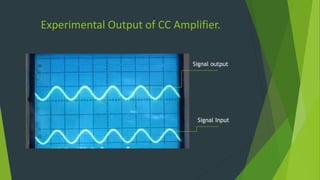
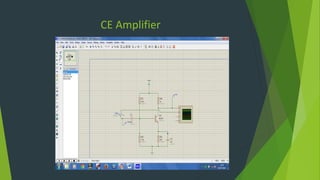
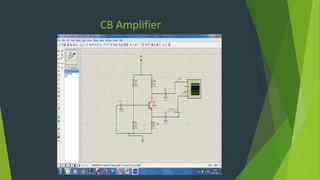
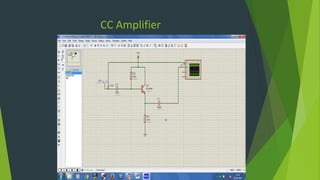
This document summarizes a student project presentation on CE, CB, and CC transistor amplifiers. It includes introductions to diodes, transistors, and the three basic transistor amplifier configurations. For each amplifier type, it provides a brief description of the configuration and key features, along with experimental output waveforms. It also includes Protel circuit design diagrams and software simulations of the three amplifier circuits on Proteus. The project aims to explain the basic workings and characteristics of common emitter, common base, and common collector transistor amplifier circuits.
![MINI PROJECT PRESENTATION ON
CE, CB, CC AMPLIFIERS
Guide: Mr. S.Sravana Kumar
Asst. Professor
Adithya.R ………………..….11E31A0401[ECE-A IV Year]
A.Sindhu Reddy………….…11E31A0402[ECE-A IV Year]
Anirudh Kulkarni…………..11E31A0403[ECE-A IV Year]
A.Bhanuteja………………….11E31A0404[ECE-A IV Year]
B.Bharath Kumar Reddy…11E31A0405[ECE-A IV Year]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/miniprojectpresentation-150407074355-conversion-gate01/75/CE-CB-CC-AMPLIFIERS-1-2048.jpg)